Abstract
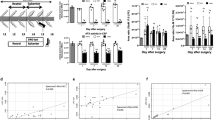
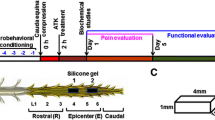
Lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. LSS pathology is associated with secondary injury caused by inflammation, oxidative damage and cell death. Apart from laminectomy, pharmacological therapy targeting secondary injury is limited. Statins are FDA-approved cholesterol-lowering drug. They also show pleiotropic anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective effects. To investigate the therapeutic efficacy of simvastatin in restoring normal locomotor function after cauda equina compression (CEC) in a rat model of LSS, CEC injury was induced in rats by implanting silicone gels into the epidural spaces of L4 and L6. Experimental group was treated with simvastatin (5 mg/kg body weight), while the injured (vehicle) and sham operated (sham) groups received vehicle solution. Locomotor function in terms of latency on rotarod was measured for 49 days and the threshold of pain was determined for 14 days. Rats were sacrificed on day 3 and 14 and the spinal cord and cauda equina fibers were extracted and studied by histology, immunofluorescence, electron microscopy (EM) and TUNEL assay. Simvastatin aided locomotor functional recovery and enhanced the threshold of pain after the CEC. Cellular Infiltration and demyelination decreased in the spinal cord from the simvastatin group. EM revealed enhanced myelination of cauda equina in the simvastatin group. TUNEL assay showed significantly decreased number of apoptotic neurons in spinal cord from the simvastatin group compared to the vehicle group. Simvastatin hastens the locomotor functional recovery and reduces pain after CEC. These outcomes are mediated through the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of simvastatin. The data indicate that simvastatin may be a promising drug candidate for LSS treatment in humans.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamson EE, Ikonomovic MD, Dixon CE, DeKosky ST (2009) Simvastatin therapy prevents brain trauma-induced increases in beta-amyloid peptide levels. Ann Neurol 66(3):407–414. doi:10.1002/ana.21731
Adamova B, Vohanka S, Dusek L (2003) Differential diagnostics in patients with mild lumbar spinal stenosis: the contributions and limits of various tests. Eur Spine J 12(2):190–196. doi:10.1007/s00586-002-0503-x
Bethea JR (2000) Spinal cord injury-induced inflammation: a dual-edged sword. Prog Brain Res 128:33–42. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(00)28005-9
Bresnahan L, Fessler RG, Natarajan RN (2010) Evaluation of change in muscle activity as a result of posterior lumbar spine surgery using a dynamic modeling system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35(16):E761–E767. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181e45a6e
Brosamle C, Schwab ME (2000) Ipsilateral, ventral corticospinal tract of the adult rat: ultrastructure, myelination and synaptic connections. J Neurocytol 29(7):499–507
Cahill KS, Wang MY (2012) Cost effectiveness of lumbar fusion improves with time. Neurosurgery 70(2):N21. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000410938.46452.b600006123-201202000-00009
Carloni S, Girelli S, Buonocore G, Longini M, Balduini W (2009) Simvastatin acutely reduces ischemic brain damage in the immature rat via Akt and CREB activation. Exp Neurol 220(1):82–89. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.07.026
Chauhan NB, Gatto R (2011) Restoration of cognitive deficits after statin feeding in TBI. Restor Neurol Neurosci 29(1):23–34. doi:10.3233/RNN-2011-0573
Chen G, Zhang S, Shi J, Ai J, Qi M, Hang C (2009) Simvastatin reduces secondary brain injury caused by cortical contusion in rats: possible involvement of TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Exp Neurol 216(2):398–406. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.12.019
Chu LW, Chen JY, Yu KL, Cheng KI, Wu PC, Wu BN (2012) Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory activities of atorvastatin in a rat chronic constriction injury model. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 25(1):219–230
Cimino M, Balduini W, Carloni S, Gelosa P, Guerrini U, Tremoli E, Sironi L (2005) Neuroprotective effect of simvastatin in stroke: a comparison between adult and neonatal rat models of cerebral ischemia. Neurotoxicology 26(5):929–933. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2005.03.009
Dembowski E, Davidson MH (2009) A review of lipid management in primary and secondary prevention. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev 29(1):2–12. doi:10.1097/HCR.0b013e318192754e
Die J, Wang K, Fan L, Jiang Y, Shi Z (2010) Rosuvastatin preconditioning provides neuroprotection against spinal cord ischemia in rats through modulating nitric oxide synthase expressions. Brain Res 1346:251–261. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.05.068
Dommisse GF, Grobler L (1976) Arteries and veins of the lumbar nerve roots and cauda equina. Clin Orthop Relat Res 115:22–29
Eroglu H, Nemutlu E, Turkoglu OF, Nacar O, Bodur E, Sargon MF, Beskonakli E, Oner L (2010) A quadruped study on chitosan microspheres containing atorvastatin calcium: preparation, characterization, quantification and in-vivo application. Chem Pharm Bull 58(9):1161–1167
Gibson JN, Waddell G (2005) Surgery for degenerative lumbar spondylosis: updated Cochrane Review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30(20):2312–2320
Habtemariam A, Gronblad M, Virri J, Seitsalo S, Karaharju E (1998) A comparative immunohistochemical study of inflammatory cells in acute-stage and chronic-stage disc herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23(20):2159–2165, discussion 2166
Han X, Yang N, Xu Y, Zhu J, Chen Z, Liu Z, Dang G, Song C (2011) Simvastatin treatment improves functional recovery after experimental spinal cord injury by upregulating the expression of BDNF and GDNF. Neurosci Lett 487(3):255–259. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.007
Hausmann ON (2003) Post-traumatic inflammation following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 41(7):369–378. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.31014833101483
Igel M, Sudhop T, von Bergmann K (2002) Pharmacology of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors (statins), including rosuvastatin and pitavastatin. J Clin Pharmacol 42(8):835–845
Ito T, Ohtori S, Inoue G, Koshi T, Doya H, Ozawa T, Saito T, Moriya H, Takahashi K (2007) Glial phosphorylated p38 MAP kinase mediates pain in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation and induces motor dysfunction in a rat model of lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32(2):159–167. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000251437.10545.e900007632-200701150-00004
Kawaguchi S, Yamashita T, Yokogushi K, Murakami T, Ohwada O, Sato N (2001) Immunophenotypic analysis of the inflammatory infiltrates in herniated intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26(11):1209–1214
Khan M, Im YB, Shunmugavel A, Gilg AG, Dhindsa RK, Singh AK, Singh I (2009) Administration of S-nitrosoglutathione after traumatic brain injury protects the neurovascular unit and reduces secondary injury in a rat model of controlled cortical impact. J Neuroinflammation 6:32. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-6-32
Kiernan J (1990) Interactions between mast cells and nerves. Neurogenic inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11(8):316
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Wedge JH, Yong-Hing K, Tchang S, de Korompay V, Shannon R (1982) Lumbar spinal nerve lateral entrapment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 169:171–178
Koike Y, Uzuki M, Kokubun S, Sawai T (2003) Angiogenesis and inflammatory cell infiltration in lumbar disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28(17):1928–1933. doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000083324.65405.AE
Koyanagi I, Tator CH, Lea PJ (1993) Three-dimensional analysis of the vascular system in the rat spinal cord with scanning electron microscopy of vascular corrosion casts. Part 1: normal spinal cord. Neurosurgery 33(2):277–283, discussion 283–274
Kwak B, Mulhaupt F, Myit S, Mach F (2000) Statins as a newly recognized type of immunomodulator. Nat Med 6(12):1399–1402. doi:10.1038/82219
Lassmann H, Wisniewski HM (1979) Chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: clinicopathological comparison with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 36(8):490–497
Li B, Mahmood A, Lu D, Wu H, Xiong Y, Qu C, Chopp M (2009) Simvastatin attenuates microglial cells and astrocyte activation and decreases interleukin-1beta level after traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 65(1):179–185. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000346272.76537.DC, discussion 185–176
Markovic-Plese S, Singh AK, Singh I (2008) Therapeutic potential of statins in multiple sclerosis: immune modulation, neuroprotection and neurorepair. Futur Neurol 3(2):153. doi:10.2217/14796708.3.2.153
Mascitelli L, Grant WB, Goldstein MR (2011) Statins, vitamin D, and neuropathic pain. Pain 152(7):1686–1687. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2011.04.022, author reply 1687
Miranda HF, Noriega V, Olavarria L, Zepeda RJ, Sierralta F, Prieto JC (2011) Antinociception and anti-inflammation induced by simvastatin in algesiometric assays in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109(6):438–442. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00746.x
Ohtori S, Suzuki M, Koshi T, Takaso M, Yamashita M, Inoue G, Yamauchi K, Orita S, Eguchi Y, Kuniyoshi K, Ochiai N, Kishida S, Nakamura J, Aoki Y, Ishikawa T, Arai G, Miyagi M, Kamoda H, Toyone T, Takahashi K (2010) Proinflammatory cytokines in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with lumbar radiculopathy. Eur Spine J. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1595-3
Orendacova J, Cizkova D, Kafka J, Lukacova N, Marsala M, Sulla I, Marsala J, Katsube N (2001) Cauda equina syndrome. Prog Neurobiol 64(6):613–637
Pahan K, Sheikh FG, Namboodiri AM, Singh I (1997) Lovastatin and phenylacetate inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthase and cytokines in rat primary astrocytes, microglia, and macrophages. J Clin Invest 100(11):2671–2679. doi:10.1172/JCI119812
Paintlia AS, Paintlia MK, Singh AK, Stanislaus R, Gilg AG, Barbosa E, Singh I (2004) Regulation of gene expression associated with acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by Lovastatin. J Neurosci Res 77(1):63–81. doi:10.1002/jnr.20130
Paintlia AS, Paintlia MK, Singh I, Skoff RB, Singh AK (2009) Combination therapy of lovastatin and rolipram provides neuroprotection and promotes neurorepair in inflammatory demyelination model of multiple sclerosis. Glia 57(2):182–193. doi:10.1002/glia.20745
Pan HC, Yang DY, Ou YC, Ho SP, Cheng FC, Chen CJ (2010) Neuroprotective effect of atorvastatin in an experimental model of nerve crush injury. Neurosurgery 67(2):376–388. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000371729.47895.A0, discussion 388–379
Pannu R, Barbosa E, Singh AK, Singh I (2005) Attenuation of acute inflammatory response by atorvastatin after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurosci Res 79(3):340–350. doi:10.1002/jnr.20345
Pannu R, Christie DK, Barbosa E, Singh I, Singh AK (2007) Post-trauma Lipitor treatment prevents endothelial dysfunction, facilitates neuroprotection, and promotes locomotor recovery following spinal cord injury. J Neurochem 101(1):182–200. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04354.x
Porter RW, Ward D (1992) Cauda equina dysfunction. The significance of two-level pathology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 17(1):9–15
Qu C, Lu D, Goussev A, Schallert T, Mahmood A, Chopp M (2005) Effect of atorvastatin on spatial memory, neuronal survival, and vascular density in female rats after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 103(4):695–701. doi:10.3171/jns.2005.103.4.0695
Qu C, Xiong Y, Mahmood A, Kaplan DL, Goussev A, Ning R, Chopp M (2009) Treatment of traumatic brain injury in mice with bone marrow stromal cell-impregnated collagen scaffolds. J Neurosurg 111(4):658–665. doi:10.3171/2009.4.JNS081681
Reichert F, Levitzky R, Rotshenker S (1996) Interleukin 6 in intact and injured mouse peripheral nerves. Eur J Neurosci 8(3):530–535
Schonbeck U, Libby P (2004) Inflammation, immunity, and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: statins as antiinflammatory agents? Circulation 109(21 Suppl 1):II18–II26. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000129505.34151.23
Schwab ME, Bartholdi D (1996) Degeneration and regeneration of axons in the lesioned spinal cord. Physiol Rev 76(2):319–370
Schwab JM, Brechtel K, Mueller CA, Failli V, Kaps HP, Tuli SK, Schluesener HJ (2006) Experimental strategies to promote spinal cord regeneration–an integrative perspective. Prog Neurobiol 78(2):91–116. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.12.004
Seichi A, Takeshita K, Kawaguchi H, Nakajima S, Akune T, Nakamura K (2004) Postoperative expansion of intramedullary high-intensity areas on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging after cervical laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(13):1478–1482, discussion 1482
Sekiguchi M, Kikuchi S, Myers RR (2004) Experimental spinal stenosis: relationship between degree of cauda equina compression, neuropathology, and pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(10):1105–1111
Shi XQ, Lim TK, Lee S, Zhao YQ, Zhang J (2011) Statins alleviate experimental nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Pain 152(5):1033–1043. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2011.01.006
Shunmugavel A, Khan M, Te Chou PC, Dhindsa RK, Martin MM, Copay AG, Subach BR, Schuler TC, Bilgen M, Orak JK, Singh I (2010) Simvastatin protects bladder and renal functions following spinal cord injury in rats. J Inflamm (Lond) 7:17. doi:10.1186/1476-9255-7-17
Shunmugavel A, Khan M, Chou PC, Singh I (2012a) Spinal cord injury induced arrest in estrous cycle of rats is ameliorated by S-nitrosoglutathione: novel therapeutic agent to treat amenorrhea. J Sex Med 9(1):148–158. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02526.x
Shunmugavel A, Khan M, Martin MM, Copay AG, Subach BR, Schuler TC, Singh I (2012b) S-Nitrosoglutathione administration amelioratescauda equina compression injury in rats. Neurosci Med 3(3):294–305. doi:10.4236/nm.2012.33034
Siebert E, Pruss H, Klingebiel R, Failli V, Einhaupl KM, Schwab JM (2009) Lumbar spinal stenosis: syndrome, diagnostics and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol 5(7):392–403. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2009.90
Stanislaus R, Singh AK, Singh I (2001) Lovastatin treatment decreases mononuclear cell infiltration into the CNS of Lewis rats with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res 66(2):155–162. doi:10.1002/jnr.1207
Takenobu Y, Katsube N, Marsala M, Kondo K (2001) Model of neuropathic intermittent claudication in the rat: methodology and application. J Neurosci Methods 104(2):191–198
Tator CH, Fehlings MG (1991) Review of the secondary injury theory of acute spinal cord trauma with emphasis on vascular mechanisms. J Neurosurg 75(1):15–26. doi:10.3171/jns.1991.75.1.0015
Walker KM, Urban L, Medhurst SJ, Patel S, Panesar M, Fox AJ, McIntyre P (2003) The VR1 antagonist capsazepine reverses mechanical hyperalgesia in models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304(1):56–62. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.042010
Wang Y, Hashizume Y, Yoshida M, Inagaki T, Kameyama T (1999) Pathological changes of the spinal cord in centenarians. Pathol Int 49(2):118–124
Watanabe K, Konno S, Sekiguchi M, Kikuchi S (2007) Spinal stenosis: assessment of motor function, VEGF expression and angiogenesis in an experimental model in the rat. Eur Spine J 16(11):1913–1918. doi:10.1007/s00586-007-0394-y
Weber MS, Youssef S, Dunn SE, Prod'homme T, Neuhaus O, Stuve O, Greenwood J, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2006) Statins in the treatment of central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Neuroimmunol 178(1–2):140–148. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.06.006
Wong AP, Smith ZA, Lall RR, Bresnahan LE, Fessler RG (2012) The microendoscopic decompression of lumbar stenosis: a review of the current literature and clinical results. Minim Invasive Surg 2012:325095. doi:10.1155/2012/325095
Wu H, Mahmood A, Lu D, Jiang H, Xiong Y, Zhou D, Chopp M (2010) Attenuation of astrogliosis and modulation of endothelial growth factor receptor in lipid rafts by simvastatin after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 113(3):591–597. doi:10.3171/2009.9.JNS09859
Yagi M, Okada E, Ninomiya K, Kihara M (2009) Postoperative outcome after modified unilateral-approach microendoscopic midline decompression for degenerative spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg Spine 10(4):293–299. doi:10.3171/2009.1.SPINE08288
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Abdelhady M, Mourad MS, Hassouna MM (2002) Change of vanilloid receptor 1 following neuromodulation in rats with spinal cord injury. J Surg Res 107(1):140–144
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from The Spinal Research Foundation VA and by grants from Betty L. Beatty and Guy E. Beatty Foundations. The work was also supported in part by grants NS-72511,NS-22576, and NS-37766 and DC00422; 07506 from the NIH, CO6 RR018823 and CO6 RR0015455 from the Extramural Research Facilities Program of the National Center for Research Resources. The authors thank Dr. Hainan Lang, Ph.D., Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine for help in histology, Ms. Danielle Clark Lowe for help in proof reading and Ms. Joyce Bryan and Ms. Chara Williams for help in animal and reagents procurement.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shunmugavel, A., Martin, M.M., Khan, M. et al. Simvastatin Ameliorates Cauda Equina Compression Injury in a Rat Model of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8, 274–286 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9419-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9419-3