Abstract
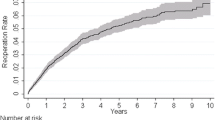
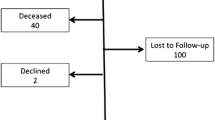
Many studies have looked at the learning curve associated with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication (LNF) in a given institution. This study looks at the learning curve of a single surgeon with a large cohort of patients over a 10-year period. Prospective data were collected on 400 patients undergoing laparoscopic fundoplication for over 10 years. The patients were grouped consecutively into cohorts of 50 patients. The operating time, the length of postoperative hospital stay, the conversion rate to open operation, the postoperative dilatation rate, and the reoperation rate were analyzed. Results showed that the mean length of operative time decreased from 143 min in the first 50 patients to 86 min in the last 50 patients. The mean postoperative length of hospital stay decreased from 3.7 days initially to 1.2 days latterly. There was a 14% conversion to open operation rate in the first cohort compared with a 2% rate in the last cohort. Fourteen percent of patients required reoperation in the first cohort and 6% in the last cohort. Sixteen percent required postoperative dilatation in the first cohort. None of the last 150 patients required dilatation. In conclusion, laparoscopic fundoplication is a safe and effective operation for patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. New techniques and better instrumentation were introduced in the early era of LNF. The learning curve, however, continues well beyond the first 20 patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Voitk A, Joffe J, Alvarez C, Rosenthal G. Factors contributing to laparoscopic failure during the learning curve for laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in a community hospital. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 1999;9:243–248.
Watson DI, Baigrie RJ, Jamieson G. A learning curve for laparoscopic fundoplication. Definable, avoidable, or a waste of time? Ann Surg 1996;224:198–203.
Booth M, Stratford J, Jones L, Dehn T. Initial results of a randomised trial of laparoscopic total (NISSEN) versus posterior partial (TOUPET) fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (Abstract). Br J Surg 2002;89(Supp1):36.
Dallemange B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C, Markiewicz S, Lombard R. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1991;1:138–143.
Watson DI, De Beaux AC. Complications of anti-reflux surgery: review article. Surg Endosc 2001;15:344–352.
Laine S, Rantala A, Gullichsen R, Ovaska J. Laparoscopic vs. conventional Nissen fundoplication. A prospective randomised study. Surg Endosc 1997;11:441–444.
Bais JE, Bartelsman JF, Bonjer HJ, Cuesta MA, Go PM, Klinkenberg-Knol EC, van Lanschot JJ, Nadorp JH, Smout AJ, van der Graaf Y, Gooszen HG. Laparoscopic or conventional Nissen fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux: randomised clinical trial. The Netherlands Antireflux Surgery Study Group. Lancet 2000;335:170–174.
Tan LC, Samanta S, Hosking SW. Safe transition from open to laparoscopic by an established consultant—the importance of repeated audit. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2002;84:84–88.
Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Crookes P, Oberg S, de Vos Shoop M, Hagen JA, Bremner CG, Cedric G. The treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: prospective evaluation of 100 patients with “typical” symptoms. Ann Surg 1998;228:40–50.
Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jeahes C, Markiewitz S. Results of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Hepatogastroenterology 1998;45:1338–1343.
Frantzides CT, Richards C. A study of 362 consecutive laparoscopic Nissen fundoplications. Surgery 1998;124:651–655.
Gaudric M, Sabate JM, Artru P, Chaussade S, Couturier D. Results of pneumatic dilatation in patients with dysphagia after antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 1999;86:1088–1091.
Malhi-Chowla N, Gorecki P, Bammer T, Achem SR, Hinder RA, DeVault KR. Dilatation after fundoplication: timing, frequency, indications, and outcome. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;55:219–223.
Hunter JG, Swanstrom L, Waring JP. Dysphagia after laparoscopic antireflux surgery. The impact of operative technique. Ann Surg 1996;1:51–57.
O’Boyle CJ, Heer K, Smith A, Sedman PC, Brough WA, Royston CM. Iatrogenic thoracic migration of the stomach complicating laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 2000;14:540–542.
Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Devitt PG, Mitchell PC, Game PA. Paraoesophageal hiatus hernia: an important complication of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg 1995;82:521–523.
Basso N, De Leo A, Genco A, Rosato P, Rea S, Spaziani E, Primavera A. 360° laparoscopic fundoplication with tension-free hiatoplasty in the treatment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 2000;14:164–169.
Swanstron LL, Pennings JL. Safe laparoscopic dissection of the gastroesophageal junction. Am J Surg 1995;169:507–511.
Watson DI, Mitchell P, Game PA, Jamieson GG. Pneumothorax during laparoscopic mobilization of the oesophagus. Aust N Z J Surg 1996;66:711–712.
Wu JS, Dunnegan DL, Luttmann DR, Soper NJ. The influence of surgical technique on clinical outcome of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 1996;10:1164–1170.
Smith DC, McClusky DA, Rajad MA, Lederman AB, Hunter JG. When fundoplication fails: redo? Ann Surg 2005;241(6):861–871.
Szwerc MF, Wiechmann RJ, Maley RH, Santucci TS, Macherey RN, Landreneau RJ. Reoperative laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Surgery 1999;126:723–729.
Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Game PA, Williams RS, Devitt PG. Laparoscopic reoperation following failed antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 1999;86:98–101.
Bammer T, Hinder RA, Klaus A, Klingler PJ. Five-to eight-year outcome of the first laparoscopic Nissen fundoplications. J Gastrointest Surg 2001;5:42–48.
Booth M, Jones L, Stratford J, Dehn TCB. Results of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication at 2 to 8 years after surgery. Br J Surg 2002;89:476–481.
Lafullarde T, Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Myers JC, Game PA, Devitt PG. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Five year results and beyond. Arch Surg 2001;136:180–184.
Peters JH, Ellison EC, Innes JT, Liss JL, Nichols KE, Lomano JM, Front ME, Carey LC. Safety and efficacy of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. A prospective analysis of 100 patients. Ann Surg 1991;213:3–12.
Bittner R, Schmedt CG, Schwartz J, Kraft K, Leibl BJ. Laparoscopic transperitoneal procedure for routine repair of hernia. Br J Surg 2002;89:1062–1066.
Edwards CC 2nd, Bailey RW. Laparoscopic hernia repair: the learning curve. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 2000;10:149–153.
Menon KV, Booth M, Stratford J, Dehn TCBD. Laparoscopic fundoplication in mentally normal children with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dis Esophagus 2002;15:163–166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, J., Booth, M.I., Stratford, J. et al. The Extended Learning Curve for Laparoscopic Fundoplication: A Cohort Analysis Of 400 Consecutive Cases. J Gastrointest Surg 11, 487–492 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-007-0132-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-007-0132-0