Abstract
Purpose
Finding a novel biomarker for determining the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer (CRC) is critical. The aim of this study is to evaluate the role of two main miRNAs including miR-222 and miR-155 in radiation response of CRC.
Materials and methods
The radioresistant CRC cell lines were established by exposing the HCT 116 cell line to fractional X-ray radiation. SubG1 fraction analysis, MTT and clonogenic assays were applied to evaluate acquired radioresistant cell line radiosensitivity. miR-222/PTEN and miR-155/FOXO3a expressions were detected by RT PCR.
Results
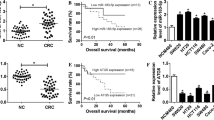
The clonogenic assay and sub-G1fraction analysis indicated that the RR2 sub-line was significantly more resistant than the parental cell line. MiR-222 and miR-155 were significantly upregulated in the radioresistant cell lines compared with the parental cell lines. The PTEN and FOXO3a expressions in the radioresistant cell lines were significantly higher than in the parental line.
Conclusion
These observations indicate that miR-222 and miR-155 could induce radiation resistance in colorectal cancer by targeting PTEN and FOXO3a genes, respectively. Therefore, miR-222 and miR-155 can be suggested as good biomarkers of CRC radiation response.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Huang J, Gao F, Lin X, He L, et al. MiR-124 radiosensitizes human colorectal cancer cells by targeting PRRX1. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e93917.
Sandur SK, Deorukhkar A, Pandey MK, Pabón AM, Shentu S, Guha S, et al. Curcumin modulates the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by suppressing constitutive and inducible NF-κB activity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75(2):534–42.
Zheng L, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhou M, Lu Y, Yuan L, et al. MiR-106b induces cell radioresistance via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathways and p21 in colorectal cancer. J Transl Med. 2015;13(1):1.
Barker HE, Paget JT, Khan AA, Harrington KJ. The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(7):409–25.
Das P, Skibber JM, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Feig BW, Chang GJ, Wolff RA, et al. Predictors of tumor response and downstaging in patients who receive preoperative chemoradiation for rectal cancer. Cancer. 2007;109(9):1750–5.
Kremser C, Trieb T, Rudisch A, Judmaier W, de Vries A. Dynamic T1 mapping predicts outcome of chemoradiation therapy in primary rectal carcinoma: sequence implementation and data analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;26(3):662–71.
Jiang S, Wang R, Yu J, Zhu K, Mu D, Xu Z. Correlation of VEGF and Ki67 expression with sensitivity to neoadjuvant chemoradiation in rectal adenocarcinoma. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi. 2008;30(8):602–5 (Chinese Journal of Oncology).
Colibaseanu DT, Mathis KL, Abdelsatter ZM, Larson DW, Haddock MG, Dozois EJ. Is curative resection and long-term survival possible for locally re-recurrent colorectal cancer in the pelvis? Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56(1):14–9.
Corté H, Manceau G, Blons H, Laurent-Puig P. MicroRNA and colorectal cancer. Dig Liver Dis. 2012;44(3):195–200.
Yang L, Belaguli N, Berger DH. MicroRNA and colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2009;33(4):638–46.
Ma W, Yu J, Qi X, Liang L, Zhang Y, Ding Y, et al. Radiation-induced microRNA-622 causes radioresistance in colorectal cancer cells by down-regulating Rb. Oncotarget. 2015;6(18):15984.
Riffo-Campos ÁL, Riquelme I, Brebi-Mieville P. Tools for sequence-based miRNA target prediction: what to choose? Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):1987.
Lin R-J, Lin Y-C, Chen J, Kuo H-H, Chen Y-Y, Diccianni MB, et al. MicroRNA signature and expression of Dicer and Drosha can predict prognosis and delineate risk groups in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2010;70(20):7841–50.
MacFarlane L-A, Murphy RP. MicroRNA: biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr Genom. 2010;11(7):537–61.
Zhao L, Lu X, Cao Y. MicroRNA and signal transduction pathways in tumor radiation response. Cell Signal. 2013;25(7):1625–34.
Joye I, Haustermans K, editors. Which patients with rectal cancer do not need radiotherapy? Seminars in radiation oncology. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2016.
Agostini M, Crotti S, Bedin C, Cecchin E, Maretto I, D’Angelo E, et al. Predictive response biomarkers in rectal cancer neoadjuvant treatment. Front Biosci. 2014;6:110–9.
Chun-zhi Z, Lei H, An-ling Z, Yan-chao F, Xiao Y, Guang-xiu W, et al. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 regulate gastric carcinoma cell proliferation and radioresistance by targeting PTEN. BMC Cancer. 2010;10(1):1.
Jurkovicova D, Magyerkova M, Kulcsar L, Krivjanska M, Krivjansky V, Gibadulinova A, et al. MiR-155 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in hematological and solid malignancies. Neoplasma. 2014;61(3):241–51.
Simone NL, Soule BP, Ly D, Saleh AD, Savage JE, DeGraff W, et al. Ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress alters miRNA expression. PLoS One. 2009;4(7):e6377.
Templin T, Paul S, Amundson SA, Young EF, Barker CA, Wolden SL, et al. Radiation-induced micro-RNA expression changes in peripheral blood cells of radiotherapy patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;80(2):549–57.
Vincenti S, Brillante N, Lanza V, Bozzoni I, Presutti C, Chiani F, et al. HUVEC respond to radiation by inducing the expression of pro-angiogenic microRNAs. Radiat Res. 2011;175(5):535–46.
Chaudhry MA, Omaruddin RA, Kreger B, de Toledo SM, Azzam EI. Micro RNA responses to chronic or acute exposures to low dose ionizing radiation. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(7):7549–58.
Chaudhry MA, Sachdeva H, Omaruddin RA. Radiation-induced micro-RNA modulation in glioblastoma cells differing in DNA-repair pathways. DNA Cell Biol. 2010;29(9):553–61.
Gasparini P, Lovat F, Fassan M, Casadei L, Cascione L, Jacob NK, et al. Protective role of miR-155 in breast cancer through RAD51 targeting impairs homologous recombination after irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(12):4536–41.
Su H, Jin X, Zhang X, Xue S, Deng X, Shen L, et al. Identification of microRNAs involved in the radioresistance of esophageal cancer cells. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(3):318–25.
Nikzad S, Hashemi B. MTT assay instead of the clonogenic assay in measuring the response of cells to ionizing radiation. J Radiobiol. 2014;1(1):3–8.
Pozarowski P, Darzynkiewicz Z. Analysis of cell cycle by flow cytometry. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;281:301–11.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Riffo-Campos AL, Riquelme I, Brebi-Mieville P. Tools for sequence-based miRNA target prediction: What to choose? Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):1987.
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW, Grimson A, Bartel DP. Weak seed-pairing stability and high target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18(10):1139–46.
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C, Leslie C. Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol. 2010;11(8):R90.
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M, Giegerich R. Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. RNA. 2004;10(10):1507–17.
Essaghir A, Dif N, Marbehant CY, Coffer PJ, Demoulin J-B. The transcription of FOXO genes is stimulated by FOXO3 and repressed by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(16):10334–42.
Anastasov N, Hofig I, Vasconcellos IG, Rappl K, Braselmann H, Ludyga N, et al. Radiation resistance due to high expression of miR-21 and G2/M checkpoint arrest in breast cancer cells. Radiat Oncol. 2012;7:206.
Yang XD, Xu XH, Zhang SY, Wu Y, Xing CG, Ru G, et al. Role of miR-100 in the radioresistance of colorectal cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(2):545–59.
Huang MY, Wang JY, Chang HJ, Kuo CW, Tok TS, Lin SR. CDC25A, VAV1, TP73, BRCA1 and ZAP70 gene overexpression correlates with radiation response in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011;25(5):1297–306.
Chendil D, Oakes R, Alcock RA, Patel N, Mayhew C, Mohiuddin M, et al. Low dose fractionated radiation enhances the radiosensitization effect of paclitaxel in colorectal tumor cells with mutant p53. Cancer. 2000;89(9):1893–900.
Matsuzaki J, Suzuki H. Role of microRNAs-221/222 in digestive systems. J Clin Med. 2015;4(8):1566–77.
Yang X-D, Xu X-H, Zhang S-Y, Wu Y, Xing C-G, Ru G, et al. Role of miR-100 in the radioresistance of colorectal cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:545–59.
Ge H, Cao Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Chen Z, Wen D, et al. PTEN polymorphisms and the risk of esophageal carcinoma and gastric cardiac carcinoma in a high incidence region of China. Dis Esophagus. 2008;21(5):409–15.
Cinti C, Vindigni C, Zamparelli A, La Sala D, Epistolato MC, Marrelli D, et al. Activated Akt as an indicator of prognosis in gastric cancer. Virchows Arch. 2008;453(5):449–55.
Pappas G, Zumstein L, Munshi A, Hobbs M, Meyn R. Adenoviral-mediated PTEN expression radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing DNA repair capacity. Cancer Gene Ther. 2007;14(6):543–9.
He XC, Yin T, Grindley JC, Tian Q, Sato T, Tao WA, et al. PTEN-deficient intestinal stem cells initiate intestinal polyposis. Nat Genet. 2007;39(2):189–98.
Qiao Y, Badduke C, Mercier E, Lewis SM, Pavlidis P, Rajcan-Separovic E. miRNA and miRNA target genes in copy number variations occurring in individuals with intellectual disability. BMC Genom. 2013;14(1):544.
Miranda KC, Huynh T, Tay Y, Ang Y-S, Tam W-L, Thomson AM, et al. A pattern-based method for the identification of microRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell. 2006;126(6):1203–17.
Gironella M, Seux M, Xie M-J, Cano C, Tomasini R, Gommeaux J, et al. Tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 expression is repressed by miR-155, and its restoration inhibits pancreatic tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104(41):16170–5.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu C-G, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(16):7065–70.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(3):189–98.
Chaudhry MA, Kreger B, Omaruddin RA. Transcriptional modulation of micro-RNA in human cells differing in radiation sensitivity. Int J Radiat Biol. 2010;86(7):569–83.
Chaudhry MA, Omaruddin RA, Brumbaugh CD, Tariq MA, Pourmand N. Identification of radiation-induced microRNA transcriptome by next-generation massively parallel sequencing. J Radiat Res. 2013;54(5):808–22.
de Mattos SF, Villalonga P, Clardy J, Lam EW. FOXO3a mediates the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin in colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(10):3237–46.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120(1):15–20.
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105–11.
Civenni G, Walter A, Kobert N, Mihic-Probst D, Zipser M, Belloni B, et al. Human CD271-positive melanoma stem cells associated with metastasis establish tumor heterogeneity and long-term growth. Cancer Res. 2011;71(8):3098–109.
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444(7120):756–60.
Diehn M, Cho RW, Lobo NA, Kalisky T, Dorie MJ, Kulp AN, et al. Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stem cells. Nature. 2009;458(7239):780–3.
Oravecz-Wilson KI, Philips ST, Yilmaz ÖH, Ames HM, Li L, Crawford BD, et al. Persistence of leukemia-initiating cells in a conditional knockin model of an imatinib-responsive myeloproliferative disorder. Cancer Cell. 2009;16(2):137–48.
Zhao C, Chen A, Jamieson CH, Fereshteh M, Abrahamsson A, Blum J, et al. Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2009;458(7239):776–9.
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao M-J, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008;133(4):704–15.
Chang L, Graham PH, Hao J, Bucci J, Cozzi PJ, Kearsley JH, et al. Emerging roles of radioresistance in prostate cancer metastasis and radiation therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33(2–3):469–96.
Lagadec C, Vlashi E, Della Donna L, Dekmezian C, Pajonk F. Radiation-induced reprogramming of breast cancer cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30(5):833–44.
Acknowledgements
This study has been adapted from MSc and PhD theses at Hamadan University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
The study was funded by Vice-chancellor for Research and Technology, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (Nos. 9412257365 and 9411136348).
About this article
Cite this article
Khoshinani, H.M., Afshar, S., Pashaki, A.S. et al. Involvement of miR-155/FOXO3a and miR-222/PTEN in acquired radioresistance of colorectal cancer cell line. Jpn J Radiol 35, 664–672 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-017-0679-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-017-0679-y