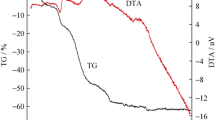
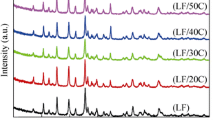
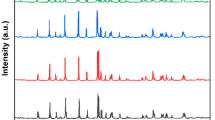
Abstract
Organic electrolyte is widely used for lithium-ion rechargeable batteries but might cause flammable fumes or fire due to improper use such as overcharge or short circuit. That weakness encourages the development of tools and materials which are cheap and environmental friendly for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries with aqueous electrolyte. Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) with olivine structure is a potential candidate to be used as the cathode in aqueous electrolyte lithium-ion battery. However, LiFePO4 has a low electronic conductivity compared to other cathodes. Conductive coating of LiFePO4 was applied to improve the conductivity using sucrose as carbon source by heating to 600 °C for 3 h on an Argon atmosphere. The carbon-coated LiFePO4 (LiFePO4/C) was successfully prepared with three variations of the weight percentage of carbon. From the cyclic voltammetry, the addition of carbon coatings could improve the stability of cell battery in aqueous electrolyte. The result of galvanostatic charge/discharge shows that 9 % carbon exhibits the best result with the first specific discharge capacity of 13.3 mAh g−1 and capacity fading by 2.2 % after 100 cycles. Although carbon coating enhances the conductivity of LiFePO4, excessive addition of carbon could degrade the capacity of LiFePO4.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wakira M (2001) J Mater Sci Eng R 33:109–134
Mi CH, Zhang CG, Li HLJ (2007) Electroanal Chem 602:245–254
Meijie Z, Dahn JR (1996) J Electrochem Soc 143:9
Wu L, Dahn JR, Wainwright DS (1994) Science 264:1115–1117
Wang GJ et al (2007) Angew Chem Int 46:295–297
Tang W et al (2011) Electrochem Commun 13:205–208
Qu QT et al (2011) Energy Environ Sci 4:3985–3990
Tang W et al (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:1524–1526
Manickam M, Singh P, Thurgate S, Prince K (2006) J Power Sources 158:646–649
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:4
Wu B, Ren Y, Li N (2011) “LiFePO4 cathode material”. Electric vehicles the benefits and barriers. ISBN: 978-953-307-287-6
Noerochim L, Wang J-Z, Chou S-L, Li H-J, Liu H-K (2010) Electrochim Acta 56(1):314–320
Liu Q, Liu Z, Xiao G, Liao S (2013) Ionics 19:445–450
Zeng X, Liu Q, Chen M, Leng L, Shu T, Du L, Song H, Liao S (2015) Electrochim Acta in press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noerochim, L., Yurwendra, A.O. & Susanti, D. Effect of carbon coating on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C as cathode materials for aqueous electrolyte lithium-ion battery. Ionics 22, 341–346 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1560-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1560-6