Summary
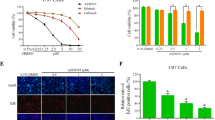
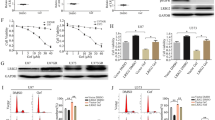
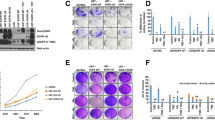
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is found to express at high levels in a variety of solid tumors including gliomas. This study was to examine the effect of an EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (AG1478) alone or in combination with cisplatin (CDDP) on the growth of glioma cells (U87). U87 glioma cells were treated with AG1478 (10 μmol/L) or CDDP (25 μmol/L) as a single agent or in combination for 24 or 48 h. The expression of EGFR and the components in its downstream signaling pathway [extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), protein kinase B (AKT)] in U87 glioma cells was detected by Western blotting. Cell growth, cell cycle distribution and cell apoptosis were determined by MTT method and flow cytometry, respectively. The results showed that CDDP could induce the activation of EGFR and the components in its downstream signaling pathways in a concentration-dependent manner. The combined treatment of AG1478 with CDDP could inhibit the proliferation of U87 glioma cells, arrest the cell cycle and promote cell apoptosis. In the EGFR signaling pathway, AG1478 decreased the phosphorylation of ERK, AKT and EGFR in U87 glioma cells. It was concluded that the combined treatment of AG1478 and CDDP may exert synergistic inhibitory effects on the growth of glioma cells by suppressing the activities of EGFR, AKT and ERK.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frederick L, Wang XY, Eley G, et al. Diversity and frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res, 2000,60(5):1383–1387
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, et al. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 1995,19(3): 183–232
Prenzel N, Fischer OM, Streit S, et al. The epidermal growth factor receptor family as a central element for cellular signal transduction and diversification. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2001,8(1):11–31
Huang SM, Harari PM. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in cancer therapy: Biology, rationale and preliminary clinical results. Invest New Drugs, 1999,17(3): 259–269
Hiraishi Y, Wada T, Nakatani K, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of EGFR and p-EGFR in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Pathol Oncol Res, 2006,12(2): 87–91
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, et al. Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2003,21(12):2237–2246
Saltz LB, Meropol NJ, Loehrer PJ, et al. Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that express the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Oncol, 2004,22(7):1201–1208
Gibbs JB. Anticancer drug targets: growth factors and growth factor signaling. J Clin Invest, 2000,105(1):9–13
Herbst RS, Kim ES, Harari PM. IMC-C225, an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody for treatment of head and neck cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2001,1(4):719–732
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2003,21(14):2787–2799
Mendelsohn J. The epidermal growth factor receptor as a target of cancer therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2001,8(1):3–9
Hiraishi Y, Wada T, Nakatani K, et al. EGFR inhibitor enhances cisplatin sensitivity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Pathol Oncol Res, 2008,14(1):39–43
Johns TG, Luwor RB, Murone C, et al. Antitumor efficacy of cytotoxic drugs and the monoclonal antibody 806 is enhanced by the EGF receptor inhibitor AG1478. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2003,100(26):15871–15876
Kim SH, Song YC, Kim SH, et al. Effect of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor alone and in combination with cisplatin on growth of vulvar cancer cells. Ann NY Acad Sci, 2009,1171:642–648
Gieseg MA, de Bock C, Ferguson LR, et al. Evidence for epidermal growth factor receptor enhanced chemosensitivity in combination of cisplatin and the new irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitor CI-1033. Anti-Cancer Drugs, 2001,12(8):683–690
Rosell R, Robinet G, Szczesna A, et al. Randomized phase II study of cetuximab plus cisplatin/vinorelbine compared with cisplatin/vinorelbine alone as firet-line therapy in EGFR-expressing advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol, 2008,19(2):362–369
Klass CM, Choe MS, Hurwitz SJ, et al. Sequence dependence of cell growth inhibition by EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839, Docetaxel, and cisplatin in head and neck cancer. Head Neck, 2009,31(10):1263–1273
Kuroda H, Takeno M, Murakami S, et al. Inhibition of hemeoxygenase-1 with an epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor and cisplatin decreases proliferation of lung cancer A549 cells. Lung Cancer, 2010,67(1):31–36
Benhar M, Engelberg D, Levitzki A, et al. Cisplatin-induced activation of the EGF receptor. Oncogene, 2002,21(57):8723–8731
Michaelis M, Bliss J, Arnold SC, et al. Cisplatin-resistant neuroblastoma cells express enhanced levels of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and are sensitive to treatment with EGFR-specific toxins. Clin Cancer Res, 2008,14(20):6531–6537
Chan JK, Pham H, You XJ, et al. Suppression of ovarian cancer cell tumorigenicity and evasion of cisplatin resistance using a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor in a rat model. Cancer Res, 2005,65(8):3243–3248
Bourhis J. New approaches to enhance chemotherapy in SCCHN. Ann Oncol, 2005,16(Suppl 6):vi20–vi24
Takaoka S, Iwase M, Uchida M, et al. Effect of combining epidermal growth factor receptor inhibits and cisplatin on proliferation and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol, 2007,30(6):1469–1476
Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene, 2003,22(47): 7265–7279
Ivanov VN, Hei TK. Combined treatment with EGFR inhibitors and arsenite upregulated apoptosis in human EGFR-positive melanomas: a role of suppression of the PI3K-AKT pathway. Oncogene, 2005,24(4):616–626
Franke TF, Homik CP, Segev L, et al. PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene, 2003,22(56):8983–8998
She QB, Solit DB, Ye Q, et al. The BAD protein integrates survival signaling by EGFR/MAPK and PI3K/Akt kinase pathways in PTEN-deficient tumor cells. Cancer Cell, 2005,8(4):287–297
Gurumurthy S, Goswami A, Vasudevan KM, et al. Phosphorylation of Par-4 by protein kinase A is critical for apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol, 2005,25(3):1146–1161
Katz M, Amit I, Yarden Y. Regulation of MAPKs by growth factors and receptor tyrosine kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2007,1773(8):1161–1176
Roberts PJ, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene, 2007,26(22):3291–3310
Kraskstad C, Chekenya M. Survival signalling and apoptosis resistance in glioblastomas:opportunities for targeted therapeutics. Mol Cancer, 2010,9:135
Yarden Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. Signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer, 2001,37(Suppl 4):S3–S8
El-Rayes BF, LoRusso PM. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Br J Cancer, 2004,91(3):418–24
Yoshid T, Okamoto I, Iwas T, et al. The anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody blocks cisplatin-induced action of EGFR signaling mediated by HB-EGF. FEBS Letters, 2008,582(30):4125–4130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xing, X., Zhan, H. et al. EGFR inhibitor enhances cisplatin sensitivity of human glioma cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 773–778 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0675-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0675-x