Abstract
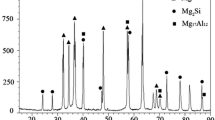
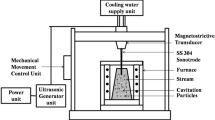
In situ A356-x%PVF (particle volume fraction) ZrB2 (x=1, 3, 5) composites were prepared via magneto-chemistry in situ reaction and the dry sliding wear properties of the composites were investigated. The experimental results show that ZrB2 reinforcement particle is obtained and its morphology mainly present in spherical and regular hexagon. Wear test results show that the values of wear weight loss of the composites decrease with the increase of value under a given sliding time and a certain load of 60 N. Especially, when x=5, the weight loss of the as-prepared composite is 43.1 mg, which is only 36.4% to that of A356 alloy, 118 mg. The wear mechanism is changed from adhesion wear to adhesion wear and abrasive wear and then to abrasive wear with the increase of x value.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miyajima T, Iwai Y. Effects of Reinforcements on Sliding Wear Behavior of Aluminum Matrix Composites[J]. Wear, 2003, 255: 606–616
Natarajan N, Vijayarangan S, Rajendran I. Wear Behaviour of A356/25SiCp Aluminium Matrix Composites Sliding Against Automobile Friction Material [J]. Wear, 2006, 261: 812–822
Urena A, Martinez EE, Rodrigo P, Gil L. Oxidation Treatments for SiC Particles Used as Reinforcement in Aluminium Matrix Composites[J]. Comp. Sci. Technol., 2004, 64: 1 843–1 854
Srivatsan TS, Al-Hajri M. The Fatigue and Final Fracture Behavior of SiC Particle Reinforced 7034 Aluminum Matrix Composites[J]. Composites: Part B, 2002, 33: 391–404
Sivaprasad K, Kumaresh Babu SP, Natarajan S. Study on Abrasive and Erosive Wear Behaviour of Al 6063/TiB2 in Situ Composites [J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 498: 495–500
G Naveen Kumar, R Narayanasamy, S Natarajan. Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of AA 6351-ZrB2 in Situ Composite at Room Temperature[J]. Mater. Des., 2010, 31: 1526–1532
Setoudeh N, Welham NJ. Formation of Zirconium Diboride (ZrB2) by Room Temperature Mechanochemical Reaction between ZrO2, B2O3 and Mg [J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2006, 420: 225–8
Takeshi Tsuchida, Satoshi Yamamoto. MA-SHS and SPS of ZrB2-ZrC Composites[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2004, 172: 215–216
Zhao YT, Zhang SL, Chen G, et al. (ZrB2+Al2O3+Al3Zr)p/Al-4Cu Composite Synthesized by Magneto-chemical Melt Reaction [J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 487: 1–6
Li GR, Zhao YT, Dai QX, et al. Fabrication and Properties of in Situ Synthesized Particles Reinforced Aluminum Mmatrix Composites of Al-Zr-O-B System[J]. J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42: 5 442–5 447
Yucel Birol. Production of Al-Ti-B Grain Refining Master Alloys from Na2B4O7 and K2TiF6[J]. J.Alloys Compd., 2008, 458: 271–276
Jonas Fjellstedt, Anders E W Jarfors. On the Precipitation of TiB2 in Aluminum Melts from the Reaction with KBF4 and K2TiF6 [J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 413–414: 527–532
Xu Q, Ma YM, Qiu ZX. Calculation of Thermodynamic Properties of LiF-AlF3, NaF-AlF3 and KF-AlF3 [J]. Calphad, 2001, 25: 31–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50971066), the Jiangsu Provincial ‘333’ Project of training the Highlevel Talents Foundation (No.2008-46) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Zhao, Y., Zhu, H. et al. Microstructures and dry sliding wear properties of ZrB2/A356 composites synthesized by magneto-chemistry in situ reaction. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 28, 384–388 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0700-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0700-y