Abstract
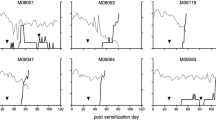
Non-human primate models of human disease have an important role in the translation of a new scientific finding in lower species into an effective treatment. In this study, we tested a new therapeutic antibody against the IL-7 receptor α chain (CD127), which in a C57BL/6 mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) ameliorates disease, demonstrating an important pathogenic function of IL-7. We observed that while the treatment was effective in 100 % of the mice, it was only partially effective in the EAE model in common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus), a small-bodied Neotropical primate. EAE was induced in seven female marmoset twins and treatment with the anti-CD127 mAb or PBS as control was started 21 days after immunization followed by weekly intravenous administration. The anti-CD127 mAb caused functional blockade of IL-7 signaling through its receptor as shown by reduced phosphorylation of STAT5 in lymphocytes upon stimulation with IL-7. Group-wise analysis showed no significant effects on the clinical course and neuropathology. However, paired twin analysis revealed a delayed disease onset in three twins, which were high responders to the immunization. In addition, we observed markedly opposite effects of the antibody on pathological changes in the spinal cord in high versus low responder twins. In conclusion, promising clinical effect of CD127 blockade observed in a standard inbred/SPF mouse EAE model could only be partially replicated in an outbred/non-SPF non-human primate EAE model. Only in high responders to the immunization we found a positive response to the treatment. The mechanism underpinning this dichotomous response will be discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABL:
-
Abelson
- ALN:
-
Axillary lymph node
- CLN:
-
Cervical lymph node
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- cpm:
-
Counts per minute
- EAE:
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- IFA:
-
Incomplete freunds adjuvant
- ILN:
-
Inguinal lymph node
- LLN:
-
Lumbar lymph nodes
- MNC:
-
Mononuclear cells
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PD1:
-
Programmed death receptor 1
- PLP:
-
Proteolipid protein
- rhMOG:
-
Recombinant human myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein
- SLO:
-
Secondary lymphoid organ
- SPF:
-
Specific-pathogen free
References
‘t Hart BA, Gran B, Weissert R (2011) EAE: imperfect but useful models of multiple sclerosis. Trends Mol Med 17:119–125
Ashbaugh JJ, Brambilla R, Karmally SA, Cabello C, Malek TR, Bethea JR (2013) IL7Ralpha contributes to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through altered T cell responses and nonhematopoietic cell lineages. J Immunol 190:4525–4534
Beillard E et al (2003) Evaluation of candidate control genes for diagnosis and residual disease detection in leukemic patients using ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR) - a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia 17:2474–2486
Benjamin D, Sharma V, Knobloch TJ, Armitage RJ, Dayton MA, Goodwin RG (1994) B cell IL-7. Human B cell lines constitutively secrete IL-7 and express IL-7 receptors. J Immunol 152:4749–4757
Bielekova B, Muraro PA, Golestaneh L, Pascal J, McFarland HF, Martin R (1999) Preferential expansion of autoreactive T lymphocytes from the memory T-cell pool by IL-7. J Neuroimmunol 100:115–123
Bonifati C et al (1997) Increased interleukin-7 concentrations in lesional skin and in the sera of patients with plaque-type psoriasis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 83:41–44
Haanstra KG et al (2013) Induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with recombinant human myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant in three non-human primate species. J Neuroimmune Pharm 8:1251–1264
Jagessar SA et al (2010) Induction of progressive demyelinating autoimmune encephalomyelitis in common marmoset monkeys using MOG34-56 peptide in incomplete freund adjuvant. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:372–385
Jagessar SA, Heijmans N, Bauer J, Blezer EL, Laman JD, Hellings N, ‘t Hart BA (2012) B-cell depletion abrogates T cell-mediated demyelination in an antibody-nondependent common marmoset experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:716–728
Jagessar SA et al (2013a) The different clinical effects of anti-BLyS, anti-APRIL and anti-CD20 antibodies point at a critical pathogenic role of gamma-herpesvirus infected B cells in the marmoset EAE model. J Neuroimmune Pharm 8:727–738
Jagessar SA, Vierboom M, Blezer EL, Bauer J, ‘t Hart BA, Kap YS (2013b) Overview of models, methods, and reagents developed for translational autoimmunity research in the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Exp Anim 62:159–171
Kaech SM, Tan JT, Wherry EJ, Konieczny BT, Surh CD, Ahmed R (2003) Selective expression of the interleukin 7 receptor identifies effector CD8 T cells that give rise to long-lived memory cells. Nat Immunol 4:1191–1198
Kap YS et al (2010) Late B cell depletion with a human anti-human CD20 IgG1kappa monoclonal antibody halts the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in marmosets. J Immunol 185:3990–4003
Kap YS, van Driel N, Laman JD, Tak PP, ‘t Hart BA (2014) CD20+ B cell depletion alters T cell homing. J Immunol 192:4242–4253
Kreft KL, Verbraak E, Wierenga-Wolf AF, van Meurs M, Oostra BA, Laman JD, Hintzen RQ (2012) The IL-7Ralpha pathway is quantitatively and functionally altered in CD8 T cells in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 188:1874–1883
Lee LF et al (2011) IL-7 promotes T(H)1 development and serum IL-7 predicts clinical response to interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis. Sci Transl Med 3:93ra68
Lundmark F et al (2007) Variation in interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) influences risk of multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 39:1108–1113
Mackall CL, Fry TJ, Gress RE (2011) Harnessing the biology of IL-7 for therapeutic application. Nat Rev Immunol 11:330–342
Namen AE et al (1988) Stimulation of B-cell progenitors by cloned murine interleukin-7. Nature 333:571–573
Walline CC, Kanakasabi S, Bright JJ (2011) IL-7α confers susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Genes Immun 12:1–14
Yilmaz M, Kendirli SG, Altintas D, Bingol G, Antmen B (2001) Cytokine levels in serum of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 20:30–35
Acknowledgments
The authors like to thank Henk van Westbroek (BPRC) for the artwork and Dr. Ed Remarque (BPRC) for statistical advice. Jordon Dunham was funded by the European Union with a Marie Curie Fellowship (ITN NeuroKine; 316722), and the authors are grateful for this support.
Conflict of Interest
Li-Fen Li, Irene Ni, Wenwu Zhai, Guang-Huan Tu and John Lin were full-time employees of Rinat-Pfizer when the study was performed. The other authors report no conflict of interest. Publication of the data, irrespective of outcome, was part of the contractual agreement between Rinat-Pfizer and the BPRC as an independent research center.
Author Contributions
J.D., N.v.D. and Y.K have designed the study and performed the in vivo study as well as the ex vivo experiments and analyses. JB has performed the histology. J.D., J.D.L., B.t.H., and Y.K. have written the paper. B.t.H. and J.D.L. have supervised the in vivo study. L.L., G.T. and J.C.L. designed and performed the in vitro assays of the therapeutic antibodies. I.N. and W.Z. screened, cloned and generated the therapeutic antibodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental figure 1
(PDF 103 kb)
Supplemental figure 2
(PDF 118 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunham, J., Lee, LF., van Driel, N. et al. Blockade of CD127 Exerts a Dichotomous Clinical Effect in Marmoset Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 11, 73–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9629-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9629-6