Abstract
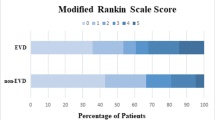
The efficacy and applied value of endoscopic hematoma evacuation vs. external ventricular drainage (EVD) in the treatment of severe ventricular hemorrhage (IVH) were explored and compared. From Jan. 2015 to Dec. 2016, the clinical data of 42 cases of IVH were retrospectively analyzed, including 18 patients undergoing endoscopic hematoma evacuation (group A), and 24 patients receiving EVD (group B). The hematoma clearance rate was calculated by 3D Slicer software, and complications and outcomes were compared between the two groups. There were no significant differences in age, sex and Graeb score between groups A and B (P>0.05). The hematoma clearance rate was 70.81%±27.64% in group A and 48.72%±36.58% in group B with a statistically significant difference (P<0.05). The operative time in groups A and B was 72.45±25.26 min and 28.54±15.27 min, respectively (P<0.05). The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score increased from 9.28±2.72 at baseline to 11.83±2.91 at 1 week postoperatively in group A, and from 8.25±2.62 at baseline to 10.79±4.12 at 1 week postoperatively in group B (P<0.05). The length of hospital stay was 12.67±5.97 days in group A and 17.33±8.91 days in group B with a statistically significant difference (P<0.05). The GOS scores at 6 months after surgery were 3.83±1.12 in group A, and 2.75±1.23 in group B (P<0.05). These results suggested that endoscopic hematoma evacuation has an advantage of a higher hematoma clearance rate, fewer complications and better outcomes in the treatment of severe IVH, indicating it is a safe, effective and promising approach for severe IVH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattathiri PS, Gregson B, Prasad KS, et al. Intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: results from the STICH trial. Acta Neurochir Suppl, 2006,96:65–68
Huttner HB, Kohrmann M, Berger C, et al. Influence of intraventricular hemorrhage and occlusive hydrocephalus on the long-term outcome of treated patients with basal ganglia hemorrhage: a casecontrol study. J Neurosurg, 2006,105(3):412–417
Graeb DA, Robertson WD, Lapointe JS, et al. Computed tomographic diagnosis of intraventricular hemorrhage. Etiology and prognosis. Radiology, 1982,143(1):91–96
Wang HJ, Ye YF, Shen Y, et al. Surgical treatment of poor grade middle cerebral artery aneurysms associated with large sylvian hematomas following prophylactic hinged craniectomy. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2014,34(5):716–721
Beynon C, Schiebel P, Bosel J, et al. Minimally invasive endoscopic surgery for treatment of spontaneous intracerebral haematomas. Neurosurg Rev, 2015,38(3):421–428; discussion 428
Chen CC, Liu CL, Tung YN, et al. Endoscopic surgery for intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) caused by thalamic hemorrhage: comparisons of endoscopic surgery and external ventricular drainage (EVD) surgery. World Neurosurg, 2011,75(2):264–268
Li YP, Zhang H. The efficacy and safety of neuroendoscopic surgery for intraventricular hemorrhage: A meta-analysis. Zhongguo Shenjing Jingshen Jibing Zazhi (Chinese), 2013,39(3):135–141
Basaldella L, Marton EA, Fiorindi A, et al. External ventricular drainage alone versus endoscopic surgery for severe intraventricular hemorrhage: a comparative retrospective analysis on outcome and shunt dependency. Neurosurg Focus, 2012,32(4):E4
Li Y, Zhang H, Wang X, et al. Neuroendoscopic surgery versus external ventricular drainage alone or with intraventricular fibrinolysis for intraventricular hemorrhage secondary to spontaneous supratentorial hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2013,8(11):e80599
Kuo LT, Chen CM, Li CH, et al. Early endoscopeassisted hematoma evacuation in patients with supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage: case selection, surgical technique, and long-term results. Neurosurg Focus, 2011,30(4):E9
Fiorella D, Zuckerman SL, Khan IS, et al. Intracerebral hemorrhage: a common and devastating disease in need of better treatment. World Neurosurg, 2015,84(4):1136–1141
Nishihara T, Nagata K, Tanaka S, et al. Newly developed endoscopic instruments for the removal of intracerebral hematoma. Neurocrit Care, 2005,2(1):67–74
Luo M, Min Q, Chen X, et al. Application of Selfmade Flexible Transparent Endoscopic Working Passage in Endoscopic Evacuation of Intracranial Hematoma. Huazhong Keji Daxue Xuebao (Yixueban) (Chinese), 2015,44(5):595–597
Gaberel T, Magheru C, Parienti JJ, et al. Intraventricular fibrinolysis versus external ventricular drainage alone in intraventricular hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. Stroke, 2011,42(10):2776–2781
Longatti P, Basaldella L. Endoscopic management of intracerebral hemorrhage. World Neurosurg, 2013,79(2 Suppl):S17 e11–17
Auer LM. Ultrasound Stereotaxic endoscropy in neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien), 1992,52:34–41
Qiu Y, Lin Y, Tian X, et al. Hypertensive intracranial hematomas: endoscopic-assisted keyhole evacuation and application of patent viewing dissector. Chin Med J (Engl), 2003,116(2):195–199
Hori T, Okada Y, Maruyama T, et al. Endoscopecontrolled removal of intrameatal vestibular schwannomas. Minim Invasive Neurosurg, 2006,49(1):25–29
Li Y, Yang R, Li Z, et al. Surgical Evacuation of Spontaneous Supratentorial Lobar Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Comparison of Safety and Efficacy of Stereotactic Aspiration, Endoscopic Surgery, and Craniotomy. World Neurosurg, 2017,105:332–340
Xu X, Chen X, Li F, et al. Effectiveness of endoscopic surgery for supratentorial hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage: a comparison with craniotomy. J Neurosurg, 2018,128(2):553–559
Wang G, Tian LX, Zhang HB, et al. Clinical observation of surgical treatment under neuroendoscope for intraventricular hemorrhage. Beijing Yixue (Chinese), 2013,35(11):917–919
Zhang ZQ, Li XG, Shao Y, et al. Comparative study of minimally invasive treatment in intraventricular hemorrhage. J Shandong Univ (Chinese), 2005,43(11):1007–1009
Passero S, Ulivelli M, Reale F. Primary intraventricular haemorrhage in adults. Acta Neurol Scand, 2002,105(2):115–119
Zhu H, Wang Z, Shi W. Keyhole endoscopic hematoma evacuation in patients. Turk Neurosurg, 2012,22(3):294–299
Hwang SC, Yeo DG, Shin DS, et al. Soft Membrane Sheath for Endoscopic Surgery of Intracerebral Hematomas. World Neurosurg, 2016,90:268–272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was funded by the Science and Technology Commission of Wuhan City (No. WX16B02) and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2018CFB353).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, P., Duan, Fl., Cai, Q. et al. Endoscopic Surgery versus External Ventricular Drainage Surgery for Severe Intraventricular Hemorrhage. CURR MED SCI 38, 880–887 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1957-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1957-3