Abstract
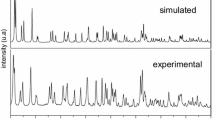
A soft solid crystal composed of isoquinoline (IQ) and LiCl was prepared based on the concept of Pearson’s hard-soft acid-base (HSAB) theory. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction best described the isoquinoline3•(LiCl)2 as consisting of molecular Li4Cl4(isoquinoline)6 units, where the LiCl cluster is an array of edge-fused Li2Cl2 rhombs. Electrochemical impedance measurements on pressed pellets showed that conductivity occurs mainly through the bulk via a hopping mechanism, with a calculated activation energy of Ea = 67 kJ/mol. The high value of the activation energy was due to Li4Cl4 clusters that were well separated by intervening IQ ligands in the crystal structure, requiring large hops for ions to migrate through the lattice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue Z, He D, Xie X (2015) Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:19218–19253
Hallinan DT Jr, Balsara NP (2013) Polymer electrolytes. Annu Rev Mater Res 43:503–525
Li YT, Han JT, Wang CA, Vogel SC, Xie H, Xu MW et al (2012) Ionic distribution and conductivity in lithium garnet Li7La3Zr2O12. J Power Sources 209:278–281
Li YT, Han JT, Wang CA, Xie H, Goodenough JB (2012) Optimizing Li+ conductivity in a garnet framework. J Mater Chem 22:15357–15361
Fergus JW (2010) Ceramic and polymeric solid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 195:4554–4569
Abitelli E, Ferrari S, Quartarone E, Mustarelli P, Magistris A, Fagnoni M et al (2010) Polyethylene oxide electrolyte membranes with pyrrolidinium-based ionic liquids. Electrochim Acta 55:5478–5484
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 394:456–458
Croce F, Curini R, Martinelli A, Persi L, Ronci F, Scrosati B et al (1999) Physical and chemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 103:10632–10638
Stephan AM, Kumar TP, Kulandainathan MA, Lakshmi NA (2009) Chitin-incorporated poly(ethylene oxide)-based Nanocomposite electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Phys Chem B 113:1963–1971
Zhang JW, Huang XB, Wei H, Fu JW, Huang YW, Tang XZ (2010) Effect of surface modified porous inorganic-organic hybrid polyphosphazene nanotubes on the properties of polyethylene oxide based solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 55:5966–5974
Zhang JW, Huang XB, Fu JW, Huang YW, Liu W, Tang XZ (2011) Novel PEO-based composite solid polymer electrolytes incorporated with active inorganic organic hybrid polyphosphazene microspheres. Mater Chem Phys 121:511–518
Zhang JW, Huang XB, Wei H, Fu JW, Huang YW, Tang XZ (2011) Novel PEO-based solid composite polymer electrolytes with inorganic-organic hybrid polyphosphazene microspheres as fillers. J Appl Electrochem 40:1475–1481
Uvarov NF (2011) Composite solid electrolytes: recent advances and design strategies. J Solid State Electrochem 15:367–389
Tsuchida E, Kobayashi N, Ohno H (1988) Single-ion conduction in poly[oligo(oxyethylene) methacrylate-co-(allkali-metal methacrylates)]. Macromolecules 21:96–100
Ryu SW, Trapa PE, Olugebefola SC, Gonzalez-Leon JA, Sadoway DR, Mayes AM (2005) Effect of counter ion placement on conductivity in single-ion conducting block copolymer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 152:A158–AA63
Park CH, Sun YK, Kim DW (2004) Blended polymer electrolytes based on poly(lithium 4-styrene sulfonate) for the rechargeable lithium polymer batteries. Electrochim Acta 50:375–378
Borodin O, Smith GD (2006) Mechanism of ion transport in amorphous poly(ethylene oxide)/LiTFSI from molecular dynamics simulations. Macromolecules 39:1620–1629
Diddens D, Heuer A, Borodin O (2010) Understanding the lithium transport within a rouse-based model for a PEO/LiTFSI polymer electrolyte. Macromolecules 43:2028–2036
Bruce PG (1996) Rechargeable lithium batteries. Philos Trans R Soc Math Phys Eng Sci 354:1577–1593
Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2000) Polymer electrolyte structure and its implications. Electrochim Acta 45:1417–1423
Dias FB, Batty SV, Gupta A, Ungar G, Voss JP, Wright PV (1998) Ionic conduction of lithium, sodium and magnesium salts within organised smectic liquid crystal polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 43:1217–1224
Wright PV, Zheng Y, Bhatt D, Richardson T, Ungar G (1998) Supramolecular order in new polymer electrolytes. Polym Int 47:34–42
Golodnitsky D, Peled E (2000) Stretching-induced conductivity enhancement of LiI-(PEO)-polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 45:1431–1436
Lightfoot P, Nowinski JL, Bruce PG (1994) Crystal-structures of the polymer electrolytes poly(ethylene oxide)4-MSCN (M= NH4, K). J Am Chem Soc 116:7469–7470
Lightfoot P, Mehta MA, Bruce PG (1993) Crystal structure of the polymer electrolyte poly(ethylene oxide)3LiCF3SO3. Science 262:883–885
Andreev YG, MacGlashan GS, Bruce PG (1997) Ab initio solution of a complex crystal structure from powder-diffraction data using simulated-annealing method and a high degree of molecular flexibility. Phys Rev B 55:12011–12017
Zhang CH, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2007) Crystalline small-molecule electrolytes. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:2848–2850
Zhang CH, Ainsworth D, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2007) Ionic conductivity in the solid glyme complexes [CH3O(CH2CH2O)(n)CH3]: LiAsF6 (n=3,4). J Am Chem Soc 129:8700–8701
Moriya M, Kitaguchi H, Nishibori E, Sawa H, Sakamoto W, Yogo T (2012) Molecular Ionics in supramolecular assemblies with channel structures containing lithium ions. Chem Eur J 18:15305–15309
Henderson WA, Brooks NR, Brennessel WW, Young VG (2003) Triglyme-Li+ cation solvate structures: models for amorphous concentrated liquid and polymer electrolytes (I). Chem Mater 15:4679–4684
MacGlashan GS, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (1999) Structure of the polymer electrolyte poly(ethylene oxide)(6): LiAsF6. Nature 398:792–794
Gadjourova Z, Marero DM, Andersen KH, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2001) Structures of the polymer electrolyte complexes PEO6: LiXF6 (X = P, Sb), determined from neutron powder diffraction data. Chem Mater 13:1282–1285
Pearson RG (1963) Hard and soft acids and bases. J Am Chem Soc 85:3533-&
Chinnam PR, Clymer RN, Jalil AA, Wunder SL, Zdilla MJ (2015) Bulk-phase ion conduction in cocrystalline LiCl·N,N-dimethylformamide: a new paradigm for solid electrolytes based upon the Pearson hard-soft acid-base concept. Chem Mater 27:5479–5482
Chinnam PR, Fall B, Dikin DA, Jalil A, Hamilton CR, Wunder SL et al (2016) A self-binding, melt-castable, crystalline organic electrolyte for sodium ion conduction. Angew Chem 128:15480–15483
Gondek E, Kityk IV, Danel A, Wisla A, Pokladko M, Sanetra J et al (2006) Electroluminescence of several pyrazoloquinoline and quinoksaline derivatives. Mater Lett 60:3301–3306
Moriya M, Kato D, Hayakawa Y, Sakamoto W, Yogo T (2016) Crystal structure and solid state ionic conductivity of molecular crystal composed of lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide and 1,2-dimethoxybenzene in a 1:1 molar ratio. Solid State Ionics 285:29–32
Stoeva Z, Martin-Litas I, Staunton E, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2003) Ionic conductivity in the crystalline polymer electrolytes PEO6:LiXF6, X = P, As, Sb. J Am Chem Soc 125:4619–4626
Staunton E, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2005) Structure and conductivity of the crystalline polymer electrolyte β-PEO6:LiAsF6. J Am Chem Soc 127:12176–12177
Irvine JTS, Sinclair DC, West AR (1990) Electroceramics: characterization by impedance spectroscopy. Adv Mater 2:132–138
Ramakumar S, Janani N, Murugan R (2015) Influence of lithium concentration on the structure and Li+ transport properties of cubic phase lithium garnets. Dalton Trans 44:539–552
Acknowledgments
Support of this work by the National Science Foundation under award CBET 1437814 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fall, B., Jalil, A., Gau, M. et al. Crystal structure and ionic conductivity of the soft solid crystal: isoquinoline3•(LiCl)2 . Ionics 24, 343–349 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2206-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2206-7