Abstract
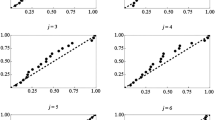
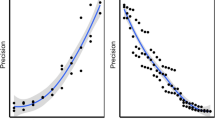
Quantitative data are essential to an appropriate characterization of vegetation. In the past few years, considerable attention has been paid to vegetation sampling techniques. A number of methods have been developed for plant density estimations that utilize spacing distances instead of fixed-area quadrats. In this paper, we review the main distance methods for estimating density and propose a new distance method denominated the quartered neighbor method. In this method, the sampling point is considered the center, and the area around it is divided into four quadrants. The distance from the closest individual in each quadrant to its closest neighbor in the same quadrant is measured, and the average of them is the distance we need. It is actually an integration of two old distance methods, the nearest neighbor method, and the point-centered quarter method. With our new method and an old distance method (the point-centered quarter method), we calculated the average spacing distances of the Larix principis-rupprechtii population in the larch forests of the Donglingshan Mountain. Comparing the two methods with the quadrat method, we found they were almost the same in accuracy, but the precision of the new one was better. Meanwhile, it is adequate in sampling intensity and adaptable for general use in rapid ecological survey work.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batcheler C L (1971). Estimation of density from a sample of joint point and nearest-neighbor distances. Ecology, 52: 703–709
Catana A J Jr (1963). The wandering quarter method of estimating population density. Ecology, 44: 349–360
Cottam G, Curtis J T (1949). A method for making rapid surveys of woodlands by means of pairs of randomly selected trees. Ecology, 30: 101–104
Cottam G, Curtis J T (1955). Correction for various exclusion angles in the random pairs method. Ecology, 36: 767
Cottam G, Curtis J T (1956). The use of distance measures in phytosociological sampling. Ecology, 37: 451–460
Cottam G, Curtis J T, Hale B W (1953). Some sampling characteristics of a population of randomly dispersed individuals. Ecology, 34: 741–757
Cox GW (1972). Laboratory Manual of General Ecology. 2nd ed. Lowa: Brown Company
Curtis J T, McIntosh R P (1951). An upland forest continuum in the prairie-forest border region of Wisconsin. Ecology, 32: 476–496
Dai X H, Yu S X (2004). Sampling methods of vegetation investigation in a tropical rain forest at Bawangling Nature Reserve, Hainan. Journal of Tropical and subtropical Botany, 12(5): 405–410 (in Chinese)
Greig-Smith P (1983). Quantitative Plant Ecology. 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications
Wang B S (1987). Phytocoenology. Beijing: Higher Education Press
Wang N, Zhang Y Y, Zheng G M (2006). Home ranges and habitat vegetation characters in breeding season of Narcissus Flycatcher and Yellow-rumped Flycatcher. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 42(3): 295–299 (in Chinese)
Wu Z F, Wang H S (1995). The application of plotless sampling methods in investigation of Shan Dong fall-leaf broad-leaf complex forest association. Journal of Shandong Normal University (Natural Science), 10(2): 178–181 (in Chinese)
Zhang J T (2004). Quantitative Ecology. Beijing: Science Press
Zheng S F, Zheng D Z, Liao B W (1992). Study on the distributive pattern of principal tree populations in Bruguiera sexangula and B. gymnorrhiza communities. Forest Research, 5(2): 149–157 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Zhang, J. Quartered neighbor method: A new distance method for density estimation. Front. Biol. China 4, 574–578 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-009-0039-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-009-0039-0