Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to determine the prognostic significance of the preoperatively assessed tumor doubling time (DT) in patients undergoing liver resection for mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHC).
Methods
We evaluated 79 patients who underwent curative resection for IHC, and in whom the same imaging technique was preoperatively available in two consecutive occasions, to allow the calculation of the DT. The influence of DT and other clinical and pathological variables on tumor recurrence and patient survival was determined by the Kaplan–Meier method and uni- and multivariate analysis.
Results
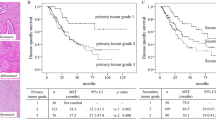
Median overall survival was 40 months; 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 86.1, 55.1, and 35.1 %, respectively. Median disease-free survival was 17 months; 1-, 3-, and 5-year disease-free survival rates were 62.0, 29.1, and 23.3 %, respectively. At univariate analysis, DT <70 days (p < 0.001) and advanced tumor stage (p = 0.024) were associated with worse overall survival and maintained significance at multivariate analysis.
Conclusions
DT is a clinically useful parameter to estimate the prognosis of “mass-forming” IHC in patients undergoing liver resection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edmondson HA, Steiner PE. Primary carcinoma of the liver. A study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer 1954;7:462–503.
Murakami Y, Uemura K, Sudo T, Hashimoto Y, Nakashima A, Sueda T: Intrahepatic cholangioarcinoma: clinicopathological differences between peripheral type and hilar type. J Gastrointest Surg 2012; 16: 540–548
Anderson JE, Hemming AVV, Chang DC, Talamini MA, Mekeel KL (2012) Surgical management trends for cholangiocarcinoma in the USA 1998–2009. J Gastrointest Surg 16(12): 2225–2232.
Singal AK, Vauthey JN, Grady JJ, Stroehlein JR. Intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma-frequency and demographic patterns: thirty-year data from the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2011;137:1071–8.
Patel T. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatology 2001;33:1353–1357.
Farges O, Fuks D, Boleslawski E, Le Treut YP, Castaing D, Laurent A, Ducerf C, Rivoire M, Bachellier P, Chiche L, Nuzzo G, Regimbeau JM: Influence of Surgical Margins on Outcome in Patients With Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Multicenter Study by the AFC-IHCC-2009 Study Group. Ann Surg. 2011;254:824–29.
Farges O, Fuks D. Clinical presentation and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010;34:191–199.
Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC, Dalal KM, Zhou Q, Klimstra D, D’Angelica M, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Schwartz L, Kemeny N, O’Reilly E, Abou-Alfa GK, Shimada H, Blumgart LH, Jarnagin WR: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg 2008;248:84–96.
Guglielmi A, Ruzzenente A, Campagnaro T, Pachera S, Valdegamberi A, Nicoli P, Cappellani A, Malfermoni G, Iacono C: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: prognostic factors after surgical resection. World J Surg 2009;33: 1247–1254.
Shirai K, Ebata T, Oda K, Nishio H, Nagasaka T, Nimura Y, Nagino M: Perineural invasion is a prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg 2008;32: 2395–402.
Inoue K, Makuuchi M, Takayama T, Torzilli G, Yamamoto J, Shimada K, Kosuge T, Yamasaki S, Konishi M, Kinoshita T, Miyagawa S, Kawasaki S: Long term survival and prognostic factors in the surgical treatment of mass-forming type cholangiocarcinoma. Surgery 2000; 127:498–505.
Saxena A, Chua TC, Sarkar A, Chu F, Morris DL: Clinicopathologic and treatment-related factors influencing recurrence and survival after hepatic resection of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a 19-year experience from an established Australian hepatobiliary unit. J Gastrointest Surg 2010; 14: 1128–1138
Tamandl D, Kaczirek K, Gruenberger B, Koelblinger C, Maresch J, Jakesz R, Gruenberger T: Lymph node ratio after surgery for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Surg 2009;96:919–925.
Nathan H, Aloia TA, Vauthey JN, Abdalla EK, Zhu AX, Schulick RD, Choti MA, Pawlik TM: Proposed staging system for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2009;16:14–22.
Jonas S, Thelen A, Benckert C, Biskup W, Neumann U, Rudolph B, Lopez Haanninen E, Neuhaus P: Extended liver resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a comparison of the prognostic accuracy of the fifth and sixth editions of the TNM classification. Ann Surg 2009; 249: 303–309.
Tamandl D, Herberger B, Gruenberger B, Puhalla H, Klinger M, Gruenberger T. Influence of hepatic resection margin on recurrence and survival in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2008;15:2787–94.
Collins VP, Loeffler RK, Tivey H. Observation on growth rates of human tumors. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1956;76:988–1000.
Schwartz M. A biomathematical approach to clinical tumor growth. Cancer 1961;14:1272–1294.
Spratt JS, Meyer JS, Spratt JA: Rates of growth of human neoplasms: part II. J Surg Oncol 1996;61:68–83.
Cucchetti A, Vivarelli M, Piscaglia F, Nardo B, Montalti R, Grazi GL, Ravaioli M, La Barba G, Cavallari A, Bolondi L, Pinna AD: Tumor doubling time predicts recurrence after surgery and describes the histological pattern of hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2005; 43: 310–316.
Strasberg SM, Belghiti J, Clavien PA, Gadzijev E, Garden JO, Lau WY, Makuuchi M: The Brisbane 2000 terminology of liver anatomy and resections. HPB 2000 ; 2 : 333–9
Nuzzo G, Giuliante F, Ardito F, De Rose AM, Vellone M, Clemente G, Chiarla C, Giovannini I: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: prognostic factors after liver resection. Updates Surg 2010;62:11–9.
Ercolani G, Vetrone G, Grazi GL, Aramaki O, Cescon M, Ravaioli M, Serra C, Brandi G, Pinna AD: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Primary Liver resection and aggressive multimodal treatment of recurrence significantly prolong survival. Ann Surg 2010; 252: 107–114.
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Carducci MA, Compton CC (2009) eds. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (eds) (2002). TNM classification of malignant tumours, 6th ed. Wiley: New York.
Wang N-P, Zee S, Zarbo RJ, Bacchi CE, Gown AM. Coordinate expression of cytokeratins 7 and 20 defines unique subsets of carcinomas. Appl Immunohistochem 1995;3:99–107.
Maeda T, Kajiyama K, Adachi E, Takenaka K, Sugimachi K, Tsuneyoshi M: The expression of cytokeratins 7, 19, and 20 in primary and metastatic carcinomas of the liver. Mod Pathol 1996;9:901–9.
Zhou HB, Wang H, Li YQ, Li SX, Wang H, Zhou DX, Tu QQ, Wang Q, Zou SS, Wu MC, Hu HP: Hepatitis B virus infection: a favorable prognostic factor for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after resection. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17: 1292–303.
Li YY, Li H, Lv P Liu G, Li XR, Tian BN, Chen DJ: Prognostic value of cirrhosis for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after surgical treatment. J Gastrointest Surg 2011; 15: 608–613
Guedj N, Zhan Q, Perigny M, Rautou PE, Degos F, Belghiti J, Farges O, Bedossa P, Paradis V: Comparative protein expression profiles of hilar and peripheral hepatic cholangiocarcinomas J Hepatol 2009;51: 93–101.
Acknowledgments
Supported by a contribution of the Catholic University and the Italian Ministry for Instruction, University and Research (D.1 Funds)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Rose, A.M., Cucchetti, A., Clemente, G. et al. Prognostic Significance of Tumor Doubling Time in Mass-Forming Type Cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 17, 739–747 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-012-2129-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-012-2129-6