Abstract
Purpose
In stage II colorectal cancer (CRC), high-risk patient selection is required, but no candidate markers have been elucidated. Our concern was whether anastomotic leakage (Lk) is a potential available clinicopathological factor for selecting high-risk stage II.
Methods
Two hundred seven patients with stage II CRC who underwent curative resection were analyzed. Clinical variables were tested for their relationship to survival.
Results
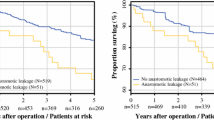
The 5-year disease-free survival rate (DFS) was 87.0%. The univariable prognostic analyses indicated that Lk (P = 0.003) was the only significant factor. The multivariable prognostic analysis revealed that Lk remained to be potently independent [hazard ratio (HR), 4.21, P = 0.021), and the DFS was 58.3% in cases with Lk, while 88.7% in the counterpart. The multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed perioperative blood transfusion (P = 0.001) was independently associated with Lk. Intriguingly, Lk was closely associated with hematogenic recurrence (P = 0.003) rather than peritoneal or local recurrence. Although sustained increase of the serum C-reactive protein at 2 weeks after operation predicted poor prognosis, the mutitivariable analysis including the C-reactive protein level revealed that Lk still indicated the prognostic potential (HR, 3.70, P = 0.075).
Conclusions
The findings concluded that Lk may be a high risk for systemic recurrence in stage II CRC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P: Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2005;55:74–108.
Cunningham D, Starling N: Adjuvant chemotherapy of colorectal cancer. Lancet 2007;370:1980–1981.
Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, Fuchs CS, Ramanathan RK, Williamson SK, Findlay BP, Pitot HC, Alberts SR: A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:23–30. Epub 2003 Dec 2009.
Kuebler JP, Wieand HS, O’Connell MJ, Smith RE, Colangelo LH, Yothers G, Petrelli NJ, Findlay MP, Seay TE, Atkins JN, Zapas JL, Goodwin JW, Fehrenbacher L, Ramanathan RK, Conley BA, Flynn PJ, Soori G, Colman LK, Levine EA, Lanier KS, Wolmark N: Oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: results from NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol 2007;25:2198–2204.
Andre T, Sargent D, Tabernero J, O’Connell M, Buyse M, Sobrero A, Misset JL, Boni C, de Gramont A: Current issues in adjuvant treatment of stage II colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2006;13:887–898. Epub 2006 Apr 2014.
Benson AB, 3 rd, Schrag D, Somerfield MR, Cohen AM, Figueredo AT, Flynn PJ, Krzyzanowska MK, Maroun J, McAllister P, Van Cutsem E, Brouwers M, Charette M, Haller DG: American Society of Clinical Oncology recommendations on adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:3408–3419. Epub 2004 Jun 3415.
Diep CB, Thorstensen L, Meling GI, Skovlund E, Rognum TO, Lothe RA: Genetic tumor markers with prognostic impact in Dukes’ stages B and C colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:820–829.
Wang Y, Jatkoe T, Zhang Y, Mutch MG, Talantov D, Jiang J, McLeod HL, Atkins D: Gene expression profiles and molecular markers to predict recurrence of Dukes’ B colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:1564–1571.
Ribic CM, Sargent DJ, Moore MJ, Thibodeau SN, French AJ, Goldberg RM, Hamilton SR, Laurent-Puig P, Gryfe R, Shepherd LE, Tu D, Redston M, Gallinger S: Tumor microsatellite-instability status as a predictor of benefit from fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 2003;349:247–257.
Branagan G, Finnis D: Prognosis after anastomotic leakage in colorectal surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 2005;48:1021–1026.
Fujita S, Teramoto T, Watanabe M, Kodaira S, Kitajima M: Anastomotic leakage after colorectal cancer surgery: a risk factor for recurrence and poor prognosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol 1993;23:299–302.
Ptok H, Marusch F, Meyer F, Schubert D, Gastinger I, Lippert H: Impact of anastomotic leakage on oncological outcome after rectal cancer resection. Br J Surg 2007;94:1548–1554.
McArdle CS, McMillan DC, Hole DJ: Impact of anastomotic leakage on long-term survival of patients undergoing curative resection for colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 2005;92:1150–1154.
Walker KG, Bell SW, Rickard MJ, Mehanna D, Dent OF, Chapuis PH, Bokey E L: Anastomotic leakage is predictive of diminished survival after potentially curative resection for colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 2004;240:255–259.
Yamashita K, Sakuramoto S, Kikuchi S, Katada N, Kobayashi N, Watanabe M: Transfusion alert for patients with curable cancer. World J Surg 2007;31:2315–2322.
Morris M, Platell C, de Boer B, McCaul K, Iacopetta B: Population-based study of prognostic factors in stage II colonic cancer. Br J Surg 2006;93:866–871.
Rubin DB: Estimating causal effects from large data sets using propensity scores. Ann Intern Med 1997;127:757–763.
McMillan DC, Canna K, McArdle CS: Systemic inflammatory response predicts survival following curative resection of colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 2003;90:215–219.
Law WL, Choi HK, Lee YM, Ho JW, Seto CL: Anastomotic leakage is associated with poor long-term outcome in patients after curative colorectal resection for malignancy. J Gastrointest Surg 2007;11:8–15.
Alves A, Panis Y, Trancart D, Regimbeau JM, Pocard M, Valleur P: Factors associated with clinically significant anastomotic leakage after large bowel resection: multivariate analysis of 707 patients. World J Surg 2002;26:499–502.
Lipska MA, Bissett IP, Parry BR, Merrie AE: Anastomotic leakage after lower gastrointestinal anastomosis: men are at a higher risk. ANZ J Surg 2006;76:579–585.
Peeters KC, Tollenaar RA, Marijnen CA, Klein Kranenbarg E, Steup WH, Wiggers T, Rutten HJ, van de Velde CJ: Risk factors for anastomotic failure after total mesorectal excision of rectal cancer. Br J Surg 2005;92:211–216.
Yeh CY, Changchien CR, Wang JY, Chen JS, Chen HH, Chiang JM, Tang R: Pelvic drainage and other risk factors for leakage after elective anterior resection in rectal cancer patients: a prospective study of 978 patients. Ann Surg 2005;241:9–13.
Figueredo A, Charette ML, Maroun J, Brouwers MC, Zuraw L: Adjuvant therapy for stage II colon cancer: a systematic review from the Cancer Care Ontario Program in evidence-based care’s gastrointestinal cancer disease site group. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:3395–3407.
Quasar Collaborative G, Gray R, Barnwell J, McConkey C, Hills RK, Williams NS, Kerr DJ (2007) Adjuvant chemotherapy versus observation in patients with colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Lancet;370:2020–2029.
Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Tabah-Fisch I, de Gramont A: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2343–2351.
Caplin S, Cerottini JP, Bosman FT, Constanda MT, Givel JC: For patients with Dukes’ B (TNM Stage II) colorectal carcinoma, examination of six or fewer lymph nodes is related to poor prognosis. Cancer 1998;83:666–672.
Petersen VC, Baxter KJ, Love SB, Shepherd NA: Identification of objective pathological prognostic determinants and models of prognosis in Dukes’ B colon cancer. Gut 2002;51:65–69.
Nakamura T, Mitomi H, Kanazawa H, Ohkura Y, Watanabe M: Tumor budding as an index to identify high-risk patients with stage II colon cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 2008;51:568–572.
Garrity MM, Burgart LJ, Mahoney MR, Windschitl HE, Salim M, Wiesenfeld M, Krook JE, Michalak JC, Goldberg RM, O’Connell MJ, Furth AF, Sargent DJ, Murphy LM, Hill E, Riehle DL, Meyers CH, Witzig TE: Prognostic value of proliferation, apoptosis, defective DNA mismatch repair, and p53 overexpression in patients with resected Dukes’ B2 or C colon cancer: a North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:1572–1582.
Noura S, Yamamoto H, Ohnishi T, Masuda N, Matsumoto T, Takayama O, Fukunaga H, Miyake Y Ikenaga M, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N, Monden M: Comparative detection of lymph node micrometastases of stage II colorectal cancer by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. J Clin Oncol 2002;20:4232–4241.
Koch M, Kienle P, Kastrati D, Antolovic D, Schmidt J, Herfarth C, von Knebel Doeberitz M, Weitz J: Prognostic impact of hematogenous tumor cell dissemination in patients with stage II colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 2006;118:3072–3077.
Benson AB, 3rd: New approaches to assessing and treating early-stage colon and rectal cancers: cooperative group strategies for assessing optimal approaches in early-stage disease. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:6913 s–6920 s.
Gertsch P, Baer HU, Kraft R, Maddern GJ, Altermatt HJ: Malignant cells are collected on circular staplers. Dis Colon Rectum 1992;35:238–241.
Umpleby HC, Fermor B, Symes MO, Williamson RC: Viability of exfoliated colorectal carcinoma cells. Br J Surg 1984;71:659–663.
Gabay C, Kushner I: Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 1999;340:448–454.
Nozoe T, Matsumata T, Sugimachi K: Preoperative elevation of serum C-reactive protein is related to impaired immunity in patients with colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 2000;23:263–266.
Oka M, Hirazawa K, Yamamoto K, Iizuka N, Hazama S, Suzuki T, Kobayashi N: Induction of Fas-mediated apoptosis on circulating lymphocytes by surgical stress. Ann Surg 1996;223:434–440.
Eilber FR, Morton DL: Impaired immunologic reactivity and recurrence following cancer surgery. Cancer 1970;25:362–367.
Waymack JP, Rapien J, Garnett D, Tweddell JS, Alexander JW: Effect of transfusion on immune function in a traumatized animal model. Arch Surg 1986;121:50–55.
Jensen LS, Andersen AJ, Christiansen PM, Hokland P, Juhl CO, Madsen G, Mortensen J, Moller-Nielsen C, Hanberg-Sorensen F, Hokland M: Postoperative infection and natural killer cell function following blood transfusion in patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 1992;79:513–516.
Barbul A, Breslin RJ, Woodyard JP, Wasserkrug HL, Efron G: The effect of in vivo T helper and T suppressor lymphocyte depletion on wound healing. Ann Surg 1989;209:479–483.
Tadros T, Wobbes T, Hendriks T: Opposite effects of interleukin-2 on normal and transfusion-suppressed healing of experimental intestinal anastomoses. Ann Surg 1993;218:800–808.
Kaplan RN, Rafii S, Lyden D: Preparing the “soil”: the premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 2006;66:11089–11093.
Lyden D, Hattori K, Dias S, Costa C, Blaikie P, Butros L, Chadburn A, Heissig B, Marks W, Witte L, Wu Y, Hicklin D, Zhu Z, Hackett NR, Crystal RG, Moore MA, Hajjar KA, Manova K, Benezra R, Rafii S: Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nat Med 2001;7:1194–1201.
Rafii S, Lyden D: S100 chemokines mediate bookmarking of premetastatic niches. Nat Cell Biol 2006;8:1321–1323.
Du R, Lu KV, Petritsch C, Liu P, Ganss R, Passegue E, Song H, Vandenberg S, Johnson RS, Werb Z, Bergers G: HIF1alpha induces the recruitment of bone marrow-derived vascular modulatory cells to regulate tumor angiogenesis and invasion. Cancer Cell 2008;13:206–220.
Katoh H, Hosono K, Ito Y, Suzuki T, Ogawa Y, Kubo H, Kamata H, Mishima T, Tamaki H, Sakagami H, Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S, Watanabe M, Majima M: COX-2 and prostaglandin EP3/EP4 signaling regulate the tumor stromal proangiogenic microenvironment via CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine systems. Am J Pathol 2010;176:1469–1483.
Yang L, DeBusk LM, Fukuda K, Fingleton B, Green-Jarvis B, Shyr Y, Matrisian LM, Carbone DP, Lin PC: Expansion of myeloid immune suppressor Gr + CD11b + cells in tumor-bearing host directly promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 2004;6:409–421.
Li MO, Flavell RA: TGF-beta: a master of all T cell trades. Cell 2008;134:392–404.
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil A, Aakre M, Carbone DP, Matrisian LM, Richmond A, Lin PC, Moses HL: Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1 + CD11b + myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2008;13:23–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Fig. 1
Kaplan–Meier analysis of 5-year DFS according to (A) lymphatic involvement (ly), (B) vascular involvement (v), and (C) both ly and v involvement (VI) (GIF 22 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 2
Kaplan–Meier analysis of 5-year DFS according to CRP at 2 week after operation [post-CRP (2w)] (n = 175) (GIF 18 kb)
Supplemental Table 1
Diagnostic details of the patients with anastomotic leakage (XLS 14.5 kb)
Supplemental Table 2
Correlation between CRP and clinicopathological factors in stage II patients (XLS 46.0 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katoh, H., Yamashita, K., Wang, G. et al. Anastomotic Leakage Contributes to the Risk for Systemic Recurrence in Stage II Colorectal Cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 15, 120–129 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-010-1379-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-010-1379-4