Abstract
Background
Microwave ablation (MWA) is postulated to have several advantages over other thermoablative modalities in the treatment of hepatic tumors. Herein, we use an in vivo porcine model to determine the effect of hepatic blood flow on a novel MWA applicator.
Methods
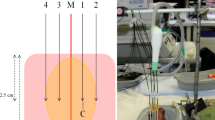
Four 100-kg pigs underwent hepatic MWA (2,450 MHz, 100 W, 4 min) using a 5.7-mm diameter applicator (Microsulis Americas, Sulis™ V) inserted near large intrahepatic blood vessels. Real-time monitoring was performed using 3, 5, and 12 MHz diagnostic ultrasound transducers. The ablated zones were sectioned for gross and histological processing.
Results
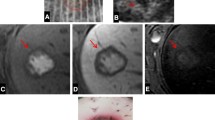
Ablation zones were uniform in shape and size (3–4 cm) and related to power deliver only. Gross and microscopic examination revealed direct extension of ablation zones to the margin of major hepatic blood vessels and occasionally beyond the intended target. Of note, a momentary acoustic white-out occurred around the probe at 25 ± −1 s in every ablation.
Discussion
The Sulis VTM MWA applicator produced uniform zones of ablation that remain unaffected by convective heat loss. The applicator induced a reproducible but temporary event as seen by ultrasound. Further study is warranted to define the physics, benefits, limits, and clinical safety of this new MWA technology.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garrean S, Hering J, Helton WS, Espat NJ. A primer on transarterial, chemical and thermal ablative therapies for hepatic tumors. Am J Surg 2007;194(1):79–88. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.11.025.
Ryan TP, Samulski TV, Lyons BE, Lee E, Holdren D, Fessenden P, Strohbehn JW. Thermal conduction effects associated with temperature measurements in proximity to radiofrequency electrodes and microwave antennas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1989;16(6):1557–1564.
Hines-Peralta AU, Pirani N, Clegg P, Cronin N, Ryan TP, Liu Z, Goldberg SN. Microwave ablation: results with a 2.45-GHz applicator in ex vivo bovine and in vivo porcine liver. Radiology 2006;239(1):94–102. doi:10.1148/radiol.2383050262.
Cha CH, Lee FT Jr, Gurney JM, Markhardt BK, Warner TF, Kelcz F, Mahvi DM. CT versus sonography for monitoring radiofrequency ablation in a porcine liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;175(3):705–711.
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Solbiati L, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR. Radiofrequency tissue ablation: increased lesion diameter with a perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol 1996;3(8):636–644. doi:10.1016/S1076-6332(96)80188-7.
Tamaki K, Shimizu I, Oshio A, Fukuno H, Inoue H, Tsutsui A, Shibata H, Sano N, Ito S. Influence of large intrahepatic blood vessels on the gross and histological characteristics of lesions produced by radiofrequency ablation in a pig liver model. Liver Int 2004;24(6):696–701. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.0952.x.
Chinn SB, Lee FT Jr, Kennedy GD, Chinn C, Johnson CD, Winter TC 3rd, Warner TF, Mahvi DM. Effect of vascular occlusion on radiofrequency ablation of the liver: results in a porcine model. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001;176(3):789–795.
Solbiati L, Ierace T, Goldberg SN, Sironi S, Livraghi T, Fiocca R, Servadio G, Rizzatto G, Mueller PR, Del Maschio A, Gazelle GS. Percutaneous US-guided radio-frequency tissue ablation of liver metastases: treatment and follow-up in 16 patients. Radiology 1997;202(1):195–203.
Lu DS, Raman SS, Vodopich DJ, Wang M, Sayre J, Lassman C. Effect of vessel size on creation of hepatic radiofrequency lesions in pigs: assessment of the “heat sink” effect. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002;178(1):47–51.
Wright AS, Sampson LA, Warner TF, Mahvi DM, Lee FT. Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology 2005;236(1):132–139. doi:10.1148/radiol.2361031249.
Tabuse K, Katsumi M, Kobayashi Y, Noguchi H, Egawa H, Aoyama O, Kim H, Nagai Y, Yamaue H, Mori K et al. Microwave surgery: hepatectomy using a microwave tissue coagulator. World J Surg 1985;9(1):136–143. doi:10.1007/BF01656265.
Izzo F. Other thermal ablation techniques: microwave and interstitial laser ablation of liver tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 2003;10(5):491–497. doi:10.1245/ASO.2003.07.016.
Haemmerich D, Lee FT. Multiple applicator approaches for radiofrequency and microwave ablation. Int J Hyperthermia 2005;21(2):93–106. doi:10.1080/02656730412331286894.
Tabuse K. Basic knowledge of a microwave tissue coagulator and its clinical applications. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 1998;5(2):165–172. doi:10.1007/s005340050028.
Sato M, Watanabe Y, Ueda S, Iseki S, Abe Y, Sato N, Kimura S, Okubo K, Onji M. Microwave coagulation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 1996;110(5):1507–1514. doi:10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8613057.
Organ LW. Electrophysiologic principles of radiofrequency lesion making. Appl Neurophysiol 1976–1977;39(2):69–76. doi:10.1159/000102478.
Tungjitkusolmun S, Staelin ST, Haemmerich D, Tsai JZ, Webster JG, Lee FT Jr, Mahvi DM, Vorperian VR. Three-Dimensional finite-element analyses for radio-frequency hepatic tumor ablation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2002;49(1):3–9. doi:10.1109/10.972834.
Skinner MG, Iizuka MN, Kolios MC, Sherar MD. A theoretical comparison of energy sources—microwave, ultrasound and laser—for interstitial thermal therapy. Phys Med Biol 1998;43(12):3535–3547. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/43/12/011.
Wright AS, Lee FT Jr, Mahvi DM. Hepatic microwave ablation with multiple antennae results in synergistically larger zones of coagulation necrosis. Ann Surg Oncol 2003;10(3):275–283. doi:10.1245/ASO.2003.03.045.
Topp SA, McClurken M, Lipson D, Upadhya GA, Ritter JH, Linehan D, Strasberg SM. Saline-linked surface radiofrequency ablation: factors affecting steam popping and depth of injury in the pig liver. Ann Surg 2004;239(4):518–527. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000118927.83650.a4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrean, S., Hering, J., Saied, A. et al. Ultrasound Monitoring of a Novel Microwave Ablation (MWA) Device in Porcine Liver: Lessons Learned and Phenomena Observed on Ablative Effects Near Major Intrahepatic Vessels. J Gastrointest Surg 13, 334–340 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0715-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0715-4