Abstract
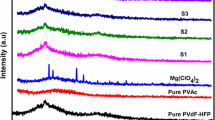
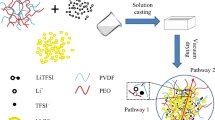
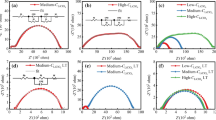
Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) have attracted ever increasing attention due to their huge potential applications in all-solid-state Li-ion batteries. High ionic conductivity and large extended electrochemical stability of SPEs are crucial for the high performance of Li-ion batteries. In this article, we demonstrate the effects of PVAc in P(VdF-HFP)-LiTFSI-EC complex, resulting in blend solid polymer electrolytes (BSPEs), were successfully prepared via solution casting technique. This method utilized the advantages of both polymers, resulting in superior ionic conductivity with enhanced mechanical integrity. Among the various concentrations, 10 wt% PVAc in P(VdF-HFP)-LiTFSI-EC exhibited a maximum ionic conductivity of 1.1 × 10−3 S cm−1, which is attributable to the suppression of PVdF crystalline phase and high Li-salt dissociation. The complex formation, surface morphology, thermal behavior, and thermal stability of BSPEs were systematically analyzed by FTIR, SEM, DSC, and TGA respectively. In addition, this sample shows a good electrochemical stability window (4.7 V) and Li transference number (0.29), which suggest that this could be a promising candidate for Li-ion batteries.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramesh S, Ng H-M (2011) An investigation on PAN–PVC–LiTFSI based polymer electrolytes system. Solid State Ionics 192:2–5
Kalnaus S, Sabau A-S, Tenhaeff W-E, Dudney N-J, Daniel C (2012) Design of composite polymer electrolytes for Li ion batteries based on mechanical stability of criteria. J Power Sources 20:280–287
Sun B, Mindemark J, Edstrdm K, Brandell D (2014) Polycarbonate-based solid polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 262:738–742
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Bhuvaneswari M-S (2004) Vibrational, ac impedance and dielectric spectroscopic studies of poly(vinylacetate)–N,N–dimethylformamide–LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. J Power Sources 134:235–240
Sun J, Liao X, Minor A-M, Balsara N-P, Zuckermann R-N (2014) Morphology-conductivity relationship in crystalline and amorphous sequence. J Am Chem Soc 136:14990–14997
Yang L-Y, Wei D-X, Xiu M, Yao Y-F, Chen Q (2014) Transferring lithium ions in nanochannels: a PEO/Li+ solid polymer electrolyte design. Angew Chem 126:3705–3709
Gupta R-K, Jung H-Y, Whang C-M (2002) Transport properties of a new Li+ ion-conducting ormolyte: (SiO2–PEG)–LiCF3SO3. J Mater Chem 12:3779–3782
Tao C, Gao M-H, Yin B-H, Li B, Huang Y-P, Xu G, Bao J-J (2017) A promising TPU/PEO blend polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 257:31–39
Liu W, Liu N, Sun J, Hau P-C, Li Y, Lee H-W, Cui Y (2015) Ionic conductivity enhancement of polymer electrolytes with ceramic nanowires fillers. Nano Lett 15:2740–2745
Zhang D, Zhang L, Yang K, Wang H, Yu C, Xu D, Xu B, Wang L-M (2017) Superior blends solid polymer electrolyte with integrated hierarchical architectures for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:36886–36896
Yu L, Dean K, Li L (2006) Polymer blends and composites from renewable resources. Prog Polym Sci 31:576–602
Kesavan K, Mathew C-M, Rajendran S (2014) Lithium ion conduction and ion-polymer interaction in poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) based electrolytes blended with different plasticizers. Chin Chem Lett 25:1428–1434
Deka M, Nath A-K, Kumar A (2009) Effect of dedoped (insulating) polyaniline nanofibers on the ionic transport and interfacial stability of poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) based composite polymer electrolyte membranes. J Membr Sci 327:188–194
Ramesh S, Ling O-P (2010) Effect of ethylene carbonate on the ionic conduction in poly(vinylidenefluoride-hexafluoropropylene) based solid polymer electrolytes. Polym Chem 1:702–707
Rajendran S, Kesavan K, Nithya R, Ulaganathan M (2012) Transport, structural and thermal studies on nanocomposite polymer blend electrolytes for Li-ion battery applications. Curr Appl Phys 12:789–793
Arunkumar D, Selvasekarapandian S, Baskaran R, Savitha T, Nithya H (2012) Thermal, vibrational and Ac impedance studies on proton conducting polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinyl acetate). J Non-Cryst Solids 358:531–536
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamura J, Hatton T (2007) Structure, thermal and transport properties of PVAc–LiClO4 solid polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem Solids 68:407–412
Choi N-S, Lee Y-G, Park J-K, Ko J-M (2001) Preparation and electrochemical characteristic of plasticized polymer electrolytes based upon a P(VdF-co-HFP)/PVAc blend. Electrochim Acta 46:1581–1586
Ulaganathan M, Rajendran S (2010) Preparation and characterizations of PVAc/P(VdF-HFP)-based polymer blend electrolytes. Ionics 16:515–521
Nishimoto A, Agehara K, Furuya N, Watanabe T, Watanabe M (1999) High ionic conductivity of polyether-based network polymer electrolytes with hyperbranched side chains. Macromolecules 32:1541–1548
Saikia D, Kumar A (2004) Ionic conduction in P(VDF-HFP)/PVDF–(PC + DEC)–LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 49:2581–2589
Ulaganathan M, Nithya R, Rajendran S, Raghu S (2012) Li-ion conduction on nanofiller incorporated PVdF-co-HFP based composite polymer blend electrolytes for flexible battery applications. Solid State Ionics 218:7–1
Bormashenko Y, Pogreb R, Stanevsky O, Bormashenko E (2004) Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym Test 23:791–796
Sim L-N, Majid S-R, Arof A-K (2012) FTIR studies of PEMA/PVdF-HFP blend polymer electrolyte system incorporated with LiCF3SO3 salt. Vib Spectrosc 58:57–66
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2006) ac impedance, DSC and FTIR investigations on (x)PVAc–(1−x)PVdF blends with LiClO4. Mater Chem Phys 98:55–61
Selvasekarapandian S, Baskaran R, Kamishima O, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2006) Laser Raman and FTIR studies on Li+ interaction in PVAc–LiClO4 polymer electrolytes. Spectrochim Acta A 65:1234–1240
Elashmawi I-S, Hakeem N-A, Abdelrazek E-M (2008) Spectroscopic and thermal studies of PS/PVAc blends. Physica B 403:3547–3552
Ramesh S, Liew C-W (2013) Dielectric and FTIR studies on blending of [xPMMA–(1 - x) PVC] with LiTFSI. Measurement 46:1650–1656
Wong D-H-C, Vitale A, Devaux D, Taylor A, Pandya A-A, Hallinan D-T, Thelen J-L, Mecham S-J, Lux S-F, Lapides A-M, Resnick P-R, Meyer T-J, Kostecki R-M, Balsara N-P DeSimone J-M (2015) Phase behavior and electrochemical characterization of blends of perfluoropolyether, poly(ethylene glycol), and a lithium salt. Chem Mater 27:597–603
Ikezawa Y, Nishi H (2008) In situ FTIR study of the Cu electrode/ethylene carbonate + dimethyl carbonate solution interface. Electrochim Acta 53:3663–3669
Wen S-J, Richardson T-J, Ghantous D-I, Striebel K-A, Ross P-N, Cairns E-J-J (1996) FTIR characterization of PEO+LiN(CF3SO2)2 electrolytes. J Electroanal Chem 408:113–118
Agrawal R-C, Pandey G-P (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:223001–223018
Wang Z, Tang Z (2003) Characterization of the polymer electrolyte based on the blend of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) for lithium ion battery. Mater Chem Phys 82:16–20
Dias F-B, Plomp L, Veldhuis J-B-J (2000) Trends in polymer electrolytes for secondary lithium batteries. J Power Sources 88:169–191
Kim K-M, Park N-G, Ryu K-S, Chong S-H (2006) Characteristics of PVdF-HFP/TiO2 composite membrane electrolytes prepared by phase inversion and conventional casting methods. ElectrochimActa 51:5636–5564
Aravindan V, Gnanaraj J, Lee Y-S, Madhavi S (2013) LiMnPO4 – a next generation lithium cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 1:3518–3539
Wu N, Cao Q, Wang X, Chen Q (2011) Study of a novel porous gel polymer electrolyte based on electrospinning technique. Solid State Ionics 203:42–46
Acknowledgments
M. Raja would like to thank DST-SERB for N-PDF Scheme of India. The authors are grateful to Dr. Helen Annal Therese (NRC, SRM-IST, Kattankulathur, Chennai) for his help in lithium-ion cell fabrication and Dr. M. N. Chandra Prabha (MSRIT) Bangalore for helpful discussion.
Funding
M. Sasikumar received financial support from the University Grants Commission (No. F. MRP-5633/15 (SERO/UGC)) of India. P. Sivakumar received financial support from the University Grants Commission (UGC –MRP NO. F. 42-807/2013 (SR)), New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasikumar, M., Jagadeesan, A., Raja, M. et al. The effects of PVAc on surface morphological and electrochemical performance of P(VdF-HFP)-based blend solid polymer electrolytes for lithium ion-battery applications. Ionics 25, 2171–2181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2679-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2679-z