Abstract
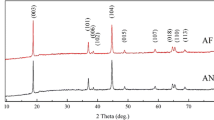
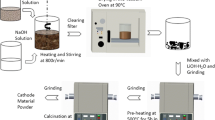
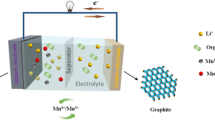
0.5Li2MnO3·0.5LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 powders were synthesized by coprecipitation, and high temperature sintered with different cooled methods, such as cooled with furnace material, water material, and in liquid nitrogen (N-material). The effect of cooling methods on physical and electrochemical properties are discussed through the characterizations of X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and discharge, cyclic, and rate tests. XRD results show that all samples exhibit layered characteristics. The electrochemical performance results indicate that the N-material has the best electrochemical performance. The discharge capacity at 0.1 and 5 C are 279 and 99 mAhg−1, respectively. The coulomb efficiency is highest, 78.4 %. The capacity retention after 50 cycles at 0.2 C is 97.1 %. EIS results show that the charge transfer resistance of N-materials is lowest, which is responsible for higher rate capacity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim DH, Kang SH, Balasubramanian M, Johnson CS (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:1618
Jeong JH, Jin BS, Kim WS, Wang G, Kim HS (2011) J Power Sources 196:3439
Sivaprakash S, Majumder SB (2010) Solid State Ionics 181:730
Koenig GM, Belharouak I, Wu HM, Amine K (2011) Electrochem Acta 56:1426
Kang SH, Thackeray MM (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:748
Park SH, Kang SH, Johnson CS, Amine K, Thackeray MM (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:262
Madhu C, Garret J, Manivannan V (2010) Ionics 16:591
Li J, Klopsch R, Stan MC, Nowak S, Kunze M, Winter M, Passerini S (2011) J Power Sources 196:4821
Chen Z, Dahn JR (2002) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 5:A213
Belharouak I, Gary MK, Jiwei M, Wang DP, Amine AI (2011) Electrochem Commun 13:232–236
Kang SH, Thackeray MM (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:748
Armstrong AR, Holzapfel M, Novak P, Johnson CS, Kang SH, Thackeray MM, Bruce PG (2006) J Am Chem Soc 128:8694
Johnson CS, Li N, Vaughey JT, Hackney SA, Thackeray MM (2005) Electrochem Commun 7:528
Liu J, Wang Q, Jayan BR, Manthiram A (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:750
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Postdoctoral Foundation of China (2012 M511211) and Postdoctoral Foundation of Jiangsu Province (1102121C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liu, S. Effect of cooling method on the electrochemical performance of 0.5Li2MnO3·0.5LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 cathodes. Ionics 19, 477–481 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-012-0787-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-012-0787-8