Abstract
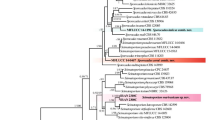
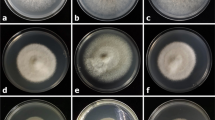
Sooty blotch and flyspeck is caused by a complex of epiphytic fungi on diverse hosts. A fungus morphologically similar to Scolecobasidium humicola was isolated from a banana fruit exhibiting SBFS signs in Hainan, China. ITS and LSU sequences of rDNA corroborated that it was a Scolecobasidium species. The results of LSU rDNA analysis support the interpretation that Ochroconis is synonymous with Scolecobasidium. Five new combinations, S. anomalum, S. calidifluminale, S. gallopavum, S. gamsii, and S. lascauxense, were proposed. A new species, S. musae, was described based on morphological characteristics and sequence comparison with previous species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott EV (1927) Scolecobasidium, a new genus of soil fungi. Mycologia 19:29–31
Abreu LM, Almeida AR, Salgado M, Pfenning LH (2010) Fungal endophytes associated with the mistletoe Phoradendron perrottettii and its host tree Tapirira guianensis. Mycol Prog 9:559–566
Ajello L, Mcginnis MR, Camper J (1977) An outbreak of phaeohyphomycosis in rainbow trout caused by Scolecobasidium humicola. Mycopathologia 62:15–22
Barron GL, Busch LV (1962) Studies on the soil hyphomycete Scolecobasidium. Can J Bot 40:77–84
Batzer JC, Gleason ML, Harrington TC, Tiffany LH (2005) Expansion of the sooty blotch and flyspeck complex on apples based on analysis of ribosomal DNA gene sequences and morphology. Mycologia 97:1268–1286
Bishy DW, Megalla SE, Soliman MMA, Abdel-Fattah HM (1981) Comparative studies on simple lipids of Scolerotium cepivorum, the causal agent of white rot of onion, and other fungi the class Deuteromycetes. Plant Soil 60:301–307
de Hoog GS (1985) Taxonomy of the Dactylaria complex IV. Dactylaria, Neta, Subulispora and Scolecobasidium. Stud Mycol 26:52–53
de Hoog GS, Van Oorschot CAN (1985) Taxonomy of the Dactylaria complex VI. Key to the genera and check-list of epithets. Stud Mycol 26:97–121
de Hoog GS, Von Arx JA (1973) Revision of Scolecobasidium and Pleurographium. Kavaka 1:55–60
de Hoog GS, Rahman MA, Boekhout T (1983) Ramichloridium, Veronaea and Stenella: generic delimitation, new combinations and two new species. Trans Br Mycol Soc 81:485–490
Domsch KH, Gams W (1980) Compendium of soil fungi. Academic Press
Ellis, MB (1976) More dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Kew, Commonwealth Mycological Institute.
Gleason ML, Batzer JC, Sun GY, Zhang R, Arias MMD, Sutton TB, Crous PW, Ivanović M, McManus PS, Cooley DR, Mayr U, Weber RWS, Yoder KS, Del Ponte EM, Biggs AR, Oertel B (2011) A new view of sooty blotch and flyspeck. Plant Dis 95:368–383
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hamada N, Abe N (2009) Physiological characteristics of 13 common fungal species in bathrooms. Mycoscience 50:421–429
Hamayun M, Khan SA, Kim HY, Chaudhary MF, Hwang YH, Shin DH, Kim IK, Lee BH, Lee IJ (2009) Gibberellin production and plant growth enhancement by newly isolated strain of Scolecobasidium tshawytschae. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19(6):560–565
Horré R, de Hoog GS, Kluczny C, Marklein G, Schaal KP (1999) rDNA diversity and physiology of Ochroconis and Scolecobasidium species reported from humans and other vertebrates. Stud Mycol 43:194–205
Kirk PM (1994) IMI Descriptions of fungi and bacteria. Set 121, No. 1204
Kirschner R, Chen CJ (2010) Two new species of Ramichloridium-like hyphomycetes from senescent leaves of Night-scented Lily (Alocasia odora) in Taiwan. Fungal Divers 40:41–50
Li HY, Sun GY, Batzer JC, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Karakaya A, Gleason ML (2011) Scleroramularia gen. nov. associated with sooty blotch and flyspeck of apple and pawpaw from the Northern Hemisphere. Fungal Divers 46:53–66
Liu HM, Zhang TY (2006) Two new species of Scolecobasidium. Mycosystema 25:386–388
Martin-Sanchez PM, Nováková A, Bastian F, Alabouvette C, Saiz-Jimenez C (2012) Two new species of the genus Ochroconis, O. lascauxensis and O. anomala isolated from black stains in Lascaux Cave, France. Fungal Biology 116:574–589
Martyn EB (1945) A note on banana leaf speckle in Jamaica and some associated fungi. Mycol Pap 13:1–5
Nyns EJ, Auquière JP, Wiaux AL (1968) Taxonomic value of the property of fungi to assimilate hydrocarbons. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 34:441–457
Pan HQ, Yu JF, Wu YM, Zhang TY, Wang HF (2008) Diversity analysis of soil dematiaceous hyphomycetes from the Yellow River source area: I*. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9:829–834
Sun GY, Zhang R, Zhang Z, Zhang M (2003) Isolation of sooty blotch and flyspeck fungi from apple surface by picking up the thalli. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica 33:479–480
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP* Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods) version 4.0. Sinauer, Sunderland, Mass
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
VanSteenhouse JL, Padhye AA, Ajello L (1988) Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Scolecobasidium humicola in a cat. Mycopathologia 102:123–127
Wellman AM (1975) A new species of Ochroconis isolated from pelagic tar fragments. Can J Bot 53:1630–1633
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. Academic Press
Williamson SM, Sutton TB (2000) Sooty blotch and flyspeck of apple: etiology, biology, and control. Plant Dis 84:714–724
Yarita K, Sano A, Samerpitak K, Kamei K, de Hoog GS, Nishimura K (2010) Ochroconis calidifluminalis, a sibling of the neurotropic pathogen O. gallopava, isolated from hot spring. Mycopathologia 170:21–30
Yue C, Jensen HH, Mueller DS, Nonnecke GR, Bonnet D, Gleason ML (2007) Estimating consumers’ valuation of organic and cosmetically damaged apples. HortSci 42:1366–1371
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170015, 31171797), the 111 Project from Education Ministry of China (B07049), Top Talent Project of Northwest A&F University and the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (nycytx-08-04-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, L., Chen, C., Zhang, R. et al. A new species of Scolecobasidium associated with the sooty blotch and flyspeck complex on banana from China. Mycol Progress 12, 489–495 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-012-0855-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-012-0855-5