Abstract
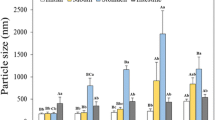
The effects of six different polyglycerol esters of fatty acids (PGEs) and two different particle sizes produced using various processing parameters on the physicochemical properties and stability of the β-carotene emulsions during digestion in simulated gastric fluid (SGF) were investigated. β-Carotene emulsions were prepared by high-pressure homogenization using β-carotene (0.1% w/w) in soybean oil as the oil phase and 1% (w/w) PGE in Milli-Q water as the water phase. The particle size of β-carotene emulsions was measured by a laser diffraction technique, and the stability of emulsions was interpreted in terms of the increase in particle size and span value of emulsion droplets and the retention of β-carotene during digestion in SGF. The average particle size ranges of emulsions were 0.17 to 0.27 μm for fine emulsions and 1.16 to 1.59 μm for coarse emulsions. In the prepared β-carotene emulsions, the particle size decreased with increasing polymerization of the glycerol in PGEs, and the higher polymerization of the glycerol also increased the stability of emulsions during digestion in SGF. Although the β-carotene content in the emulsions significantly decreased with increasing digestion period, loss of β-carotene was more severe in unstable emulsions than in stable emulsions, suggesting that the particles incorporated into droplets could provide some protective barrier for decreasing the β-carotene degradation. Therefore, β-carotene emulsions stabilized by PGEs with high polymerization of the glycerol may be useful for further applications in food and drug formulations. Decaglycerol monooleate (MO750) was demonstrated to be the most effective emulsifier in stabilizing β-carotene emulsions in this study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.B. Che Man, C.P. Tan, The Carotenoids: Lipids for Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals (The Oily Press, Bridgewater, 2003)
L. Packer, U. Obermueller-Jevic, K. Kraemer, H. Sies, Carotenoids and Retinoids: Molecular Aspects and Health Issues (AOCS Press, Champaign, USA, 2004)
S. Veda, A. Kamath, K. Platel, K. Begum, K. Srinivasan, Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 50, 1047–1052 (2006)
S. Ogawa, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, J. Agric. Food Chem. 51, 2806–2812 (2003)
D. Guzey, D.J. McClements, Food Biophys. 1, 30–40 (2006)
N.J. Krog, Food Emulsifiers and their Chemical and Physical Properties, In: Food Emulsions, edited by S.E. Friberg, and K. Larsson (Mercel Dekker, New York, 1997) pp. 141–188
M. Ishitobi, H. Kunieda, Colloid Polym. Sci. 278, 899–904 (2000)
C.P. Tan, M. Nakajima, J. Sci. Food Agric. 85, 121–126 (2005)
Q. Xu, M. Nakajima, H. Nabetani, S. Ichigawa, X. Liu, Food Sci. Technol. Res. 8, 36–41 (2002)
L.M.L. Goh, P.J. Barlow, Food Chem. 86, 195–202 (2004)
C.P. Tan, M. Nakajima, Food Chem. 92, 661–671 (2005)
K. Nakaya, H. Ushio, S. Matsukuwa, M. Shimizu, T. Ohshima, Lipids 40, 501–507 (2005)
L. Lethuaut, F. Metro, C. Genot, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 79, 425–430 (2002)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support by the Food Nanotechnology Project from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries of Japan. The first author wishes to thank Japan Society for promotion of Science for a JSPS Postdoctoral Fellowship and National Science Foundation of China through a fund (no. 20776151).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, LJ., Kobayashi, I. & Nakajima, M. Effect of Polyglycerol Esters of Fatty Acids on the Physicochemical Properties and Stability of β-Carotene Emulsions during Digestion in Simulated Gastric Fluid. Food Biophysics 3, 213–218 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-008-9077-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-008-9077-4