Abstract
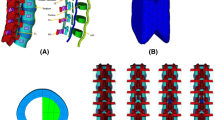
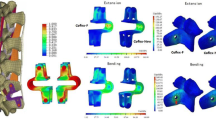
Interspinous spacers used stand-alone preserve joint movement but provide little protection for diseased segments of the spine. Used as adjuncts with fusion, interspinous spacers offer rigid stability but may accelerate degeneration on adjacent levels. Our new device is intended to balance the stability and preserves motion provided by the implant. A new interspinous spacer was devised according to the results of topology optimization studies. Four finite element (FE) spine models were created that consisted of an intact spine without an implant, implantation of the novel, the device for intervertebral assisted motion (DIAM system), and the Dynesys system. All models were loaded with moments, and their range of motions (ROMs), peak disc stresses, and facet contact forces were analyzed. The limited motion segment ROMs, shielded disc stresses, and unloaded facet contact forces of the new devices were greater than those of the DIAM and Dynesys system at L3-L4 in almost all directions of movements. The ROMs, disc stresses, and facet contact forces of the new devices at L2-L3 were slightly greater than those in the DIAM system, but much lower than those in the Dynesys system in most directions. This study demonstrated that the new device provided more stability at the instrumented level than the DIAM system did, especially in lateral rotation and the bending direction. The device caused fewer adjacent ROMs, lower disc stresses, and lower facet contact forces than the Dynesys system did. Additionally, this study conducted topology optimization to design the new device and created a smaller implant for minimal invasive surgery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbagallo GM, Olindo G, Corbino L et al (2009) Analysis of complications in patients treated with the X-Stop interspinous process decompression system: proposal for a novel anatomic scoring system for patient selection and the literature. Neurosurgery 65:111–120
Bellini CM, Galbusera F, Raimondi MT et al (2007) Biomechanics of the lumbar spine after dynamic stabilization. J Spinal Disord Tech 20:423–429
Chen HL, Guo KJ, Yuan F et al (2014) Effect of stress on intervertebral disc and facet joint of novel lumbar spine soft implant: biomechanical analysis. Biomed Res 25:199–202
Chen SH, Zhong ZC, Chen CS et al (2009) Biomechanical comparison between lumbar disc arthroplasty and fusion. Med Eng Phys 31:244–253
Chung KJ, Hwang YS, Koh SH (2009) Stress fracture of bilateral posterior facet after insertion of interspinous implant. Spine 34:E380–E383
Doulgeris JJ, Aghayev K, Gonzalez-Blohm SA et al (2015) Biomechanical comparison of an interspinous fusion device and bilateral pedicle screw system as additional fixation for lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Biomech 30:205–210
Erbulut DU, Zafarparandeh I, Hassan CR et al (2015) Determination of the biomechanical effect of an interspinous process device on implanted and adjacent lumbar spinal segments using a hybrid testing protocol: a finite-element study. J Neurosurg Spine 23:200–208
Fabrizi AP, Maina R, Schiabello L (2011) Interspinous spacers in the treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal disease: our experience with DIAM and Aperius devices. Eur Spine J 20:20–26
Fujiwara A, Lim TH, An HS et al (2000) The effect of disc degeneration and facet joint osteoarthritis on the segmental flexibility of the lumbar spine. Spine 25:3036–3044
Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Neroni M et al (2015) Failure rates and complications of interspinous process decompression devices: a European multicenter study. Neurosurg Focus 39:E14
Godzik J, Kalb S, Martinez-del-Campo E et al (2016) Biomechanical evaluation of the CD HORIZON Spire Z spinal system with pedicle and facet fixation. Spine 41:E902–E907
Gonzalez-Blohm SA, Doulgeris JJ, Aghayev K et al (2014) Biomechanical analysis of an interspinous fusion device as a stand-alone and as supplemental fixation to posterior expandable interbody cages in the lumbar spine: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine 20:209–219
Hoskins J, Zaglama R, Smith S et al (2011) Interspinous process devices for motion preservation and fusion. Contem Spine Surg 12:1–5
Karahalios DG, Kaibara T, Porter RW et al (2010) Biomechanics of a lumbar interspinous anchor with anterior lumbar interbody fusion: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine 12:372–380
Kettler A, Drumm J, Heuer F et al (2008) Can a modified interspinous spacer prevent instability in axial rotation and lateral bending? A biomechanical in vitro study resulting in a new idea. Clin Biomech 23:242–247
Kim DH, Albert TJ (2007) Interspinous process spacers. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 15:200–207
Kim DH, Tantorski M, Shaw J et al (2011) Occult spinous process fractures associated with interspinous process spacers. Spine 36:E1080–E1085
Korovessis P, Repantis T, Zacharatos S et al (2009) Does Wallis implant reduce adjacent segment degeneration above lumbosacral instrumented fusion? Eur Spine J 18:830–840
Krismer M, Haid C, Behensky H et al (2000) Motion in lumbar functional spine units during side bending and axial rotation moments depending on the degree of degeneration. Spine 25:2020–2027
Lafage V, Gangnet N, Sénégas J et al (2007) New interspinous implant evaluation using an in vitro biomechanical study combined with a finite-element analysis. Spine 32:1706–1713
Lee J, Hida K, Seki T et al (2004) An interspinous process distractor (X STOP) for lumbar spinal stenosis in elderly patients: preliminary experiences in 10 consecutive cases. J Spinal Disord Tech 17:72–77
Lin HM, Liu CL, Pan YN et al (2014) Biomechanical analysis and design of a dynamic spinal fixator using topology optimization: a finite element analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 52:499–508
Lindsey DP, Swanson KE, Fuchs P et al (2003) The effects of an interspinous implant on the kinematics of the instrumented and adjacent levels in the lumbar spine. Spine 28:2192–2197
Liu CL, Zhong ZC, Shih SL et al (2010) Influence of Dynesys system screw profile on adjacent segment and screw. J Spinal Disord Tech 23:410–417
Panjabi MM (2007) Hybrid multidirectional test method to evaluate spinal adjacent-level effects. Clin Biomech 22:257–265
Phillips FM, Voronov LI, Gaitanis IN et al (2006) Biomechanics of posterior dynamic stabilizing device (DIAM) after facetectomy and discectomy. Spine J 6:714–722
Richards JC, Majumdar S, Lindsey DP et al (2005) The treatment mechanism of an interspinous process implant for lumbar neurogenic intermittent claudication. Spine 30:744–749
Roh TH, Kim KN, Yoon DH et al (2009) Clinical and radiological outcome of an interspinous dynamic stabilization system in degenerative lumbar disease: 24 cases with over 24 months of follow-up. Korean J Spine 6:175–180
Shih SL, Chen CS, Lin HM et al (2012) Effect of spacer diameter of the Dynesys dynamic stabilization system on the biomechanics of the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. J Spinal Disord Tech 25:E140–E149
Shih SL, Liu CL, Huang LY et al (2013) Effects of cord pretension and stiffness of the Dynesys system spacer on the biomechanics of spinal decompression—a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 14:191
Siddiqui M, Karadimas E, Nicol M et al (2006) Influence of X Stop on neural foramina and spinal canal area in spinal stenosis. Spine 31:2958–2962
Sur YJ, Kong CG, Park JB (2011) Survivorship analysis of 150 consecutive patients with DIAM™ implantation for surgery of lumbar spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Eur Spine J 20:280–288
Swanson KE, Lindsey DP, Hsu KY et al (2003) The effects of an interspinous implant on intervertebral disc pressures. Spine 28:26–32
Tamburrelli FC, Proietti L, Logroscino CA (2011) Critical analysis of lumbar interspinous devices failures: a retrospective study. Eur Spine J 20:27–35
Tanaka N, An HS, Lim TH et al (2001) The relationship between disc degeneration and flexibility of the lumbar spine. Spine J 1:47–56
Techy F, Mageswaran P, Colbrunn RW et al (2013) Properties of an interspinous fixation device (ISD) in lumbar fusion constructs: a biomechanical study. Spine J 13:572–579
Tsai KJ, Murakami H, Lowery GL et al (2006) A biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous device (Coflex device) used to stabilize lumbar spine. Paradigm Spine J 1:1–4
Wan Z, Wang S, Kozánek M et al (2012) Biomechanical evaluation of the X-Stop device for surgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 25:374–378
Wang JC, Spenciner D, Robinson JC (2006) SPIRE spinous process stabilization plate: biomechanical evaluation of a novel technology: invited submission from the joint section meeting on disorders of the spine and peripheral nerves. J Neurosurg Spine 4:160–164
Wilke HJ, Drumm J, Häussler K et al (2008) Biomechanical effect of different lumbar interspinous implants on flexibility and intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J 17:1049–1056
Wiseman CM, Lindsey DP, Fredrick AD et al (2005) The effect of an interspinous process implant on facet loading during extension. Spine 30:903–907
Zhong ZC, Chen SH, Hung C (2009) Load- and displacement controlled finite element analyses on fusion and non-fusion spinal implants. Proc Inst Mech Eng H J Eng Med 223:143–157
Zhong ZC, Wei SH, Wang JP et al (2006) Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine with a new cage using a topology optimization method. Med Eng Phys 28:90–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CS., Shih, SL. Biomechanical analysis of a new lumbar interspinous device with optimized topology. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 1333–1341 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1767-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1767-y