Abstract
Introduction
Although laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication has been recognized as the standard of care for hiatal hernia (HH) repair, HH recurrence due to breakdown of the hiatoplasty have been reported as a common mechanism of failure after primary repair. Different surgical techniques for diaphragmatic pillars closure have been proposed, but the problem remains unsolved. The authors hypothesized that ultrastructural illness may be implicated in this recurrence. The aim of this study was to investigate the presence of changes at esophageal hiatal area in patients with and without HH.
Materials and Methods
One hundred and thirty-two laparoscopic samples from phrenoesophageal membrane and diaphragmatic crura were collected from 33 patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and HH (HH group) and 60 samples from 15 patients without HH enrolled as the control group (NHH group). All specimens were processed and analyzed by transmission electron microscopy.
Results
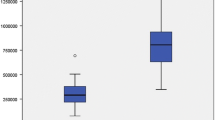
Muscular and connective samples from the NHH group showed no ultrastructural alterations; similar results were found in phrenoesophageal ligament samples from the HH group. In contrast, 94% of the muscular samples obtained from the crura of the HH group have documented four main types of alterations. In 75% of HH patients, the pillar lesions were severe.
Conclusion
Patients with hiatal hernia have ultrastructural abnormalities at the muscular tissue of the crura that are not present in patients with a normal gastroesophageal junction. There is no difference in the microscopic damage at the connective tissue of the phrenoesophageal membrane surrounding the esophagus of the two groups of patients. The outcome of antireflux surgery could depend not only on the adopted surgical technique but also on the underlying status of the diaphragmatic crura.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fei L, Di Martino N, Amato G, Landolfi V, Ambrosio A, Del Genio A. Effect of a slipped hiatal hernia on the activity of the lower esophageal sphincter and of the abdominal portion of the esophagus. A pH-manometric study. Minerva Med 1984;75:2155–2160.
Catarci M, Gentileschi P, Papi C, Carrara A, Marrese R, Gaspari AL, Grassi GB. Evidence-based appraisal of antireflux fundoplication. Ann Surg 2004;239:325–337. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000114225.46280.fe.
del Genio G, Collard JM. Acute complications of antireflux surgery. In Ferguson MK, Fennerty MB, eds. Managing Failed Anti-reflux Therapy. London: Springer, 2006ISBN:1-85233-909-8.
Altorki NK, Yankelevitz D, Skinner DB. Massive hiatal hernias: the anatomic basis of repair. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1998;115:828–835. doi:10.1016/S0022-5223(98)70363-0.
Hogan S, Pohi D, Bogetti D, Eubanks T, Pellegrini C. Failed antireflux surgery. Arch Surg. 1999;134:809–817. doi:10.1001/archsurg.134.8.809.
Granderath FA, Carlson MA, Champion JK, Szold A, Basso N, Pointner R, Frantzides CT. Prosthetic closure of the esophageal hiatus in large hiatal hernia repair and laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Surg Endosc 2006;20:367–379. doi:10.1007/s00464-005-0467-0.
Fei L, Del Genio G, Brusciano L, Esposito V, Cuttitta D, Pizza F, Rossetti G, Trapani V, Filippone G, Moccia F, Del Genio A. Crura ultrastructural alterations in patients with hiatal hernia: a pilot study. Surg Endosc 2007;21:907–911. doi:10.1007/s00464-006-9043-5.
Pace F, Annese V, Ceccatelli P, Fei L. Ambulatory oesophageal pH-metry. Position paper of the working team on oesophageal pH-metry by the GISMAD (Gruppo Italiano di Studio sulla Motilità dell'Apparato Digerente). Dig Liver Dis 2000;32:357–364. doi:10.1016/S1590-8658(00)80030-4.
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, Johnson F, Hongo M, Richter JE, Spechler SJ, Tytgat GN, Wallin L. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut 1999;45:172–180.
Del Genio G, Rossetti G, Brusciano L, Limongelli P, Pizza F, Tolone S, Fei L, Maffettone V, Napolitano V, Del Genio A. Laparoscopic Nissen-Rossetti fundoplication with routine use of intraoperative endoscopy and manometry: Technical aspects of a standardized technique. World J Surg 2007;31:1099–1106. doi:10.1007/s00268-006-0495-5.
Hinder RA, Klingler PJ, Perdikis G, Smith L. Mana of the failed antireflux operation. Surg Clin North Am 1997;77:1083–1098. doi:10.1016/S0039-6109(05)70606-X.
Stirling MC, Orringer MB. Surgical treatment after the failed antireflux operation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1986;92:667–672.
Bochkarev V, Lee YK, Vitamvas M, Oleynikov D. Short esophagus: how much length can we get? Surg Endosc 2008;22:2123–2127. doi:10.1007/s00464-008-9999-4.
Casaccia M, Torelli T, Panaro F, Ventura A. Laparoscopic physiological hiatoplasty for hiatal hernia: new composite ‘‘A’’ shaped mesh. Surg Endosc. 2002;16:1441–1445. doi:10.1007/s00464-002-9029-x.
Tatum RP, Shalhub S, Oelschlager BK, Pellegrini CA. Complications of PTFE mesh at the diaphragmatic hiatus. J Gastrointest Surg 2008;12:953–957. doi:10.1007/s11605-007-0316-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fei, L., del Genio, G., Rossetti, G. et al. Hiatal Hernia Recurrence: Surgical Complication or Disease? Electron Microscope Findings of the Diaphragmatic Pillars. J Gastrointest Surg 13, 459–464 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0741-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0741-2