Abstract
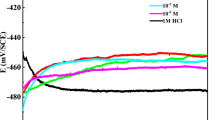
The electrochemical behavior of a pyrite electrode in a sulfuric acid solution with different concentrations of ferric iron (Fe3+) was investigated using electrochemical techniques including measurements of open circuit potential, cyclic voltammetry, Tafel polarization curves and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The results show that the pyrite oxidation process takes place via a two-step reaction at the interface of the pyrite electrode and the electrolyte, and that a passivation film composed of elemental sulfur, polysulfides, and metal-deficient sulfide is formed during the process of the first-step reaction. Ferric iron plays an important role in the dissolution of pyrite by enhancing the direct oxidation. The Tafel polarization curves indicate that the polarization current of the pyrite electrode increases with an increase in Fe3+ concentration. It has also been shown that the higher concentration of Fe3+, the more easily the pyrite can be transformed into the passivation region. Moreover, the EIS response is found to be sensitive to changes in Fe3+ concentration.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perdicakis M, Geoffroy S, Grosselin N, Bessière J (2001) Application of the scanning reference electrode technique to evidence the corrosion of a natural conducting mineral: pyrite. Inhibiting role of thymol. Electrochim Acta 47:211–216
Gleisner M, Herbert JRB, Frogner Kockum PC (2006) Pyrite oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans at various concentrations of dissolved oxygen. Chem Geol 225:16–29
Janzen MP, Nicholson RV, Scharer JM (2000) Pyrrhotite reaction kinetics: reaction rates for oxidation by oxygen, ferric iron, and for nonoxidative dissolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:1511–1522
Long H, Dixon DG (2004) Pressure oxidation of pyrite in sulfuric acid media: a kinetic study. Hydrometallurgy 73:335–349
Holmes PR, Crundwell FK (2000) The kinetics of the oxidation of pyrite by ferric ions and dissolved oxygen: an electrochemical study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:263–274
Cai M-F, Dang Z, Chen Y-W, Belzile N (2005) The passivation of pyrrhotite by surface coating. Chemosphere 61:659–667
Gleisner M, Herbert RB (2002) Sulfide mineral oxidation in freshly processed tailings: batch experiments. J Geochem Explor 76:139–153
Liu R, Wolfe AL, Dzombak DA, Horwitz CP, Stewart BW, Capo RC (2008) Electrochemical study of hydrothermal and sedimentary pyrite dissolution. Appl Geochem 23:2724–2734
Fowler T, Crundwell F (1999) Leaching of zinc sulfide by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: bacterial oxidation of the sulfur product layer increases the rate of zinc sulfide dissolution at high concentrations of ferrous ions. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5285
da Silva G (2004) Relative importance of diffusion and reaction control during the bacterial and ferric sulphate leaching of zinc sulphide. Hydrometallurgy 73:313–324
Córdoba E, Mu oz J, Blázquez M, González F, Ballester A (2008) Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion. Part I: general aspects. Hydrometallurgy 93:81–87
Córdoba E, Mu oz J, Blázquez M, González F, Ballester A (2008) Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion. Part II: effect of redox potential. Hydrometallurgy 93:88–96
Kinnunen P, Heimala S, Riekkola-Vanhanen M, Puhakka J (2006) Chalcopyrite concentrate leaching with biologically produced ferric sulphate. Bioresour Technol 97:1727–1734
Jiang L, Zhou H, Peng X, Ding Z (2008) Bio-oxidation of galena particles by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Particuology 6:99–105
da Silva G (2004) Kinetics and mechanism of the bacterial and ferric sulphate oxidation of galena. Hydrometallurgy 75:99–110
Bevilaqua D, Acciari HA, Arena FA, Benedetti AV, Fugivara CS, Filho GT, Júnior OG (2009) Utilization of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for monitoring bornite (Cu5FeS4) oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Miner Eng 22:254–262
Shi S, Fang Z, Ni J (2005) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of marmatite-carbon paste electrode in the presence and absence of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Electrochem Commun 7:1177–1182
Bevilaqua D, Diéz-Perez I, Fugivara C, Sanz F, Benedetti A, Garcia O (2004) Oxidative dissolution of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans analyzed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. Bioelectrochemistry 64:79–84
Lázaro I, Martínez-Medina N, Rodríguez I, Arce E, González I (1995) The use of carbon paste electrodes with non-conducting binder for the study of minerals: chalcopyrite. Hydrometallurgy 38:277–287
Giannetti B, Bonilla S, Zinola C, Rabóczkay T (2001) A study of the main oxidation products of natural pyrite by voltammetric and photoelectrochemical responses. Hydrometallurgy 60:41–53
Arce EM, González I (2002) A comparative study of electrochemical behavior of chalcopyrite, chalcocite and bornite in sulfuric acid solution. Int J Miner Process 67:17–28
Antonijević MM, Dimitrijević MD, Šerbula SM, Dimitrijević VLJ, Bogdanović GD, Milić SM (2005) Influence of inorganic anions on electrochemical behaviour of pyrite. Electrochim Acta 50:4160–4167
Lin HK, Say WC (1999) Study of pyrite oxidation by cyclic voltammetric, impedance spectroscopic and potential step techniques. J Appl Electrochem 29:987–994
Almeida CMVB, Giannetti BF (2002) Comparative study of electrochemical and thermal oxidation of pyrite. J Solid State Electrochem 6:111–118
Sasaki K, Tsunekawa M, Ohtsuka T, Konno H (1995) Confirmation of a sulfur-rich layer on pyrite after oxidative dissolution by Fe(lIl) ions around pH2. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:3155–3158
Cruz R, Bertrand V, Monroy M, Gonzalez I (2001) Effect of sulfide impurities on the reactivity of pyrite and pyritic concentrates: a multi-tool approach. Appl Geochem 16:803–819
Kelsall GH, Yin Q, Vaughan DJ, England KER, Brandon NP (1999) Electrochemical oxidation of pyrite (FeS2) in aqueous electrolytes. J Electroanal Chem 471:116–125
Shi SY, Fang ZH, Ni JR (2006) Electrochemistry of marmatite—carbon paste electrode in the presence of bacterial strains. Bioelectrochemistry 68:113–118
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NO.40730741), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program; Grant NO.AA061001), and the Open Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Environmental Geochemistry of China. The authors thank Dr. Jim Irish at South China University of Technology for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Dang, Z., Wu, P. et al. Influence of ferric iron on the electrochemical behavior of pyrite. Ionics 17, 169–176 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-010-0492-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-010-0492-4