Abstract
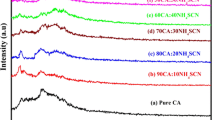
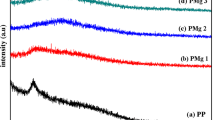
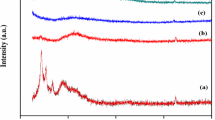
Zinc ion conducting biopolymer electrolyte has been prepared from cellulose acetate (CA) with different concentrations of zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2) by solution casting technique. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis has been adopted to investigate the amorphous nature of the samples. The complex creation of the biopolymer with the inorganic salt has been evidenced by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) studies. The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) study shows shifting of glass transition temperature to the lower temperature in the salt-doped system. The polymer electrolytes have been subjected to electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and the optimum conductivity attained was 2.7 \(\times\) 10−3 S cm−1 for the sample with the composition 45 M.wt% CA:55 M.wt% Zn(NO3)2. The linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) study reveals the electrochemical stability of the electrolyte as 3.03 V. The transference number for Zn2+ has been found to be 0.45 by Evans polarisation technique. The primary zinc battery has been constructed using optimum conducting membrane as an electrolyte. The OCV has been measured for this constructed battery and the value was found to be 1.72 V.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang-wang X, Ying W (2019) Recent progress on zinc ion rechargeable batteries. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-019-03s://doi.org/820-019-0322-9
Goodenough J, Park K (2013) The Li-ion rechargeable battery. J Am Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3091438
Ma Z, MacFarlane DR, Kar M (2019). Mg cathode materials and electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries: a review. https://doi.org/10.1002/batt.201800102
Xie ZQ, Lai JW, Zhu XP, Wang Y (2018). Green synthesis of vanadate nanobelts at room temperature for superior aqueous rechargeable zinc-ion batteries. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01378
Zhang N, Cheng FY, Liu YC, Zhao Q, Lei KX, Chen CC, Liu XS, Chen J (2016). Cation-deficient spinel ZnMn2O4 cathode in Zn(CF3SO3)2 electrolyte for rechargeable aqueous Zn-ion battery. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b05958
Tang B, Shan L, Liang S, Zhou J (2019) Issues and opportunities facing aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 12(11):3288–3304
Li Y, Fu J, Zhong C, Wu T, Chen Z, Hu W, Amine K, Lu J (2019) Batteries: recent advances in flexible zinc-basedrechargeable batteries. Adv Energy Mater 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201970001
Ming J, Guo J, Xia C, Wang W, Alshareef HN (2019) Zinc-ion batteries: materials, mechanisms, and applications. Mater Sci Eng R 135:58–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2018.10.002
Xu C, Li B, Du H, Kang F (2012) Energetic zinc ion chemistry: the rechargeable zinc ion battery. Angew Chem Int Ed 51(4):933–935. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201106307
Lee B, Lee HR, Kim H, Chung KY, Cho BW, Oh SH (2015) Elucidating the intercalation mechanism of zinc ions intoα-MnO2 for rechargeable zinc batteries. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC02585K
Yang Q, Mo FN, Liu ZX, Ma LT, Li XL et al (2019) Activating-coordinated iron of iron hexacyanoferrate for Zn hybrid-ion batteries with 10000-cycle lifespan and superior rate capability. Adv Mater 31(32):1901521. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201901521
Xu WN, Zhao KN, Huo WC, Wang YZ, Yao G et al (2019) Diethyl ether as self-healing electrolyte additive enabled long-life rechargeable aqueous zinc ion batteries. NanoEnergy 62:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.05.042
Li H, Han C, Huang Y, Huang Y, Zhu M, Pei Z, Xue Q, Wang Z, Liu Z, Tang Z, Wang Y (2018) An extremely safe and wearable solid-state zinc ion battery based on a hierarchical structured polymer electrolyte. Energy Environ Sci 11(4):941–951. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ee03232C
Liu J, Khanam Z, Muchakayala R, Song S (2020) Fabrication and characterization of Zn-ion-conducting solid polymer electrolyte films based on PVdF-HFP/Zn (Tf) 2 complex system. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31(8):6160–6173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03169-1
Wang M, Emre A, Tung S, Gerber A, Wang D, Huang Y, Cecen V, Kotov NA (2019) Biomimetic solid-state Zn2+ electrolyte for corrugated structural batteries. ACS Nano 13(2):1107–1115
Liu J, Ahmed S, Khanam Z, Wang T, Song S (2020) Ionic liquid-incorporated zn-ion conducting polymer electrolyte membranes. Polymers 12(8):1755
Ikeda S, Mori Y, Furuhashi Y, Masuda H (1999) Solid State Ionics 121:329–333
Girish Kumar G, Sampath S (2003) J Electrochem Soc 150:A608
Kim C, Ahn BY, Wei TS, Jo Y, Jeong S, Choi Y, Kim ID, Lewis JA (2018) High-power aqueous zinc-ion batteries for customized electronic devices. ACS Nano 12(12):11838–11846
Huang Y, Liu J, Zhang J, Jin S, Jiang Y, Zhang S, Li Z, Zhi C, Du G, Zhou H (2019) Flexible quasi-solid-state zinc ion batteries enabled by highly conductive carrageenan bio-polymer electrolyte. RSC Adv 9(29):16313–16319
Mahalakshmi M, Selvanayagam S, Selvasekarapandian S, Leena Chandra MV, Sangeetha P, Manjuladevi R (2020) Magnesium ion-conducting solid polymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate with magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2·6H2O) for electrochemical studies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03615-4
Monisha S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Milton Franklin Benial A, Prema latha M (2017) Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate and lithium nitrate for advanced electrochemical devices. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1886-8
Dueramae I, Okhawilai M, Kasemsiri P, Uyama H, Kita R (2020) Properties enhancement of carboxymethyl cellulose with thermo-responsive polymer as solid polymer electrolyte for zinc ion battery. Sci Rep 10(1):1–12
Ramesh S, Shanthi R, Morris E (2013) Characterization of conducting cellulose acetate based polymer electrolytes doped with “green” ionic mixture. Carbohydrate Polymer 9:14–21
Ramaswamy M, Malayandi T, Subramanian S, Srinivasalu J, Rangaswamy M (2017) Magnesium ion conducting polyvinyl alcohol–polyvinyl pyrrolidone-based blend polymer electrolyte. Ionics 23(7):1771–1781
Sikkanthar S, Karthikeyan S, Selvasekarapandian S, Vinoth Pandi D, Nithya S, Sanjeeviraja C (2015) Electrical conductivity characterization of polyacrylonitrile-ammonium bromide polymer electrolyte system. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2697-3
Ramesh S, Shanti R, Morris E (2013) Characterization of conducting cellulose acetate based polymer electrolytes doped with “green” ionic mixture. Carbohyd Polym 91(1):14–21
Chitra R, Sathya P, Selvasekarapandian S, Monisha S, Moniha V, Meyvel S (2019) Synthesis and characterization of iota-carrageenan solid biopolymer electrolytes for electrochemical applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2687-z
Bhuvaneswari R, Karthikeyan S, Selvasekarapandian S, Vinoth Pandi D, Vijaya N, Araichimani A, Sanjeeviraja C (2015) Preparation and characterization of PVA complexed with amino acid, proline. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1206-0
Mahalakshmi M, Selvanayagam S, Selvasekarapandian S, Moniha V, Manjuladevi R, Sangeetha P (2019) Characterization of biopolymer electrolytes based on cellulose acetate with magnesium perchlorate (Mg(ClO4)2) for energy storage devices. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2019.04.006
Rocco M, Pereira RP (2015) Solid electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(4-vinyl phenol-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) blends and LiClO4. Solid State Ionics 279
Janković S, Milisavić D, Okolić T, Jelić D (2018) Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles by solvent free method. Contemp Mater 9(1)
Biswicka T, Jonesa W, Pacula A, Serwickab E, Podobinskib J (2007) The role of anhydrous zinc nitrate in the thermal decomposition of the zinc hydroxy nitrates Zn5(OH)8(NO3)2 2H2O and ZnOHNO3 H2O. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2007.01.012
Arockia Mary I, Selvanayagam S, Selvasekarapandian S, Chitra R, Leena Chandra MV, Ponraj T (2020) Lithium ion conducting biopolymer membrane based on K-carrageenan with LiNO3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03604-7
Radha KP, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Hema M, Sanjeeviraja C (2013) Synthesis and impedance analysis of proton-conducting polymer electrolyte PVA:NH4 F. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-013-0866-5
Nirmala Devi G, Chitra S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M, Monisha S, Saranya J (2017) Synthesis and characterization of dextrin-based polymer electrolytes for potential applications in energy storage devices. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2135-5
Perumal P, Christopher Selvin P, Selvasekarapandian S (2018) Characterization of biopolymer pectin with lithium chloride and its applications to electrochemical devices Ionics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2507-5
Monisha S, Selvasekarapandian S, Mathavan T, Milton Franklin Benial A, Sindhuja Manoharan, Karthikeyan S (2016) Preparation and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate for potential applications in energy storage devices. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4971-x
Francis KMG, Subramanian S, Shunmugavel K, Naranappa V, Pandian SSM, Nadar SC (2016) Lithium ion-conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on PVA–PAN doped with lithium nitrate. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 55(1):25–35
Hemalatha R, Alagar M, Selvasekarapandian S, Sundaresan B, Moniha V (2019) Studies of proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA, amino acid proline and NH4 SCN. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2019.01.004
Radha KP, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Hema M, Sanjeeviraja C, Pandi DV (2014) Characterization of composite proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (vinyl alcohol). Int J Electroactive Mater 2:28–33
Hemalatha R, Alagar M, Selvasekarapandian S, Sundaresan B, Moniha V, Boopathi G, Christopher Selvin P (2019) Preparation and characterization of proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA, amino acid proline, and NH4Cl and its applications to electrochemical devices. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2564-9
Chitra R, Sathya P, Selvasekarapandian S, Meyvel S (2020) Synthesis and characterization of iota‑carrageenan biopolymer electrolyte with lithium perchlorate and succinonitrile (plasticizer). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02822-y
Boopathi G, Pugalendhi S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M, Monisha S, Aristatil G (2017) Development of proton conducting biopolymer membrane based on agar–agar for fuel cell. Ionics 23(10):2781–2790
Mangalam R, Thamilselvan M, Selvasekarapandian S, Jayakumar S, Manjuladevi R (2017) Polyvinyl pyrrolidone/Mg(ClO4)2 solid polymer electrolyte: structural and electrical studies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1931-7
Hambali D, Zainol NH, Othman L, Md Isa KB, Osman Z (2018) Magnesium ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile) (PVdC-co-AN): a comparative study between magnesium trifluoromethane sulfonate (MgTf2) and magnesium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) (Mg(TFSI)2). Ionics 15–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhuvaneswari, B., Sivabharathy, M., Prasad, L.G. et al. Structural, thermal and electrochemical characterization of cellulose acetate–based solid biopolymer electrolyte for zinc ion batteries. Ionics 28, 3865–3875 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04616-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04616-1