Abstract
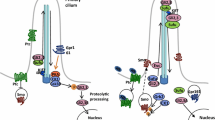
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway play critical roles in embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis. A critical step in Hh signal transduction is how Hh receptor Patched (Ptc) inhibits the atypical G proteincoupled receptor Smoothened (Smo) in the absence of Hh and how this inhibition is release by Hh stimulation. It is unlikely that Ptc inhibits Smo by direct interaction. Here we discuss how Hh regulates the phosphorylation and ubiquitination of Smo, leading to cell surface and ciliary accumulation of Smo in Drosophila and vertebrate cells, respectively. In addition, we discuss how PI(4)P phospholipid acts in between Ptc and Smo to regulate Smo phosphorylation and activation in response to Hh stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikin R A, Ayers K L, Thérond P P (2008). The role of kinases in the Hedgehog signalling pathway. EMBO Rep, 9(4): 330–336
Alcedo J, Ayzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M, Hooper J E (1996). The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the hedgehog signal. Cell, 86(2): 221–232
Apionishev S, Katanayeva N M, Marks S A, Kalderon D, Tomlinson A (2005). Drosophila Smoothened phosphorylation sites essential for Hedgehog signal transduction. Nat Cell Biol, 7(1): 86–92
Arensdorf A M, Marada S, Ogden S K (2015). Smoothened Regulation: A Tale of Two Signals. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 37(1): 62–72
Atwood S X, Li M, Lee A, Tang J Y, Oro A E (2013). GLI activation by atypical protein kinase C ι/λ regulates the growth of basal cell carcinomas. Nature, 494(7438): 484–488
Atwood S X, Sarin K Y, Whitson R J, Li J R, Kim G, Rezaee M, Ally M S, Kim J, Yao C, Chang A L, Oro A E, Tang J Y (2015). Smoothened variants explain the majority of drug resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell, 27(3): 342–353
Balla T (2013). Phosphoinositides: tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation. Physiol Rev, 93(3): 1019–1137
Balmer S, Dussert A, Collu G M, Benitez E, Iomini C, Mlodzik M (2015). Components of intraflagellar transport complex A function independently of the cilium to regulate canonical Wnt signaling in Drosophila. Dev Cell, 34(6): 705–718
Bielas S L, Silhavy J L, Brancati F, Kisseleva M V, Al-Gazali L, Sztriha L, Bayoumi R A, Zaki M S, Abdel-Aleem A, Rosti R O, Kayserili H, Swistun D, Scott L C, Bertini E, Boltshauser E, Fazzi E, Travaglini L, Field S J, Gayral S, Jacoby M, Schurmans S, Dallapiccola B, Majerus P W, Valente E M, Gleeson J G (2009). Mutations in INPP5E, encoding inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase E, link phosphatidyl inositol signaling to the ciliopathies. Nat Genet, 41(9): 1032–1036
Briscoe J, Thérond P P (2013). The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 14 (7): 416–429
Buonamici S, Williams J, Morrissey M, Wang A, Guo R, Vattay A, Hsiao K, Yuan J, Green J, Ospina B, Yu Q, Ostrom L, Fordjour P, Anderson D L, Monahan J E, Kelleher J F, Peukert S, Pan S, Wu X, Maira S M, García-Echeverría C, Briggs K J,Watkins D N, Yao Y M, Lengauer C, Warmuth M, Sellers W R, Dorsch M (2010). Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3K pathway in medulloblastoma. Sci Transl Med, 2(51): 51ra70
Callejo A, Culi J, Guerrero I (2008). Patched, the receptor of Hedgehog, is a lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 105(3): 912–917
Camp D, Currie K, Labbé A, van Meyel D J, Charron F (2010). Ihog and Boi are essential for Hedgehog signaling in Drosophila. Neural Dev, 5(1): 28
Casali A, Struhl G (2004). Reading the Hedgehog morphogen gradient by measuring the ratio of bound to unbound Patched protein. Nature, 431(7004): 76–80
Casso D J, Liu S, Iwaki D D, Ogden S K, Kornberg T B (2008). A screen for modifiers of hedgehog signaling in Drosophila melanogaster identifies swm and mts. Genetics, 178(3): 1399–1413
Chávez M, Ena S, Van Sande J, de Kerchove d’Exaerde A, Schurmans S, Schiffmann S N (2015). Modulation of ciliary phosphoinositide content regulates trafficking and sonic Hedgehog signaling output. Dev Cell, 34(3): 338–350
Chen C H, von Kessler D P, Park W, Wang B, Ma Y, Beachy P A (1999). Nuclear trafficking of Cubitus interruptus in the transcriptional regulation of Hedgehog target gene expression. Cell, 98(3): 305–316
Chen Y, Jiang J (2013). Decoding the phosphorylation code in Hedgehog signal transduction. Cell Res, 23(2): 186–200
Chen Y, Li S, Tong C, Zhao Y, Wang B, Liu Y, Jia J, Jiang J (2010). G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 promotes high-level Hedgehog signaling by regulating the active state of Smo through kinasedependent and kinase-independent mechanisms in Drosophila. Genes Dev, 24(18): 2054–2067
Chen Y, Sasai N, Ma G, Yue T, Jia J, Briscoe J, Jiang J (2011). Sonic Hedgehog dependent phosphorylation by CK1a and GRK2 is required for ciliary accumulation and activation of smoothened. PLoS Biol, 9(6): e1001083
Corbit K C, Aanstad P, Singla V, Norman A R, Stainier D Y, Reiter J F (2005). Vertebrate Smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature, 437(7061): 1018–1021
DeCaen P G, Delling M, Vien T N, Clapham D E (2013). Direct recording and molecular identification of the calcium channel of primary cilia. Nature, 504(7479): 315–318
Delling M, DeCaen P G, Doerner J F, Febvay S, Clapham D E (2013). Primary cilia are specialized calcium signalling organelles. Nature, 504(7479): 311–314
Denef N, Neubüser D, Perez L, Cohen S M (2000). Hedgehog induces opposite changes in turnover and subcellular localization of patched and smoothened. Cell, 102(4). 521–531
Di Paolo G, De Camilli P (2006). Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature, 443(7112): 651–657
Dorn K V, Hughes C E, Rohatgi R (2012). A Smoothened-Evc2 complex transduces the Hedgehog signal at primary cilia. Dev Cell, 23(4): 823–835
Du J, Zhang J, Su Y, Liu M, Ospina J K, Yang S, Zhu A J (2011). In vivo RNAi screen reveals neddylation genes as novel regulators of Hedgehog signaling. PLoS ONE, 6(9): e24168
Dussillol-Godar F, Brissard-Zahraoui J, Limbourg-Bouchon B, Boucher D, Fouix S, Lamour-Isnard C, Plessis A, Busson D (2006). Modulation of the Suppressor of fused protein regulates the Hedgehog signaling pathway in Drosophila embryo and imaginal discs. Dev Biol, 291(1): 53–66
Eaton S (2008). Multiple roles for lipids in the Hedgehog signalling pathway. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 9(6): 437–445
Fan J, Jiang K, Liu Y, Jia J (2013). Hrs promotes ubiquitination and mediates endosomal trafficking of smoothened in Drosophila hedgehog signaling. PLoS ONE, 8(11): e79021
Fan J, Liu Y, Jia J (2012). Hh-induced Smoothened conformational switch is mediated by differential phosphorylation at its C-terminal tail in a dose- and position-dependent manner. Dev Biol, 366(2): 172–184
Fan S, Hurd T W, Liu C J, Straight S W,Weimbs T, Hurd E A, Domino S E, Margolis B (2004). Polarity proteins control ciliogenesis via kinesin motor interactions. Curr Biol, 14(16): 1451–1461
Fukumoto T, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fujisawa K, Nagata S, Fukunaga R (2001). The fused protein kinase regulates Hedgehog-stimulated transcriptional activation in Drosophila Schneider 2 cells. J Biol Chem, 276(42): 38441–38448
Garcia-Gonzalo F R, Phua S C, Roberson E C, Garcia G 3rd, Abedin M, Schurmans S, Inoue T, Reiter J F (2015). Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling. Dev Cell, 34(4): 400–409
Goetz S C, Anderson K V (2010). The primary cilium: a signalling centre during vertebrate development. Nat Rev Genet, 11(5): 331–344
He Q, Wang G, Dasgupta S, Dinkins M, Zhu G, Bieberich E (2012). Characterization of an apical ceramide-enriched compartment regulating ciliogenesis. Mol Biol Cell, 23(16): 3156–3166
Heo J S, Lee M Y, Han H J (2007). Sonic hedgehog stimulates mouse embryonic stem cell proliferation by cooperation of Ca2+/protein kinase C and epidermal growth factor receptor as well as Gli1 activation. Stem Cells, 25(12): 3069–3080
Hildebrandt F, Benzing T, Katsanis N (2011). Ciliopathies. N Engl J Med, 364(16): 1533–1543
Ho K S, Suyama K, Fish M, Scott M P (2005). Differential regulation of Hedgehog target gene transcription by Costal2 and Suppressor of Fused. Development, 132(6): 1401–1412
Hooper J E, Scott M P (2005). Communicating with Hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 6(4): 306–317
Hsia E Y, Gui Y, Zheng X (2015). Regulation of Hedgehog signaling by ubiquitination. Front Biol (Beijing), 10(3): 203–220
Huangfu D, Anderson K V (2005). Cilia and Hedgehog responsiveness in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102(32): 11325–11330
Huangfu D, Liu A, Rakeman A S, Murcia N S, Niswander L, Anderson K V (2003). Hedgehog signalling in the mouse requires intraflagellar transport proteins. Nature, 426(6962): 83–87
Humbert M C, Weihbrecht K, Searby C C, Li Y, Pope R M, Sheffield V C, Seo S (2012). ARL13B, PDE6D, and CEP164 form a functional network for INPP5E ciliary targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109 (48): 19691–19696
Ingham P W, McMahon A P (2001). Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev, 15(23): 3059–3087
Jacoby M, Cox J J, Gayral S, Hampshire D J, Ayub M, Blockmans M, Pernot E, Kisseleva M V, Compère P, Schiffmann S N, Gergely F, Riley J H, Pérez-Morga D, Woods C G, Schurmans S (2009). INPP5E mutations cause primary cilium signaling defects, ciliary instability and ciliopathies in human and mouse. Nat Genet, 41(9): 1027–1031
Jia H, Liu Y, Xia R, Tong C, Yue T, Jiang J, Jia J (2010). Casein kinase 2 promotes Hedgehog signaling by regulating both smoothened and Cubitus interruptus. J Biol Chem, 285(48): 37218–37226
Jia H, Liu Y, Yan W, Jia J (2009). PP4 and PP2A regulate Hedgehog signaling by controlling Smo and Ci phosphorylation. Development, 136(2): 307–316
Jia J (2012). Phosphorylation regulation of Hedgehog signaling. Vitam Horm, 88: 253–272
Jia J, Amanai K, Wang G, Tang J, Wang B, Jiang J (2002). Shaggy/GSK3 antagonizes Hedgehog signalling by regulating Cubitus interruptus. Nature, 416(6880): 548–552
Jia J, Jiang J (2006). Decoding the Hedgehog signal in animal development. Cell Mol Life Sci, 63(11): 1249–1265
Jia J, Tong C, Jiang J (2003). Smoothened transduces Hedgehog signal by physically interacting with Costal2/Fused complex through its Cterminal tail. Genes Dev, 17(21): 2709–2720
Jia J, Tong C, Wang B, Luo L, Jiang J (2004). Hedgehog signalling activity of Smoothened requires phosphorylation by protein kinase A and casein kinase I. Nature, 432(7020): 1045–1050
Jiang J (2006). Regulation of Hh/Gli signaling by dual ubiquitin pathways. Cell Cycle, 5(21): 2457–2463
Jiang J, Hui C C (2008). Hedgehog signaling in development and cancer. Dev Cell, 15(6): 801–812
Jiang J, Struhl G (1995). Protein kinase A and hedgehog signaling in Drosophila limb development. Cell, 80(4): 563–572
Jiang J, Struhl G (1998). Regulation of the Hedgehog and Wingless signalling pathways by the F-box/WD40-repeat protein Slimb. Nature, 391(6666): 493–496
Jiang K, Liu Y, Fan J, Epperly G, Gao T, Jiang J, Jia J (2014). Hedgehog-regulated atypical PKC promotes phosphorylation and activation of Smoothened and Cubitus interruptus in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111(45): E4842–E4850
Jiang K, Liu Y, Fan J, Zhang J, Li X, Evers B M, Zhu H, Jia J (2016). PI (4). promotes phosphorylation and conformational change of Smoothened through interaction with its C-terminal tail. PLoS Biol, 14(1): e1002375
Khaliullina H, Panáková D, Eugster C, Riedel F, Carvalho M, Eaton S (2009). Patched regulates Smoothened trafficking using lipoproteinderived lipids. Development, 136(24): 4111–4121
Kim J, Hsia E Y, Brigui A, Plessis A, Beachy P A, Zheng X (2015). The role of ciliary trafficking in Hedgehog receptor signaling. Sci Signal, 8(379): ra55
Kool M, Jones D T, Jäger N, Northcott P A, Pugh T J, Hovestadt V, Piro R M, Esparza L A, Markant S L, Remke M, Milde T, Bourdeaut F, Ryzhova M, Sturm D, Pfaff E, Stark S, Hutter S, Seker-Cin H, Johann P, Bender S, Schmidt C, Rausch T, Shih D, Reimand J, Sieber L, Wittmann A, Linke L, Witt H, Weber U D, Zapatka M, König R, Beroukhim R, Bergthold G, van Sluis P, Volckmann R, Koster J, Versteeg R, Schmidt S, Wolf S, Lawerenz C, Bartholomae C C, von Kalle C, Unterberg A, Herold-Mende C, Hofer S, Kulozik A E, von Deimling A, Scheurlen W, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Hasselblatt M, Crawford J R, Grant G A, Jabado N, Perry A, Cowdrey C, Croul S, Zadeh G, Korbel J O, Doz F, Delattre O, Bader G D, McCabeMG, Collins V P, Kieran M W, Cho Y J, Pomeroy S L, Witt O, Brors B, Taylor M D, Schüller U, Korshunov A, Eils R, Wechsler-Reya R J, Lichter P, Pfister S M, (2014). Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotyperelated response to smoothened inhibition. Cancer Cell, 25(3): 393–405
Kovacs J J, Whalen E J, Liu R, Xiao K, Kim J, Chen M, Wang J, Chen W, Lefkowitz R J (2008). Beta-arrestin-mediated localization of smoothened to the primary cilium. Science, 320(5884): 1777–1781
Kuzhandaivel A, Schultz S W, Alkhori L, Alenius M (2014). Ciliamediated hedgehog signaling in Drosophila. Cell Reports, 7(3): 672–680
Li S, Chen Y, Shi Q, Yue T, Wang B, Jiang J (2012). Hedgehogregulated ubiquitination controls smoothened trafficking and cell surface expression in Drosophila. PLoS Biol, 10(1): e1001239
Li S, Ma G, Wang B, Jiang J (2014). Hedgehog induces formation of PKA-Smoothened complexes to promote Smoothened phosphorylation and pathway activation. Sci Signal, 7(332): ra62
Liu A, Wang B, Niswander L A (2005). Mouse intraflagellar transport proteins regulate both the activator and repressor functions of Gli transcription factors. Development, 132(13): 3103–3111
Liu Y, Cao X, Jiang J, Jia J (2007). Fused-Costal2 protein complex regulates Hedgehog-induced Smo phosphorylation and cell-surface accumulation. Genes Dev, 21(15): 1949–1963
Lum L, Beachy P A (2004). The Hedgehog response network: sensors, switches, and routers. Science, 304(5678): 1755–1759
Lum L, Zhang C, Oh S, Mann R K, von Kessler D P, Taipale J, Weis-Garcia F, Gong R, Wang B, Beachy P A (2003). Hedgehog signal transduction via Smoothened association with a cytoplasmic complex scaffolded by the atypical kinesin, Costal-2. Mol Cell, 12(5): 1261–1274
Marada S, Navarro G, Truong A, Stewart D P, Arensdorf A M, Nachtergaele S, Angelats E, Opferman J T, Rohatgi R, McCormick P J, Ogden S K (2015). Functional divergence in the role of N-linked glycosylation in Smoothened signaling. PLoS Genet, 11(8): e1005473
Méthot N, Basler K (2000). Suppressor of fused opposes hedgehog signal transduction by impeding nuclear accumulation of the activator form of Cubitus interruptus. Development, 127(18): 4001–4010
Mukhopadhyay S, Wen X, Chih B, Nelson C D, Lane W S, Scales S J, Jackson P K (2010). TULP3 bridges the IFT-A complex and membrane phosphoinositides to promote trafficking of G proteincoupled receptors into primary cilia. Genes Dev, 24(19): 2180–2193
Mukhopadhyay S, Wen X, Ratti N, Loktev A, Rangell L, Scales S J, Jackson P K (2013). The ciliary G-protein-coupled receptor Gpr161 negatively regulates the Sonic hedgehog pathway via cAMP signaling. Cell, 152(1–2): 210–223
Myers B R, Sever N, Chong Y C, Kim J, Belani J D, Rychnovsky S, Bazan J F, Beachy P A (2013). Hedgehog pathway modulation by multiple lipid binding sites on the smoothened effector of signal response. Dev Cell, 26(4): 346–357
Nachtergaele S, Whalen D M, Mydock L K, Zhao Z, Malinauskas T, Krishnan K, Ingham P W, Covey D F, Siebold C, Rohatgi R (2013). Structure and function of the Smoothened extracellular domain in vertebrate Hedgehog signaling. eLife, 2: e01340
Nüsslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E (1980). Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature, 287(5785): 795–801
Nybakken K, Vokes S A, Lin T Y, McMahon A P, Perrimon N (2005). A genome-wide RNA interference screen in Drosophila melanogaster cells for new components of the Hh signaling pathway. Nat Genet, 37 (12): 1323–1332
Ogden S K, Fei D L, Schilling N S, Ahmed Y F, Hwa J, Robbins D J (2008). G protein Galphai functions immediately downstream of Smoothened in Hedgehog signalling. Nature, 456(7224): 967–970
Oh S, Kato M, Zhang C, Guo Y, Beachy P A (2015). A comparison of Ci/Gli activity as regulated by Sufu in Drosophila and mammalian Hedgehog response. PLoS ONE, 10(8): e0135804
Pradhan-Sundd T, Verheyen E M (2015). The Myopic-Ubpy-Hrs nexus enables endosomal recycling of Frizzled. Mol Biol Cell, 26(18): 3329–3342
Price M A (2006). CKI, there’s more than one: casein kinase I family members in Wnt and Hedgehog signaling. Genes Dev, 20(4): 399–410
Price M A, Kalderon D (2002). Proteolysis of the Hedgehog signaling effector Cubitus interruptus requires phosphorylation by Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 and Casein Kinase 1. Cell, 108(6): 823–835
Prulière G, Cosson J, Chevalier S, Sardet C, Chenevert J (2011). Atypical protein kinase C controls sea urchin ciliogenesis. Mol Biol Cell, 22(12): 2042–2053
Pusapati G V, Hughes C E, Dorn K V, Zhang D, Sugianto P, Aravind L, Rohatgi R (2014). EFCAB7 and IQCE regulate hedgehog signaling by tethering the EVC-EVC2 complex to the base of primary cilia. Dev Cell, 28(5): 483–496
Rana R, Carroll C E, Lee H J, Bao J, Marada S, Grace C R, Guibao C D, Ogden S K, Zheng J J (2013). Structural insights into the role of the Smoothened cysteine-rich domain in Hedgehog signalling. Nat Commun, 4: 2965
Ranieri N, Ruel L, Gallet A, Raisin S, Thérond P P (2012). Distinct phosphorylations on kinesin costal-2 mediate differential hedgehog signaling strength. Dev Cell, 22(2): 279–294
Ranieri N, Thérond P P, Ruel L (2014). Switch of PKA substrates from Cubitus interruptus to Smoothened in the Hedgehog signalosome complex. Nat Commun, 5: 5034
Robbins D J, Nybakken K E, Kobayashi R, Sisson J C, Bishop J M, Thérond P P (1997). Hedgehog elicits signal transduction by means of a large complex containing the kinesin-related protein costal2. Cell, 90(2): 225–234
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Corcoran R B, Scott M P (2009). Hedgehog signal transduction by Smoothened: pharmacologic evidence for a 2-step activation process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(9): 3196–3201
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Scott M P (2007). Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science, 317(5836): 372–376
Rorick A M, Mei W, Liette N L, Phiel C, El-Hodiri H M, Yang J (2007). PP2A:B56epsilon is required for eye induction and eye field separation. Dev Biol, 302(2): 477–493
Rosenbaum J L, Witman G B (2002). Intraflagellar transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 3(11): 813–825
Ruel L, Rodriguez R, Gallet A, Lavenant-Staccini L, Thérond P P (2003). Stability and association of Smoothened, Costal2 and Fused with Cubitus interruptus are regulated by Hedgehog. Nat Cell Biol, 5 (10): 907–913
Sekulic A, Migden M R, Oro A E, Dirix L, Lewis K D, Hainsworth J D, Solomon J A, Yoo S, Arron S T, Friedlander P A, Marmur E, Rudin C M, Chang A L, Low J A, Mackey H M, Yauch R L, Graham R A, Reddy J C, Hauschild A (2012). Efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 366(23): 2171–2179
Sharpe H J, Pau G, Dijkgraaf G J, Basset-Seguin N, Modrusan Z, Januario T, Tsui V, Durham A B, Dlugosz A A, Haverty P M, Bourgon R, Tang J Y, Sarin K Y, Dirix L, Fisher D C, Rudin C M, Sofen H, Migden M R, Yauch R L, de Sauvage F J (2015). Genomic analysis of smoothened inhibitor resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell, 27(3): 327–341
Shi Q, Li S, Jia J, Jiang J (2011). The Hedgehog-induced Smoothened conformational switch assembles a signaling complex that activates Fused by promoting its dimerization and phosphorylation. Development, 138(19): 4219–4231
Sisson J C, Ho K S, Suyama K, Scott M P (1997). Costal2, a novel kinesin-related protein in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Cell, 90 (2): 235–245
Su Y, Ospina J K, Zhang J, Michelson A P, Schoen A M, Zhu A J (2011). Sequential phosphorylation of smoothened transduces graded hedgehog signaling. Sci Signal, 4(180): ra43
Swanson K D, Tang Y, Ceccarelli D F, Poy F, Sliwa J P, Neel B G, Eck M J (2008). The Skap-hom dimerization and PH domains comprise a 3'-phosphoinositide-gated molecular switch. Mol Cell, 32(4): 564–575
Taipale J, Cooper M K, Maiti T, Beachy P A (2002). Patched acts catalytically to suppress the activity of Smoothened. Nature, 418 (6900): 892–897
Tang J Y, Mackay-Wiggan J M, Aszterbaum M, Yauch R L, Lindgren J, Chang K, Coppola C, Chanana A M, Marji J, Bickers D R, Epstein E H (2012). Inhibiting the hedgehog pathway in patients with the basal-cell nevus syndrome. N Engl J Med, 366(23): 2180–2188
Thérond P P, Knight J D, Kornberg T B, Bishop J M (1996). Phosphorylation of the fused protein kinase in response to signaling from hedgehog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93(9): 4224–4228
Tuson M, He M, Anderson K V (2011). Protein kinase A acts at the basal body of the primary cilium to prevent Gli2 activation and ventralization of the mouse neural tube. Development, 138(22): 4921–4930
Wang B, Fallon J F, Beachy P A (2000a). Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate limb. Cell, 100(4): 423–434
Wang C, Wu H, Katritch V, Han G W, Huang X P, Liu W, Siu F Y, Roth B L, Cherezov V, Stevens R C (2013). Structure of the human smoothened receptor bound to an antitumour agent. Nature, 497 (7449): 338–343
Wang G, Amanai K, Wang B, Jiang J (2000b). Interactions with Costal2 and suppressor of fused regulate nuclear translocation and activity of cubitus interruptus. Genes Dev, 14(22): 2893–2905
Wang Y, Zhou Z, Walsh C T, McMahon A P (2009). Selective translocation of intracellular Smoothened to the primary cilium in response to Hedgehog pathway modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(8): 2623–2628
Williams R L, Urbé S (2007). The emerging shape of the ESCRT machinery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 8(5): 355–368
Wilson C W, Chen M H, Chuang P T (2009). Smoothened adopts multiple active and inactive conformations capable of trafficking to the primary cilium. PLoS ONE, 4(4): e5182
Wilson C W, Chuang P T (2010). Mechanism and evolution of cytosolic Hedgehog signal transduction. Development, 137(13): 2079–2094
Wollert T, Hurley J H (2010). Molecular mechanism of multivesicular body biogenesis by ESCRT complexes. Nature, 464(7290): 864–869
Xia R, Jia H, Fan J, Liu Y, Jia J (2012). USP8 promotes smoothened signaling by preventing its ubiquitination and changing its subcellular localization. PLoS Biol, 10(1): e1001238
Xie J, Murone M, Luoh S M, Ryan A, Gu Q, Zhang C, Bonifas J M, Lam C W, Hynes M, Goddard A, Rosenthal A, Epstein E H, de Sauvage F J (1998). Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma. Nature, 391(6662): 90–92
Yang C, Chen W, Chen Y, Jiang J (2012). Smoothened transduces Hedgehog signal by forming a complex with Evc/Evc2. Cell Res, 22 (11): 1593–1604
Yang L, Xie G, Fan Q, Xie J (2010). Activation of the hedgehogsignaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical implications. Oncogene, 29(4): 469–481
Yang X, Mao F, Lv X, Zhang Z, Fu L, Lu Y, Wu W, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Zhao Y (2013). Drosophila Vps36 regulates Smo trafficking in Hedgehog signaling. J Cell Sci, 126(Pt 18): 4230–4238
Yavari A, Nagaraj R, Owusu-Ansah E, Folick A, Ngo K, Hillman T, Call G, Rohatgi R, Scott M P, Banerjee U (2010). Role of lipid metabolism in smoothened derepression in hedgehog signaling. Dev Cell, 19(1): 54–65
Zeng X, Tamai K, Doble B, Li S, Huang H, Habas R, Okamura H, Woodgett J, He X (2005). A dual-kinase mechanism for Wnt coreceptor phosphorylation and activation. Nature, 438(7069): 873–877
Zhang C, Williams E H, Guo Y, Lum L, Beachy P A (2004). Extensive phosphorylation of Smoothened in Hedgehog pathway activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101(52): 17900–17907
Zhang J, Du J, Lei C, Liu M, Zhu A J (2014). Ubpy controls the stability of the ESCRT-0 subunit Hrs in development. Development, 141(7): 1473–1479
Zhang W, Zhao Y, Tong C, Wang G, Wang B, Jia J, Jiang J (2005). Hedgehog-regulated Costal2-kinase complexes control phosphorylation and proteolytic processing of Cubitus interruptus. Dev Cell, 8(2): 267–278
Zhang Y, Mao F, Lu Y, Wu W, Zhang L, Zhao Y (2011). Transduction of the Hedgehog signal through the dimerization of Fused and the nuclear translocation of Cubitus interruptus. Cell Res, 21(10): 1436–1451
Zhao X, Ponomaryov T, Ornell K J, Zhou P, Dabral S K, Pak E, Li W, Atwood S X, Whitson R J, Chang A L, Li J, Oro A E, Chan J A, Kelleher J F, Segal R A (2015). RAS/MAPK Activation Drives Resistance to Smo Inhibition, Metastasis, and Tumor Evolution in Shh Pathway-Dependent Tumors. Cancer Res, 75(17): 3623–3635
Zhao Y, Tong C, Jiang J (2007). Hedgehog regulates smoothened activity by inducing a conformational switch. Nature, 450(7167): 252–258
Zheng X, Mann R K, Sever N, Beachy P A (2010). Genetic and biochemical definition of the Hedgehog receptor. Genes Dev, 24(1): 57–71
Zwolak A, Yang C, Feeser E A, Ostap E M, Svitkina T, Dominguez R (2013). CARMIL leading edge localization depends on a noncanonical PH domain and dimerization. Nat Commun, 4: 2523
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, K., Jia, J. Smoothened regulation in response to Hedgehog stimulation. Front. Biol. 10, 475–486 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-015-1385-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-015-1385-8