Abstract
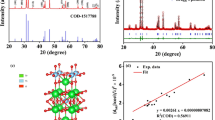
Swift heavy ion (SHI) irradiation has been used as a tool to enhance the electrochemical properties of ionic liquid-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes dispersed with dedoped polyaniline (PAni) nanorods; 100 MeV Si9+ ions with four different fluences of 5 × 1010, 1 × 1011, 5 × 1011, and 1 × 1012 ions cm−2 have been used as SHI. XRD results depict that with increasing ion fluence, crystallinity decreases due to chain scission up to fluence of 5 × 1011 ions cm−2, and at higher fluence, crystallinity increases due to cross-linking of polymer chains. Ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and dielectric properties are enhanced with increasing ion fluence attaining maximum value at the fluence of 5 × 1011 ions cm−2 and subsequently decrease. Optimum ionic conductivity of 1.5 × 10−2 S cm−1 and electrochemical stability up to 6.3 V have been obtained at the fluence of 5 × 1011 ions cm−2. Ac conductivity studies show that ion conduction takes place through hopping of ions from one coordination site to the other. On SHI irradiation, amorphicity of the polymer matrix increases resulting in increased segmental motion which facilitates ion hopping leading to an increase in ionic conductivity. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) measurements show that SHI-irradiated nanocomposite polymer electrolytes are thermally stable up to 240–260 °C.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand M, Tarascon JM (2008) Nature 451:652
Parveen A, Anilkumar KR, Patil SD, Roy AS (2013) Ionics 19:91
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nature 394:456
Pandey K, Dwivedi MM, Tripathi M, Singh M, Agrawal SL (2008) Ionics 14:515
Padmaraj O, Venkateswarlu M, Satyanarayana N (2013) Ionics 19:1835
Suthanthiraraj SA, Paul BJ (2007) Ionics 13:365
Fan LZ, Xing T, Awan R, Qiu W (2011) Ionics 17:491
Vaia RA, Jandt KD, Kramer EJ, Giannelis EP (1996) Chem Mater 8:2628
Sekhon SS, Kaur DP, Park JS, Yamada K (2012) Electrochim Acta 60:366
Nath AK, Kumar A (2014) J Membr Sci 453:192
Hofmann A, Schulz M, Hanemann T (2013) Electrochim Acta 89:823
Libo L, Jiajia W, Peixia Y, Shaowen G, Heng W, Xiuchun Y, Xuwei M, Shuo Y, Baohua W (2013) Electrochim Acta 88:147
Lavall RL, Ferrari S, Tomasi C, Marzantowicz M, Quartarone E, Fagnoni M, Mustarelli P, Saladino ML (2012) Electrochim Acta 60:359
Nan CW, Fan L, Lin Y, Cai Q (2003) Phys Rev Lett 91:266104
Raghavan P, Zhao X, Manuel J, Chauhan GS, Ahn JH, Ryu HS, Ahn HJ, Kim KW, Nah C (2010) Electrochim Acta 55:1347
Singh P, Kumar R, Prasad R (2013) Radiation Effects and defects in Solids 168:97
Deka M, Kumar A (2013) J Solid State Electrochem 17:977
Kumar A, Deka M, Banerjee S (2010) Solid State Ionics 181:609
Allen D, Baston G, Bradley AE, Gorman T, Haile A, Hamblett I, Hatter JE, Healey MJF, Hodgson B, Thied RC (2002) Green Chem 4:152
Qi M, Wu G, Li Q, Luo Y (2008) Radiat Phys Chem 77:877
Hussain AMP, Kumar A, Singh F, Avasthi DK (2006) J Phys D Appl Phys 39:750
Nath AK, Kumar A (2013) Solid State Ionics 253:8
Keijser THD, Langford JI, Mittemeijer EJ, Vogels ABP (1982) J Appl Crystallogr 15:308
Calcagno L (1995) Nucl Inst Methods B 105:63
Saikia D, Kumar A, Singh F, Avasthi DK (2006) J Phys D Appl Phys 39:4208
Lee EH (1999) Nucl Inst Methods B 151:29
Lee EH, Rao GR, Mansur LK (1999) Radiat Phys Chem 55:293
Takeuchi I, Asaka K, Kiyohara K, Sugino T, Mukai K, Randriamahazaka H (2010) J Phys Chem C 114:14627
Khaled KF, Heckerman N (2003) Electrochim Acta 48:2715
Ando RA, Siqueira LJA, Bazito FC, Torresi RM, Santos PS (2007) J Phys Chem B Lett 111:8717
Gaafar M (2001) Nucl Inst Methods B 174:507
Williams ML, Landel RF, Ferry JD (1955) J Am Chem Soc 77:3701
Dyre JC (1988) J Appl Phys 64:2456
Jonscher AK (1996) Dielectric relaxation in solids. Chelsea Dielectric, London
Roling B, Martiny C, Funke K (1999) J Non-Cryst Solids 249:201
Lewis MB, Lee EH, Rao GR (1994) J Nucl Mater 211:46
Deb B, Ghosh A (2010) J Appl Phys 108:074104
Kroon MC, Buijs W, Peters CJ, Witkamp GJ (2007) Thermochim Acta 465:40
Acknowledgments
The financial support from University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi through grant no. F.40-445/2011 (SR) is gratefully acknowledged. The authors gratefully acknowledge IUAC, New Delhi, India, for providing swift heavy ion irradiation facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nath, A.K., Kumar, A. Enhancement in electrochemical properties of ionic liquid-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes by 100 MeV Si9+ swift heavy ion irradiation. Ionics 20, 1711–1721 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1133-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1133-0