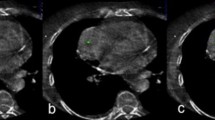
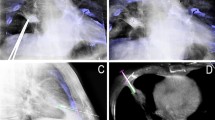
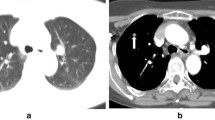
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of pulmonary nodules under cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) with “XperGuide” navigation guidance.
Materials and methods
From February 2010 to January 2012, 100 patients (63 men and 37 women; mean age 67.27 years; range 21–88 years) with 100 lung nodules (44 ≤ 3 cm, 56 > 3 cm) underwent CBCT-XperGuide guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsies. Technical success, diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and complications were evaluated.
Results
Of 100 nodules (mean size 5.19 cm), 68 were diagnosed as malignant, 27 as benign, and five as indeterminate. Technical success was 95 %. Only 33 of 100 patients underwent surgery: the final pathological diagnosis was concordant with the biopsy diagnosis in 26 cases and discordant in 7 cases (false negatives). Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV were 92.6, 90.9, 100, 100 and 72 %, respectively.
Conclusions
CBCT-XperGuide navigation is a new, accurate and safe imaging guidance for percutaneous lung biopsies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohno Y, Hatabu H, Takenaka D et al (2003) CT-guided transthoracic needle aspiration biopsy of small (≤20 mm) solitary pulmonary nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1665–1669
Gupta S, Krishnamurty S, Broemeling LD et al (2005) Small (≤2 cm) subpleural pulmonary lesions: short- versus long-needle-path CT-guided biopsy—comparison of diagnostic yields and complications. Radiology 234:631–637
Frank K, Wacker BM (2009) CT- and MR-guided interventions in radiology. In: Wacker FK, Meer B (eds) Interventions using C-arm computed tomography. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 370–381
Carlson SK, Felmlee JP, Bender CE et al (2005) CT fluoroscopy-guided biopsy of the lung or upper abdomen with a breath-hold monitoring and feedback system: a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Radiology 237:701–708
Cardella JF, Kundu S, Miller DL, Society of Interventional Radiology et al (2009) Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20(7 Suppl):S189–S191
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 4.0 Published: May 28, 2009 (v4.03: June 14, 2010) U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute
Strocchi S, Colli V, Conte L (2012) Multidetector CT fluoroscopy and cone-beam CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic biopsy: comparison based on patient dose. Radiat Prot Dosim 151:162–165
Moore EH (1998) Technical aspects of needle aspiration lung biopsy: a personal perspective. Radiology 208:303–318
Kazerooni EA, Lim FT, Mikhail A, Martinez FJ (1996) Risk of pneumothorax in CT-guided transthoracic needle aspiration biopsy of the lung. Radiology 198:371–375
Haaga JR, Alfidi RJ (1976) Precise biopsy localization by computer tomography. Radiology 118:603–607
Li H, Boiselle PM, Shepard J-AO et al (1996) Diagnostic accuracy and safety of CT-guided percutaneous needle aspiration biopsy of the lung: comparison of small and large pulmonary nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167:105–109
Daly B, Templeton PA (1999) Real-time CT fluoroscopy: evolution of an interventional tool. Radiology 211:309–315
Cheung JY, Kim Y, Shim SS et al (2011) Combined fluoroscopy- and CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy using a C-arm cone beam CT system: comparison with fluoroscopy-guided biopsy. Korean J Radiol 12:89–96
Prosch H, Stadler A, Schilling M et al (2011) CT biopsy mode-guided lung biopsies: accuracy, complications and radiation dose. Eur J Radiol 81:1029–1033
Heck SL, Blom P, Berstad A (2006) Accuracy and complications in computed tomography fluoroscopy-guided needle biopsies of lung masses. Eur Radiol 16:1387–1392
Nawfel RD, Judy PF, Silverman SG et al (2000) Patient and personnel exposure during CT fluoroscopy-guided interventional procedures. Radiology 216:180–184
Buls N, Pages J, de Mey J, Osteaux M (2003) Evaluation of patient and staff doses during various CT fluoroscopy guided interventions. Health Phys 85:165–173
Benndorf G, Strother CM, Claus B et al (2005) Angiographic CT in cerebrovascular stenting. Am J Neuroradiol 26:1813–1818
Hirota S, Nakao N, Yamamoto S et al (2006) Cone-beam CT with flat-panel-detector digital angiography system: early experience in abdominal interventional procedures. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29:1034–1038
Kang SE, Lee JW, Kim JH et al (2011) Percutaneous sacroplasty with the use of C-arm flat-panel detector CT: technical feasibility and clinical outcome. Skeletal Radiol 40:453–460
Carrafiello G, Fontana F, Mangini M et al (2012) Initial experience with percutaneous biopsies of bone lesions using XperGuide cone-beam CT (CBCT): technical note. Radiol Med 117:1386–1397
Higashihara H, Osuga K, Azuma T et al (2011) Detection of pulmonary nodules by C-arm CT using a phantom lung: comparison with CT. Acta Radiol 52:964–968
Jin KN, Park CM, Goo JM et al (2010) Initial experience of percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung nodules using C-arm cone-beam CT systems. Eur Radiol 20:2108–2115
Lee WJ, Chong S, Seo JS et al (2011) Transthoracic fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the lungs using a C-arm cone-beam CT system: diagnostic accuracy and post-procedural complications. Br J Radiol 85(1014):e217–e222
Choi MJ, Kim Y, Hong YS et al (2011) Transthoracic needle biopsy using a C-arm cone-beam CT system: diagnostic accuracy and safety. Br J Radiol 85(1014):e182–e187
Choi JW, Park CM, Goo JM et al (2012) C-arm cone-beam CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of small (≤20 mm) lung nodules: diagnostic accuracy and complications in 161 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:W322–W330
Braak SJ, van Strijen MJ, van Es HW et al (2011) Effective dose during needle interventions: cone-beam CT guidance compared with conventional CT guidance. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22:455–461
Choo JY, Park CM, Lee NK et al (2012) Percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of small (≤1 cm) lung nodules under C-arm cone-beam CT virtual navigation guidance. Eur Radiol 23:712–719
Braak SJ, Herder GJ, van Heesewijk JP, van Strijen MJ (2011) Pulmonary masses: initial results of cone-beam CT guidance with needle planning software for percutaneous lung biopsy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:1414–1421
Conflict of interest
Chiara Floridi, Anna Maria Ierardi, Federico Fontana, Nicola Rotolo, Alessandra Muollo, Ejona Duka, Carlo Pellegrino, Carlo Fugazzola, Gianpaolo Carrafiello declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Floridi, C., Muollo, A., Fontana, F. et al. C-arm cone-beam computed tomography needle path overlay for percutaneous biopsy of pulmonary nodules. Radiol med 119, 820–827 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0406-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0406-z