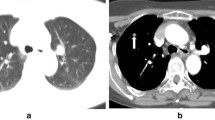
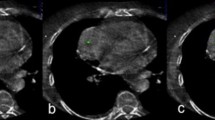
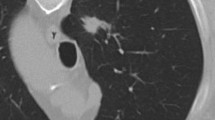
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of flat detector cone-beam CT-guided CBCT percutaneous needle biopsy (PNB) of mediastinal lesions.
Methods
A total of 100 patients with 100 solid mediastinal lesions were retrospectively enrolled to undergo percutaneous needle biopsy (PNB) procedures. The mean diameter of lesions was 4.4 ± 1.8 cm (range 1.8–9.0 cm). The needle path was carefully planned and calculated on the CBCT virtual navigation guidance system, which acquired 3D CT-like cross-sectional images. Diagnostic performance, procedure details, complication rate, and patient radiation exposure were investigated.
Results
The technical success rate of PNB under CBCT virtual navigation system was 100 % (100/100). The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of PNB of small nodules under iGuide CBCT virtual navigation guidance were 95.1 % (79/83), 100 % (12/12), and 95.7 % (91/95), respectively. The number of biopsies and CBCT acquisitions were 2.6 ± 1.2 (range 1–6) and 3.0 ± 1.1 (range 2–8), respectively. Complications occurred in five (5.0 %) cases. The mean total procedure time was 11.70 ± 3.44 min (range 6–27 min), resulting in a mean exposure dose of 9.7 ± 4.3 mSv.
Conclusion
Flat detector cone-beam CT-guided PNB is an accurate and safe diagnostic method for mediastinal lesions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lohr F, Georg D, Cozzi L et al (2014) Novel radiotherapy techniques for involved-field and involved-node treatment of mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma: when should they be considered and which questions remain open? Strahlenther Onkol 190:864–866
Jiao D, Yuan H, Zhang Q et al (2015) Flat detector C-arm-guided transthoracic needle biopsy of small (≤2.0 cm) pulmonary nodules: diagnostic accuracy and complication in 100 patients. Radiol Med. doi:10.1007/s11547-015-0604-3
Gupta S, Seaberg K, Wallace MJ et al (2005) Imaging-guided percutaneous biopsy of mediastinal lesions: different approaches and anatomic considerations. Radiographics 25:763–786
Hiraki T, Mimura H, Gobara H et al (2009) CT fluoroscopy-guided biopsy of 1000 pulmonary lesions performed with 20-gauge coaxial cutting needles: diagnostic yield and risk factors for diagnostic failure. Chest 136:1612–1617
Priola AM, Priola SM, Cataldi A et al (2008) CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic biopsy in the diagnosis of mediastinal masses: evaluation of 73 procedures. Radiol Med. 113:3–15
Kim GR, Hur J, Lee SM et al (2011) CT fluoroscopy-guided lung biopsy versus conventional CT-guided lung biopsy: a prospective controlled study to assess radiation doses and diagnostic performance. Eur Radiol 21:232–239
Bissoli E, Bison L, Gioilis E et al (2003) Multislice CT fluoroscopy: technical principles, clinical applications and dosimetry. Radiol Med 106:201–212
Jin KN, Park CM, Goo JM et al (2010) Initial experience of percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung nodules using C-arm cone-beam CT systems. Eur Radiol 20:2108–2115
Lee SM, Park CM, Lee KH et al (2014) C-arm cone-Beam CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung nodules: clinical experience in 1108 patients. Radiology 271:291–300
Wallace MJ, Kuo MD, Glaiberman C et al (2009) Three-dimensional C-arm cone-beam CT: applications in the interventional suite. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:S523–S537
Hwang HS, Chung MJ, Lee JW et al (2010) C-arm cone-beam CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic lung biopsy: usefulness in evaluation of small pulmonary nodules. Am J Roentgenol 195:W400–W407
Cheung JY, Kim Y, Shim SS et al (2011) Combined fluoroscopy- and CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy using a C-arm cone-beam CT system: comparison with fluoroscopy-guided biopsy. Korean J Radiol 12:89–96
Choi MJ, Kim Y, Hong YS et al (2012) Transthoracic needle biopsy using a C-arm cone-beam CT system: diagnostic accuracy and safety. Br J Radiol 85:e182–e187
Lee WJ, Chong S, Seo JS et al (2012) Transthoracic fine needle aspiration biopsy of the lungs using a C-arm cone-beam CT system: diagnostic accuracy and post-procedural complications. Br J Radiol 85:e217–e222
Choi JW, Park CM, Goo JM et al (2012) C-arm cone-beam CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of small (≤ 20 mm) lung nodules: diagnostic accuracy and complications in 161 patients. Am J Roentgenol 199:W322–W330
Braak SJ, Herder GJ, van Heesewijk JP et al (2012) Pulmonary masses: initial results of cone-beam CT guidance with needle planning software for percutaneous lung biopsy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:1414–1421
Choo JY, Park CM, Lee NK et al (2013) Percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of small (≤1 cm) lung nodules under C-arm cone-beam CT virtual navigation guidance. Eur Radiol 23:712–719
Floridi C, Muollo A, Fontana F et al (2014) C-arm cone-beam computed tomography needle path overlay for percutaneous biopsy of pulmonary nodules. Radiol Med. 119:820–827
Rotolo N, Floridi C, Imperatori A et al (2016) Comparison of cone-beam CT-guided and CT fluoroscopy-guided transthoracic needle biopsy of lung nodules. Eur Radiol 26:381–389
Kim H, Park CM, Lee SM et al (2015) C-arm cone-beam CT virtual navigation-guided percutaneous mediastinal mass biopsy: diagnostic accuracy and complications. Eur Radiol 25:3508–3517
Priola AM, Priola SM, Cataldi A et al (2008) CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic biopsy in the diagnosis of mediastinal masses: evaluation of 73 procedures. Radiol med 113:3–15
Kulkarni S, Kulkarni A, Roy D et al (2008) Percutaneous computed tomography-guided core biopsy for the diagnosis of mediastinal masses. Ann Thorac Med 3:13–17
De Margerie-Mellon C, de Bazelaire C, Amorim S et al (2015) Diagnostic yield and safety of computed tomography-guided mediastinal core needle biopsies. J Thorac Imaging 30:319–327
Petranovic M, Gilman MD, Muniappan A et al (2015) Diagnostic yield of CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy for diagnosis of anterior mediastinal masses. Am J Roentgenol 205:774–779
Gupta R, Cheung AC, Bartling SH et al (2008) Flat-panel volume CT: fundamental principles, technology, and applications. Radiographics 28:2009–2022
Busser WM, Braak SJ, Futterer JJ et al (2013) Cone beam CT guidance provides superior accuracy for complex needle paths compared with CT guidance. Br J Radiol 86:20130310
Brandén E, Wallgren S, Högberg H et al (2014) Computer tomography-guided core biopsies in a county hospital in Sweden: complication rate and diagnostic yield. Ann Thorac Med. 9:149–153
Schaefer PJ, Schaefer FK, Heller M et al (2007) CT fluoroscopy guided biopsy of small pulmonary and upper abdominal lesions: efficacy with a modified breathing technique. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:1241–1248
Assaad MW, Pantanowitz L, Otis CN (2007) Diagnostic accuracy of image-guided percutaneous fine needle aspiration biopsy of the mediastinum. Diagn Cytopathol 35:705–709
Guimarães MD, Hochhegger B, Benveniste MF et al (2014) Improving CT-guided transthoracic biopsy of mediastinal lesions by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 69:787–791
Gossot D, Girard P, Kerviler E (2001) Thoracoscopy or CT-guided biopsy for residual intrathoracic masses after treatment of lymphoma. Chest 120:289–294
Garnon J, Ramamurthy N, Caudrelier JJ et al (2015) MRI-guided percutaneous biopsy of mediastinal masses using a large bore magnet: technical feasibility. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00270-015-1246-5
Jiao DC, Li ZM, Yuan HF (2016) Flat detector C-arm CT-guidance system in performing percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of small (≤3 cm) pulmonary lesions. Acta Radiol 57:677–683
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Funding
This study was funded by the National High-Tech Research and Development Program (863 Program) (Grant Number: 2015AA020301).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, D., Huang, K., Wu, G. et al. Flat detector cone-beam CT-guided percutaneous needle biopsy of mediastinal lesions: preliminary experience. Radiol med 121, 769–779 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-016-0660-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-016-0660-3