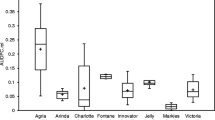
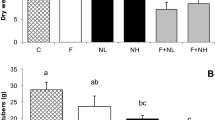
Abstract
Drycore is an important quality deficiency in Europe especially in organic potato production and after grass clover leys. The drycore symptom is attributed to Rhizoctonia solani Kühn (teleomorph: Thanatephorus cucumeris (Frank) Donk). In the framework of a 3-year survey (2001–2003), data concerning potato quality, crop rotation, management, and site parameters were analysed from 185 potato fields. The hypothesis was tested that injuries on potatoes caused by wireworms facilitate the penetration of R. solani and favour the formation of drycore. Analysis of variance showed a significant influence of wireworm damage, seed quality, and grass clover leys in the crop on the level of drycore damage. On fields which had both a low occurrence of black scurf on the seed tubers and a low occurrence of wireworm damage at harvest, significant drycore damage was never observed. The relative risk for drycore damage on tubers was significantly higher if black scurf or wireworm damage was on the same tuber. In contrast, no higher risk for drycore was observed on tubers with slug damage. Abiotic factors like farm manure application, organic matter content, texture, and pH of the soil also had no significant influence on the level of drycore. Thus, the wounding of potatoes by wireworm could be confirmed as the major variable for drycore. The mode of action has to be clarified under controlled conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson NA (1982) The genetics and pathology of Rhizoctonia solani. Annu Rev Phytophatology 20:329–347
Baker KF (1970) Types of Rhizoctonia diseases and their occurrence. In: Parmeter JR (ed) Rhizoctonia solani, biology and pathology. University of California Press, Berkley, pp 125–148
Buhr K (1989) Ermittlung sortentypischer Indikatoren hinsichtlich der Reaktion von Kartoffelpflanzen gegenüber dem Erreger der Wurzeltöterkrankheit (Rhizoctonia solani). Dissertation, Georg-August-Univertsität, Göttingen
Bundesamt für Meteorologie (2006) Annalen. Schweizerische Meteorologische Anstalt, Zürich
Campion C, Chatot C, Perraton B, Andrivon D (2003) Anastomosis groups, pathogenicity and sensitivity to fungicides of Rhizoctonia solani isolates collected on potato crops in France. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:983–992
Carling DE, Leiner RH (1986) Isolation and characterization of Rhizoctonia solani and benucleate R. solani-like fungi from aerial stems and subterranean organs of potato plants. Phytopathology 76:725–729
Carling DE, Kuninaga S, Brainard KA (2002) Hyphal anastomosis reactions, rDNA-internal transcribed spacer sequences, and virulence levels among subsets of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group-2 (AG-2) and AG-BI. Phytopathology 92:43–50
Chand T, Logan C (1983) Cultural and pathogenic variation in potato isolates of Rhizoctonia solani in Northern Ireland. Trans Br Mycol Soc 81:585–589
Cubeta MA, Vilgalys R (1997) Population biology of the Rhizoctonia solani complex. Phytopathology 87:480–484
Referenzmethoden der Forschungsanstalten Agroscope zur Bodenuntersuchung zur Düngeberatung (2004) Eidg. Volkswirtschaftsdepartement EVD
Glogoza P (2001) Wireworm management for North Dakota in field crops. North Dakota State University. http://www.ag.ndsu.nodak.edu
Gonzalez G, Carling E, Kuninaga S, Vilgalys R, Cubeta M (2001) Ribosomal DNA systematics of Ceratobasidium and Thanatephoros with Rhizoctonia anamorphs. Mycologia 93(6):1138–1150
Gratwick M (ed) (1989) Potato pests. HMSO, London, MAFF reference book 187
Grütte E (1940) Rhizoctonia solani als Schädling der Kartoffelknolle. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenkrankheiten und Pflanzenschutz 5:208–230
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Jeger MJ, Hide GA, van den Boogert PHJF, Termorshuizen AJ, van Baarlen P (1996) Pathology and control of soil-borne fungal pathogens of potato. Potato Res 39:437–469
Jossi W, Bigler F (1997) Auftreten und Schadenprognose von Drahtwürmer in Feldkulturen. Agrarforschung 4:157–160
Müller KO (1925) Untersuchungen zur Entwicklungsgeschichte und Biologie von Hypochnus solani P. & D. (Rhizoctonia solani K.). Arb Biol Reichsanst 13:197–262
Ogoshi A (1987) Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn. Annu Rev Phytopathol 25:125–143
Parker WE, Howard JJ (2001) The biology and management of wireworms (Agriotes ssp.) on potato with particular reference to the U.K. Agric For Entomol 3:85–98
Ramsey GB (1917) A form of potato disease produced by Rhizoctonia. J Agric Res 9:421–426
SSPV (Schweizerischer Saatgutproduzentenverband) (2002) Reglement über die Lieferungskontrolle von anerkannten Pflanzkartoffeln.
Scholte K (1989) Effects of soil-borne Rhizoctonia solani Kühn on yield and quality of ten cultivars. Potato Res 22:29–39
Schweizerische Kartoffelkommission (1989) Schweizerische Handelsusanzen für Kartoffeln, 3186 Düdingen
Schwinn FJ (1961) Ueber die “drycore”-Krankheit der Kartoffelknolle. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenkrankheiten und Pflanzenschutz 68:395–406
Sneh B, Burpee L, Ogoshi A (1991) Identification of Rhizoctonia Species. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul
Weinhold AR, Bowman T, Hall DH (1978) Rhizoctonia disease of potato in California. Am Potato J 55:56–57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keiser, A., Häberli, M. & Stamp, P. Drycore Appears to Result from an Interaction between Rhizoctonia solani and Wireworm (Agriotes ssp.)—Evidence from a 3-Year Field Survey. Potato Res. 55, 59–67 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-012-9207-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-012-9207-8