Abstract
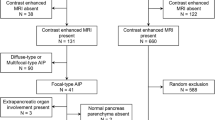
Multidetector-row computed tomography (MDCT) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging are currently the most frequently performed imaging modalities for the study of pancreatic disease. In cases of suspected autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), a dynamic quadriphasic (precontrast, contrast-enhanced pancreatic, venous and late phases) study is recommended in both techniques. In the diffuse form of autoimmune pancreatitis (DAIP), the pancreatic parenchyma shows diffuse enlargement and appears, during the MDCT and MR contrast-enhanced pancreatic phase, diffusely hypodense and hypointense, respectively, compared to the spleen because of lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and pancreatic fibrosis. During the venous phase of MDCT and MR imaging, the parenchyma appears hyperdense and hyperintense, respectively, in comparison to the pancreatic phase. In the delayed phase of both imaging modalities, it shows retention of contrast media. A “capsule-like rim” may be recognised as a peripancreatic MDCT hyperdense and MR hypointense halo in the T2-weighted images, compared to the parenchyma. DAIP must be differentiated from non-necrotizing acute pancreatitis (NNAP) and lymphoma since both diseases show diffuse enlargement of the pancreatic parenchyma. The differential diagnosis is clinically difficult, and dynamic contrast-enhanced MDCT has an important role. In the focal form of autoimmune pancreatitis (FAIP), the parenchyma shows segmental enlargement involving the head, the body-tail or the tail, with the same contrast pattern as the diffuse form on both modalities. FAIP needs to be differentiated from pancreatic adenocarcinoma to avoid unnecessary surgical procedures, since both diseases have similar clinical and imaging presentation. The differential diagnosis is clinically difficult, and dynamic contrast-enhanced MDCT and MR imaging both have an important role. MR cholangiopancreatography helps in the differential diagnosis. Furthermore, MDCT and MR imaging can identify the extrapancreatic manifestations of AIP, most commonly biliary, renal and retroperitoneal. Finally, in all cases of uncertain diagnosis, MDCT and/or MR follow-up after short-term treatment (2–3 weeks) with high-dose steroids can identify a significant reduction in size of the pancreatic parenchyma and, in FAIP, normalisation of the calibre of the upstream main pancreatic duct.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, Kamisawa T, Kawa S, Mino-Kenudson M, Kim MH, Klöppel G, Lerch MM, Löhr M, Notohara K, Okazaki K, Schneider A, Zhang L, International Association of Pancreatology (2011) International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas 40:352–358
Kamisawa T, Egawa N, Nakajima H (2003) Autoimmune pancreatitis is a systemic autoimmune disease. Am J Gastroenterol 98:2811–2812
Zhang L, Notohara K, Levy MJ et al (2007) IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Mod Pathol 20:23–28
Cavallini G (1993) Is chronic pancreatitis a primary disease of the pancreatic ducts? A new pathogenetic hypothesis. Ital J Gastroenterol 25:391–396
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T et al (1995) Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 40:1561–1568
Okazaki K (2001) Autoimmune-related pancreatitis. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 4:369–375
Sjogren I, Wengle B, Korsgren M (1979) Primary sclerosing cholangitis associated with fibrosis of the submandibular glands and the pancreas. Acta Med Scand 205:139–141
Gelrud A, Freedman SD (2005) Autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg 9:2–5
Ketikoglou I, Moulakakis A (2005) Autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Liver Dis 37:211–215
Frulloni L, Bovo P, Di Francesco V et al (1999) “Non-alcoholic duct destructive chronic pancreatitis” or “primary chronic pancreatitis”? Gut 44:579
Montefusco PP, Geiss AC, Bronzo RL et al (1984) Sclerosing cholangitis, chronic pancreatitis, and Sjogren’s syndrome: a syndrome complex. Am J Surg 147:822–826
Kloppel G, Luttges J, Lohr M et al (2003) Autoimmune pancreatitis: pathological, clinical, and immunological features. Pancreas 27:14–19
Zamboni G, Luttges J, Capelli P et al (2004) Histopathological features of diagnostic and clinical relevance in autoimmune pancreatitis: a study on 53 resection specimens and 9 biopsy specimens. Virchows Arch 445:552–563
Ghazale AH, Chari ST, Vege SS (2008) Update on the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune pancreatitis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 10:115–121
Toomey DP, Swan N, Torreggiani W, Conlon KC (2007) Autoimmune pancreatitis. Br J Surg 94:1067–1074
Cavallini G, Frulloni L, Bassi C et al (2004) Prospective multicentre survey on acute pancreatitis in Italy (ProInf AISP): results on 1005 patients. Dig Liver Dis 36:205–211
Bodily KD, Takahashi N, Fletcher JG et al (2009) Autoimmune pancreatitis: pancreatic and extrapancreatic imaging finding. Am J Roentgenol 192:431–437
Kawa S, Hamanno H, Umemura T et al (2007) Sclerosing cholangitis associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Hepatol Res 37:S487–S495
Bollen TL, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG et al (2008) The Atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis revisited. Br J Surg 95:6–21
Frulloni L, Scattolini C, Falconi M et al (2009) Autoimmune pancreatitis: differences between the focal and diffuse forms in 87 patients. Am J Gastroenterol 104:2288–2294
Kim KP, Kim MH, Song MH et al (2004) Autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 99:1605–1616
Procacci C, Carbognin G, Biasiutti C et al (2001) Autoimmune pancreatitis: possibilities of CT characterization. Pancreatology 1:246–253
Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Farrell J et al (2004) Autoimmune pancreatitis: imaging features. Radiology 233:345–352
Yang DH, Kim KW, Kim TK (2006) Autoimmune pancreatitis: radiologic findings in 20 patients. Abdom Imaging 31:94–102
Balthazar EJ (2002) Acute pancreatitis: assessment of severity with clinical and CT evaluation. Radiology 223:603–613
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T (2006) Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: revised proposal. J Gastroenterol 41:626–631
Desiree EM (2008) Imaging of acute pancreatitis and its complications. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:1077–1085
Kwon S, Kim MH, Choi EK (2007) The diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis: it is time to make a consensus. Pancreas 34:279–286
Nakazawa T, Ohara H, Sano H (2007) Difficulty in diagnosing autoimmune pancreatitis by imaging findings. Gastrointest Endosc 65:99–108
Kamisawa T (2008) Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 42:404–407
Graziani R, Cenci D, Franzoso F (2009) The role of computed tomography. In: Balthazar EJ, Megibow AJ, Pozzi Mucelli R (eds) Imaging of the pancreas. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 149–183
Graziani R, Cicero C, Casagranda G et al (2008) Pancreatite cronica. In: Graziani R, Pozzi Mucelli R (eds) TC multistrato del pancreas. Idelson Gnocchi, Sorbona, pp 45–84
Graziani R, Cicero C, Casagranda G (2008) Pancreas. In: Pozzi Mucelli R (ed) TC multistrato addome. Idelson Gnocchi, Sorbona, pp 193–262
Horiuchi A, Kaneko T, Yamamura N et al (1996) Autoimmune chronic pancreatitis simulating pancreatic lymphoma. Am J Gastroenterol 911:2607–2609
Irie H, Honda H, Baba S et al (1998) Autoimmune pancreatitis: CT and MR characteristics. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:1323–1327
Eerens I, Vanbeckevoort D, Vansteenbergen W, Van Hoe L (2001) Autoimmune pancreatitis associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis: MR imaging findings. Eur Radiol 11:1401–1404
Manfredi R, Graziani R, Cicero C et al (2008) Autoimmune pancreatitis: CT patterns and their changes after steroid treatment. Radiology 247:435–443
Takayama M, Hamano H, Ochi Y et al (2004) Recurrent attacks of autoimmune pancreatitis result in pancreatic stone formation. Am J Gastroenterol 99:932–937
Takahashi N, Fletcher JG, Hough DM et al (2009) Autoimmune pancreatitis: differentiation from pancreatic carcinoma and normal pancreas on the basis of enhancement characteristics at dual-phase CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:479–484
Sugumar A, Chari ST (2011) Autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:1368–1373 (Review)
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Tanaka M, Research Committee for Intractable Pancreatic Disease and Japan Pancreas Society (2010) Japanese consensus guidelines for management of autoimmune pancreatitis: I. Concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 45:249–265
Suzuki K, Itoh S, Nagasaka T et al (2010) CT findings in autoimmune pancreatitis: assessment using multiphase contrast-enhanced multisection CT. Clin Radiol 65:735–743
Kawai Y, Suzuki K, Itoh S et al (2012) Autoimmune pancreatitis: assessment of the enhanced duct sign on multiphase contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Eur J Radiol 81:3055–3060
Klimstra DS, Adsay NV (2004) Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing (autoimmune) pancreatitis. Semin Diagn Pathol 21:237–246
Ito T, Nakano I, Koyanagi S et al (1997) Autoimmune pancreatitis as a new clinical entity: three cases of autoimmune pancreatitis with effective steroid therapy. Dig Dis Sci 42:1458–1468
Kamisawa T, Tu Y, Egawa N et al (2006) Involvement of pancreatic and bile ducts in autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 28:612–614
Van Hoe L, Gryspeerdt S, Ectors N et al (1998) Nonalcholic duct-destructive chronic pancreatitis: imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:643–647
Kawamoto S, Siegelman SS, Hruban RH, Fishman EK (2008) Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis (autoimmune pancreatitis): evolution with multidetector CT. Radiographics 28:157–170
Furukawa N, Muranaka T, Yasumori K et al (1998) Autoimmune pancreatitis: radiologic findings in three histologically proven cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:880–883
Graziani R, Frulloni L, Mantovani W et al (2012) Autoimmune pancreatitis and non-necrotizing acute pancreatitis: computed tomography pattern. Dig Liver Dis 44:759–766
Webb TH, Lillemoe KD, Pitt HA et al (1989) Pancreatic lymphoma. Is surgery mandatory for diagnosis or treatment? Ann Surg 209:25–30
Glazer HS, Lee KJ, Balfe DM et al (1983) Non-Hodgkin lymphoma: computed tomographic demonstration of unusual extranodal involvement. Radiology 149:211–217
Sahani DV, Sainani NI, Deshpande V et al (2009) Autoimmune pancreatitis: disease evolution, staging, response, assessment and CT features that predict response to corticosteroid therapy. Radiology 250:118–129
Van Beers B, Lalonde L, Soyer P et al (1993) Dynamic CT in pancreatic lymphoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17:94–97
Ferrozzi F, Zuccoli G, Bova D, Calculli L (2000) Tumori mesenchimali del pancreas: aspetti con tomografia computerizzata. J Comput Assist Tomogr 24:622–627
Sheth S, Fishman EK (2002) Imaging of uncommon tumors of the pancreas. Radiol Clin North Am 40:1273–1287
Muhi A, Ichikawa T, Motosugi U et al (2012) Mass-forming autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma: differential diagnosis on the basis of computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, and diffusion-weighted imaging findings. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:827–836
Triantopoulou C, Giannakou N, Delis S et al (2007) Focal lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis. Pancreas 35:180–186
Wakabayashi T, Kawaura Y, Satomura Y et al (2003) Clinical and imaging features of autoimmune pancreatitis with focal pancreatic swelling or mass formation: comparison with so-called tumor forming pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 98:2679–2687
Wakabayashi T, Kawaura Y, Satomura Y et al (2002) Clinical study of chronic pancreatitis with focal irregular narrowing of the main pancreatic duct and mass formation. Comparison with chronic pancreatitis showing diffuse irregular narrowing of the main pancreatic duct. Pancreas 25:283–289
Ichikawa T, Sou H, Araki T et al (2001) Duct-penetrating sign at MRCP: usefulness for differentiating inflammatory pancreatic mass from pancreatic carcinomas. Radiology 221:107–116
Levy MJ, Wiersema MJ, Chari ST (2006) Chronic pancreatitis: focal pancreatitis or cancer? Is there a role for FNA/biopsy? Autoimmune pancreatitis. Endoscopy 38:S30–S35
Manfredi R, Frulloni L, Mantovani W et al (2011) Autoimmune pancreatitis: pancreatic and extrapancreatic MR imaging-MR cholangiopancreatography findings at diagnosis, after steroid therapy, and at recurrence. Radiology 260:428–436
Balci NC, Bieneman BK, Bilgin M et al (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging in pancreatitis. Top Magn Reson Imaging 20:25–30 (review)
Akisik MF, Aisen AM, Sandrasegaran K et al (2009) Assessment of chronic pancreatitis: utility of diffusion-weighted MR imaging with secretin enhancement. Radiology 250:103–109
Erturk SM, Ichikawa T, Motosugi U et al (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function before and after secretin stimulation. Am J Gastroenterol 101:133–136
Taniguchi T, Kobayashi H, Nishikawa K et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in autoimmune pancreatitis. Jpn J Radiol 27:138–142
Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Anjiki H et al (2010) Differentiation of autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer by diffusion-weighted MRI. Am J Gastroenterol 105:1870–1875
Choueiri NE, Balci NC, Alkaade S, Burton FR (2010) Advanced imaging of chronic pancreatitis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 12:114–120
Braganza JM, Lee SH, McCloy RF, McMahon MJ (2011) Chronic pancreatitis. Lancet 377:1184–1197
Church NI, Pereira SP, Deheragoda MG et al (2007) Autoimmune pancreatitis: clinical and radiological features and objective response to steroid therapy in a UK series. Am J Gastroenterol 102:2417–2425
Maeda E, Akahane M, Yoshioka N et al (2012) Comparison of CT findings of biliary tract changes with autoimmune pancreatitis and extrahepatic bile duct cholangiocarcinoma. Jpn J Radiol 30:227–234
Nishino T, Toki F, Oyama H et al (2005) Biliary tract involvement in autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 30:76–82
Members of the Criteria Committee for Autoimmune Pancreatitis of the Japan Pancreas Society (2002) Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis by the Japan Pancreas Society. J Jpn Pancreas 17:587
Okazaki K (2005) Autoimmune pancreatitis: etiology, pathogenesis, clinical findings and treatment: the Japanese experience. JOP 6:89–96
Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ et al (2006) Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Mayo Clinic experience. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:1010–1016
Choi EK, Kim MH, Kim JC et al (2006) The Japanese diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis: is it completely satisfactory? Pancreas 33:13–19
Kim KP, Kim MH, Kim JC et al (2006) Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis revisited. World J Gastroenterol 28:2487–2496
Conflict of interest
RGraziani, S. Mautone, M.C. Ambrosetti, R. Manfredi, T.J. Re, L. Calculli, L. Frulloni, R. Pozzi Mucelli declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graziani, R., Mautone, S., Ambrosetti, M.C. et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: multidetector-row computed tomography (MDCT) and magnetic resonance (MR) findings in the Italian experience. Radiol med 119, 558–571 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0373-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0373-9