Abstract
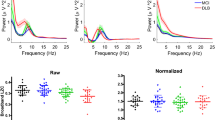
The objective of the present study was to investigate brain activity abnormalities in the early stage of Parkinson’s disease (PD). To achieve this goal, eyes-closed resting state electroencephalography (EEG) signals were recorded from 15 early-stage PD patients and 15 age-matched healthy controls. The AR Burg method and the wavelet packet entropy (WPE) method were used to characterize EEG signals in different frequency bands between the groups, respectively. In the case of the AR Burg method, an increase of relative powers in the δ- and θ-band, and a decrease of relative powers in the α- and β-band were observed for patients compared with controls. For the WPE method, EEG signals from patients showed significant higher entropy over the global frequency domain. Furthermore, WPE in the γ-band of patients was higher than that of controls, while WPE in the δ-, θ-, α- and β-band were all lower. All of these changes in EEG dynamics may represent early signs of cortical dysfunction, which have potential use as biomarkers of PD in the early stage. Our findings may be further used for early intervention and early diagnosis of PD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeli H, Zhou Z et al (2003) Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform. J Neurosci Methods 123:69–87
Akben S B, Subasi A et al (2011) Analysis of EEG signals under flash stimulation for migraine and epileptic patients. J Med Syst 35:437–443
Akin M, Kiymik MK (2000) Application of periodogram and AR spectral analysis to EEG signals. J Med Syst 24:247–256
Betarbet R, Sherer TB et al (2002) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Bioessays 24:308–318
Bosboom JL, Stoffers D et al (2006) Resting state oscillatory brain dynamics in Parkinson’s disease: an MEG study. Clin Neurophysiol 117(11):2521–2531
Caviness JN, Hentz JG et al (2007) Both early and late cognitive dysfunction affects the electroencephalogram in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13(6):348–354
Coifman R, Meyer Y et al (1990) Signal processing and compression with wavelet packets. Yale University, New Haven
Coifman RR, Wickerhauser MV (2008) Entropy-based algorithms for best basis selection. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 38:713–718
Cooper JA, Sagar HJ et al (1991) Cognitive impairment in early, untreated Parkinson’s disease and its relationship to motor disability. Brain 114(Pt 5):2095–2122
de Weerd AW, Perquin WVM et al (1990) Role of the EEG in the prediction of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Dementia 1:115–118
Elbert T, Lutzenberger W et al (1985) Removal of ocular artifacts from the EEG—a biophysical approach to the EOG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 60(5):455–463
Faust O, Acharya RU et al (2008) Analysis of EEG signals during epileptic and alcoholic states using AR modeling techniques. ITBM-RBM 29:44–52
Gandal MJ, Edgar JC et al (2012) Gamma synchrony: towards a translational biomarker for the treatment-resistant symptoms of schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 62:1504–1518
Gomez C, Olde Dubbelink KT et al (2011) Complexity analysis of resting-state MEG activity in early-stage Parkinson’s disease patients. Ann Biomed Eng 39(12):2935–2944
Hampel H, Frank R et al (2010) Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: academic, industry and regulatory perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:560–574
Herrmann CS, Munk MH et al (2004) Cognitive functions of gamma-band activity: memory match and utilization. Trends Cogn Sci 8:347–355
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1967) Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 17:427–442
Kay SM (1988) Modern spectral estimation: theory and application. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Kay SM, Marple SL (1981) Spectrum analysis-a modern perspective. Proc IEEE 69:1380–1419
Kheiri F, Bragin A et al (2012) Non-linear classification of heart rate parameters as a biomarker for epileptogenesis. Epilepsy Res 100:59–66
Kotini A, Anninos P et al (2005) Low-frequency MEG activity and MRI evaluation in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Topogr 18(1):59–63
Kyriazis M (2003) Practical applications of chaos theory to the modulation of human ageing: nature prefers chaos to regularity. Biogerontology 4(2):75–90
Leuchter AF, Cook IA et al (2009) Effectiveness of a quantitative electroencephalographic biomarker for predicting differential response or remission with escitalopram and bupropion in major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Res 169:132–138
Levy R, Hutchison WD et al (2000) High-frequency synchronization of neuronal activity in the subthalamic nucleus of parkinsonian patients with limb tremor. J Neurosci 20:7766–7775
Mallat S (1989) A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Pattern Anal Mach Intell 11:674–693
Moazami-Goudarzi M, Sarnthein J et al (2008) Enhanced frontal low and high frequency power and synchronization in the resting EEG of parkinsonian patients. Neuroimage 41(3):985–997
Muller V, Lutzenberger W et al (2001) Investigation of brain dynamics in Parkinson’s disease by methods derived from nonlinear dynamics. Exp Brain Res 137(1):103–110
Neufeld MY, Inzelberg R et al (1988) EEG in demented and non-demented parkinsonian patients. Acta Neurol Scand 78:1–5
Neufeld MY, Blumen S et al (1994) EEG frequency analysis in demented and nondemented parkinsonian patients. Dementia 5:23–28
Nunez PL, Wingeier BM et al (2001) Spatial-temporal structures of human alpha rhythms: theory, microcurrent sources, multiscale measurements, and global binding of local networks. Hum Brain Mapp 13(3):125–164
Ocak H (2009) Automatic detection of epileptic seizures in EEG using discrete wavelet transform and approximate entropy. Expert Syst Appl 36:2027–2036
Olde Dubbelink KTE, Stoffers D et al (2013) Cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease is associated with slowing of resting-state brain activity: a longitudinal study. Neurobiol Aging 34(2):408–418
Pezard L, Jech R et al (2001) Investigation of non-linear properties of multichannel EEG in the early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurophysiol 112:38–45
Savitt JM, Dawson VL et al (2006) Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: molecules to medicine. J Clin Invest 116:1744–1754
Serizawa K, Kamei S et al (2008) Comparison of quantitative EEGs between parkinson disease and age-adjusted normal controls. J Clin Neurophysiol 25(6):361–366
Shinde A (2004) A wavelet packet based sifting process and its application for structural health monitoring. Master Thesis, Faculty of Worcester Polytechnic Institute
Soikkeli R, Partanen J et al (1991) Slowing of EEG in Parkinson’s disease. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 79:159–165
Stam KJ, Tavy DL et al (1994) Non-linear dynamical analysis of multichannel EEG: clinical applications in dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Brain Topogr 7:141–150
Stam CJ, Jelles B et al (1995) Investigation of EEG non-linearity in dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 95:309–317
Stoffers D, Bosboom JL et al (2007) Slowing of oscillatory brain activity is a stable characteristic of Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Brain 130:1847–1860
Tanaka H, Koenig T et al (2000) Event-related potential and EEG measures in Parkinson’s disease without and with dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 11:39–45
Torrence C, Compo GP (1998) A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79:61–78
Valls-Sole J, Valldeoriola F (2002) Neurophysiological correlate of clinical signs in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurophysiol 113:792–805
Wang D, Miao D et al (2011) Best basis-based wavelet packet entropy feature extraction and hierarchical EEG classification for epileptic detection. Expert Syst Appl 38:14314–14320
Wang M, Wang B et al (2012) A new quantitative evaluation method of spiral drawing for patients with Parkinson’s disease based on a polar coordinate system with varying origin. Physica A Stat Mech Appl 391(18):4377–4388
Weinberger M, Hutchison WD et al (2009) Increased gamma oscillatory activity in the subthalamic nucleus during tremor in Parkinson’s disease patients. J Neurophysiol 101:789–802
Wiklund U, Akay M et al (1997) Short-term analysis of heart-rate variability by adapted wavelet transforms. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 16:113–118, 138
Wooten GF, Currie LJ et al (2004) Are men at greater risk for Parkinson’s disease than women? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:637–639
Yang BH, Yan GZ et al (2006) Feature extraction for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces by wavelet packet best basis decomposition. J Neural Eng 3:251–256
Acknowledgments
Project supported by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50537030), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61072012), and the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61104032 and 50907044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, CX., Wang, J., Yi, GS. et al. Investigation of EEG abnormalities in the early stage of Parkinson’s disease. Cogn Neurodyn 7, 351–359 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-013-9247-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-013-9247-z