Abstract
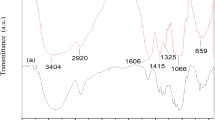
A series of crosslinked polymer electrolyte membranes were prepared by blending cellulose and sulfosuccinic acid (SA) for fuel cell applications. The crosslinking reaction of membranes occurred via the esterification between –OH of cellulose and –COOH of SA, as confirmed by FT-IR spectroscopy. Both the ion exchange capacity and the proton conductivity increased in proportion to the increase of SA concentrations due to the increasing portion of charged groups in the membrane. In contrast, the water uptake linearly increased up to 25 wt.% of SA concentration, above which it decreased abruptly. The maximum behavior of water uptake may be a result of competitive effect between the increasing number of ionic sites and the increasing degree of crosslinking with the SA concentrations. Wide angle X-ray scattering also showed that the crystalline structures of cellulose disappeared upon the introduction of SA. The mechanical properties of cellulose/SA membranes, i.e., tensile strength at break and Young’s modulus, showed a maximum at 15 wt.% of SA, as revealed by universal testing machine. These membranes exhibited good thermal stability up to 250 °C, as revealed by thermal gravimetric analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trapa PE, Huang B, Won YY, Sadoway DR, Mayes AM (2002) Electrochem Solid State Lett 5:A85
Stergiopoulos T, Arabatzis IM, Katsaros G, Falaras P (2002) Nano Lett 2:1259
Kuo SW, Wu CH, Chang FC (2004) Macromolecules 37:192
Kim JH, Kang MS, Kim YJ, Won J, Park NG, Kang YS (2004) Chem Commun 14:1662
Murai S, Mikoshiba S, Sumino H, Kato T, Hayase S (2003) Chem Commun 1534
Kim JH, Min BR, Won J, Joo SH, Kim HS, Kang YS (2003) Macromolecules 36:6183
Kim JH, Lee DH, Won J, Jinnai H, Kang YS (2006) J Membr Sci 281:369
Smitha B, Sridhar S, Khan AA (2003) J Membr Sci 225:63
Smitha B, Sridhar S, Khan AA (2005) J Membr Sci 259:10
Di Vona ML, Ahmed Z, Bellitto S, Lenci A, Traversa E, Licoccia S (2007) J Membr Sci 296:156
Licoccia S, Di Vona ML, D’Epifanio A, Ahmed Z, Bellitto S, Marani D, Mecheri B, de Bonis C, Trombetta M, Traversa E (2007) J Power Sources 167:79
Depre L, Ingram M, Poinsignon C, Popall M (2000) Electrochim Acta 45:1377
Chen SL, Benziger JB, Bocarsly AB, Zhang T (2005) Ind Eng Chem Res 44:7701
Li Z, Ding J, Robertson GP, Guiver MD (2006) Macromolecules 39:6990
Varcoe JR, Slade RCT, Yee ELH, Poynton SD, Driscoll DJ, Apperley DC (2007) Chem Mater 19:2686
Choi JK, Kim YW, Koh JH, Kim JH (2008) Polym Adv Tech 19:915
Kim JH, Min BR, Lee KB, Won J, Kang YS (2002) Chem Commun 2732
Rhim JW, Park HB, Lee CS, Jun JH, Kim DS, Lee YM (2004) J Membr Sci 238:143
Kim DS, Park HB, Rhim JW, Lee YM (2004) J Membr Sci 240:37
Kim YW, Choi JK, Park JT, Kim JH (2008) J Membr Sci 313:315
Wang Z, Ni H, Zhao C, Li X, Fu T, Na H (2006) J Polym Sci B: Polym Phys 44:1967
Kim YS, Wang F, Hickner M, Zawodzinski TA, McGrath JE (2003) J Membr Sci 212:263
Kang MS, Kim JH, Won J, Moon SH, Kang YS (2005) J Membr Sci 247:127
Cunha AG, Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP, Gandini A, Orblin E, Fardim P (2007) J Colloid Interf Sci 316:360
Kim B, Jung B (2004) Macromol Rapid Commun 25:1263
Acknowledgment
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE) and Korea Industrial Technology Foundation (KOTEF) through the Human Resource Training Project for Strategic Technology and by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) through Pioneer Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, J.A., Kim, J.C., Koh, J.K. et al. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked cellulose/sulfosuccinic acid membranes as proton conducting electrolytes. Ionics 15, 555–560 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0314-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0314-8