Abstract
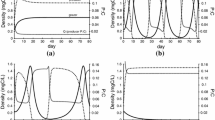
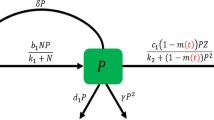
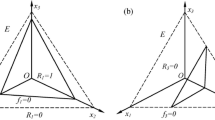
Recent discoveries in ecological stoichiometry have indicated that food quality in terms of the phosphorus/carbon (P/C) ratio affects consumers whether the imbalance involves insufficient or excess nutrients. This phenomenon is called the “stoichiometric P/C knife-edge.” In this study, we develop and analyze a producer–consumer model which captures this phenomenon. It assesses the effects of (external) nutrient (P) loading on consumer dynamics in an aquatic environment by mechanistically deriving and accounting for seasonal variation in nutrient loading. In the absence of seasonal effects, previous models suggest that the dynamics are Hopf bifurcation, saddle-node bifurcations, and limit cycles. However, seasonal effects can have major implications on the predicted solutions and enrich population dynamics. Bifurcation analyses demonstrate that seasonal forcing can cause both periodic and quasi-periodic solutions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen T (1997) Pelagic nutrient cycles: herbivores as sources and sinks. Springer, New York
Asik L, Peace A (2019) Dynamics of a producer–grazer model incorporating the effects of phosphorus loading on grazer’s growth. Bull Math Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-018-00567-9
Asik L, Kulik J, Long K, Peace A (2018) Dynamics of a stoichiometric producer–grazer system with seasonal effects on light level. Math Biosci Eng 16(1):501–515
Beman JM, Arrigo KR, Matson PA (2005) Agricultural runoff fuels large phytoplankton blooms in vulnerable areas of the ocean. Nature 434(7030):211
Boersma M, Elser JJ (2006) Too much of a good thing: on stoichiometrically balanced diets and maximal growth. Ecology 87(5):1325–1330
Carpenter SR, Caraco NF, Correll DL, Howarth RW, Sharpley AN, Smith VH (1998) Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol Appl 8(3):559–568
Demott W, Müller-Navarra D (1997) The importance of highly unsaturated fatty acids in zooplankton nutrition: evidence from experiments with daphnia, a cyanobacterium and lipid emulsions. Freshw Biol 38(3):649–664
Diehl S (2007) Paradoxes of enrichment: effects of increased light versus nutrient supply on pelagic producer-grazer systems. Am Nat 169(6):E173–E191
Elser JJ, Watts J, Schampel JH, Farmer J (2006) Early cambrian food webs on a trophic knife-edge? A hypothesis and preliminary data from a modern stromatolite-based ecosystem. Ecol Lett 9(3):295–303
Falconer L, Telfer TC, Ross LG (2018) Modelling seasonal nutrient inputs from non-point sources across large catchments of importance to aquaculture. Aquaculture 495:682–692
Grover JP (2002) Stoichiometry, herbivory and competition for nutrients: simple models based on planktonic ecosystems. J Theor Biol 214(4):599–618
Gulati R, Demott W (1997) The role of food quality for zooplankton: remarks on the state-of-the-art, perspectives and priorities. Freshw Biol 38(3):753–768
Hessen D, Bjerkeng B (1997) A model approach to planktonic stoichiometry and consumer-resource stability. Freshw Biol 38(3):447–471
Jeppesen E, Kronvang B, Meerhoff M, Søndergaard M, Hansen KM, Andersen HE, Lauridsen TL, Liboriussen L, Beklioglu M, Özen A et al (2009) Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations. J Environ Qual 38(5):1930–1941
Ji ZG (2017) Hydrodynamics and water quality: modeling rivers, lakes, and estuaries. Wiley, New York
Kot M, Sayler GS, Schultz TW (1992) Complex dynamics in a model microbial system. Bull Math Biol 54(4):619–648
Kuang Y, Huisman J, Elser JJ et al (2004) Stoichiometric plant-herbivore models and their interpretation. Math Biosci Eng 1(2):215–222
Loladze I, Kuang Y, Elser JJ (2000) Stoichiometry in producer–grazer systems: linking energy flow with element cycling. Bull Math Biol 62(6):1137–1162
Matsumura T, Sakawa Y (1980) Non-linear analysis of nitrogen cycle in aquatic ecosystems. Int J Syst Sci 11(7):803–816
Metcalfe NB, Bull CD, Mangel M (2002) Seasonal variation in catch-up growth reveals state-dependent somatic allocations in salmon. Evolut Ecol Res 4(6):871–881
Peace A, Wang H, Kuang Y (2014) Dynamics of a producer–grazer model incorporating the effects of excess food nutrient content on grazers growth. Bull Math Biol 76(9):2175–2197
Shen Z, Qiu J, Hong Q, Chen L (2014) Simulation of spatial and temporal distributions of non-point source pollution load in the three gorges reservoir region. Sci Total Environ 493:138–146
Søndergaard M, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E, Møller PH (2002) Seasonal dynamics in the concentrations and retention of phosphorus in shallow danish lakes after reduced loading. Aquat Ecosyst Health 5(1):19–29
Song D, Fan M, Chen M, Wang H (2018) Dynamics of a periodic stoichiometric model with application in predicting and controlling algal bloom in bohai sea off china. Math Biosci Eng 16(1):119–138
Sterner RW, Hessen DO (1994) Algal nutrient limitation and the nutrition of aquatic herbivores. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 25(1):1–29
Urabe J, Sterner RW (1996) Regulation of herbivore growth by the balance of light and nutrients. Proc Nat Acad Sci 93(16):8465–8469
Wang H, Smith HL, Kuang Y, Elser JJ (2007) Dynamics of stoichiometric bacteria–algae interactions in the epilimnion. SIAM J Appl Math 68(2):503–522
Wang H, Kuang Y, Loladze I (2008) Dynamics of a mechanistically derived stoichiometric producer–grazer model. J Biol Dyn 2(3):286–296
Wang H, Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2012) On the strict homeostasis assumption in ecological stoichiometry. Ecol Model 243:81–88
Wang Y, Zhao J (2016) Advances in energy, environment and materials science, In: Proceedings of the international conference on energy, environment and materials science (EEMS 2015), Guanghzou, PR China, August 25–26, 2015. CRC Press
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their sincere gratitude to Prof. James P. Grover and the second anonymous referee for their constructive suggestions and comments have improved the manuscript a great deal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asik, L., Kulik, J., Long, K.R. et al. Seasonal Variation of Nutrient Loading in a Stoichiometric Producer–Consumer System. Bull Math Biol 81, 2768–2782 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-019-00629-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-019-00629-6