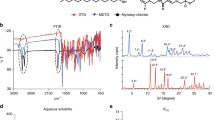
Abstract
We posit that improvements in pharmacokinetics and biodistributions of antiretroviral therapies (ART) for human immunodeficiency virus type one-infected people can be achieved through nanoformulationed drug delivery systems. To this end, we manufactured nanoparticles of atazanavir, efavirenz, and ritonavir (termed nanoART) and treated human monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) in combination therapies to assess antiretroviral responses. This resulted in improved drug uptake, release, and antiretroviral efficacy over monotherapy. MDM rapidly, within minutes, ingested nanoART combinations, at equal or similar rates, as individual formulations. Combination nanoART ingested by MDM facilitated individual drug release from 15 to >20 days. These findings are noteworthy as a nanoART cell-mediated drug delivery provides a means to deliver therapeutics to viral sanctuaries, such as the central nervous system during progressive human immunodeficiency virus type one infection. The work brings us yet another step closer to realizing the utility of nanoART for virus-infected people.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anttila S, Hukkanen J, Hakkola J, Stjernvall T, Beaune P, Edwards RJ, Boobis AR, Pelkonen O, Raunio H (1997) Expression and localization of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in human lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16:242–249
Baum MK, Rafie C, Lai S, Sales S, Page B, Campa A (2009) Crack-cocaine use accelerates HIV disease progression in a cohort of HIV-positive drug users. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 50:93–99
Best BM, Letendre SL, Brigid E, Clifford DB, Collier AC, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, McCutchan JA, Simpson DM, Ellis R, Capparelli EV, Grant I (2009) Low atazanavir concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid. Aids 23:83–87
Bruce RD, Altice FL, Gourevitch MN, Friedland GH (2006a) Pharmacokinetic drug interactions between opioid agonist therapy and antiretroviral medications: implications and management for clinical practice. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 41:563–572
Bruce RD, McCance-Katz E, Kharasch ED, Moody DE, Morse GD (2006b) Pharmacokinetic interactions between buprenorphine and antiretroviral medications. Clin Infect Dis 43(Suppl 4):S216–223
Danel C, Moh R, Chaix ML, Gabillard D, Gnokoro J, Diby CJ, Toni T, Dohoun L, Rouzioux C, Bissagnene E, Salamon R, Anglaret X (2009) Two-months-off, four-months-on antiretroviral regimen increases the risk of resistance, compared with continuous therapy: a randomized trial involving West African adults. J Infect Dis 199:66–76
Dou H, Destache CJ, Morehead JR, Mosley RL, Boska MD, Kingsley J, Gorantla S, Poluektova L, Nelson JA, Chaubal M, Werling J, Kipp J, Rabinow BE, Gendelman HE (2006) Development of a macrophage-based nanoparticle platform for antiretroviral drug delivery. Blood 108:2827–2835
Dou H, Morehead J, Destache CJ, Kingsley JD, Shlyakhtenko L, Zhou Y, Chaubal M, Werling J, Kipp J, Rabinow BE, Gendelman HE (2007) Laboratory investigations for the morphologic, pharmacokinetic, and anti-retroviral properties of indinavir nanoparticles in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Virology 358:148–158
Dou H, Grotepas CB, McMillan JM, Destache CJ, Chaubal M, Werling J, James K, Rabinow B, Gendelman HE (2009) Macrophage delivery of nanoformulated antiretroviral drug to the brain in a murine model of neuroAIDS. J Immunol 183:661–669
Ellis R, Langford D, Masliah E (2007) HIV and antiretroviral therapy in the brain: neuronal injury and repair. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:33–44
Epstein LG, Gendelman HE (1993) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of the nervous system: pathogenetic mechanisms. Ann Neurol 33:429–436
Feldt T, Oette M, Kroidl A, Gobels K, Leidel R, Sagir A, Kuschak D, Haussinger D (2005) Atazanavir for treatment of HIV infection in clinical routine: efficacy, pharmacokinetics and safety. Eur J Med Res 10:7–10
Fellay J, Boubaker K, Ledergerber B, Bernasconi E, Furrer H, Battegay M, Hirschel B, Vernazza P, Francioli P, Greub G, Flepp M, Telenti A (2001) Prevalence of adverse events associated with potent antiretroviral treatment: Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Lancet 358:1322–1327
Garvie PA, Lawford J, Flynn PM, Gaur AH, Belzer M, McSherry GD, Hu C (2009) Development of a directly observed therapy adherence intervention for adolescents with human immunodeficiency virus-1: application of focus group methodology to inform design, feasibility, and acceptability. J Adolesc Health 44:124–132
Gendelman HE, Orenstein JM, Martin MA, Ferrua C, Mitra R, Phipps T, Wahl LA, Lane HC, Fauci AS, Burke DS et al (1988) Efficient isolation and propagation of human immunodeficiency virus on recombinant colony-stimulating factor 1-treated monocytes. J Exp Med 167:1428–1441
Gianotti N, Soria A, Lazzarin A (2007) Antiviral activity and clinical efficacy of atazanavir in HIV-1-infected patients: a review. New Microbiol 30:79–88
Gisslen M, Ahlqvist-Rastad J, Albert J, Blaxhult A, Hamberg AK, Lindback S, Sandstrom E, Uhnoo I (2006) Antiretroviral treatment of HIV infection: Swedish recommendations 2005. Scand J Infect Dis 38:86–103
Gray F, Adle-Biassette H, Chretien F, Lorin de la Grandmaison G, Force G, Keohane C (2001) Neuropathology and neurodegeneration in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pathogenesis of HIV-induced lesions of the brain, correlations with HIV-associated disorders and modifications according to treatments. Clin Neuropathol 20:146–155
Hawkins T (2006) Appearance-related side effects of HIV-1 treatment. AIDS Patient Care STDS 20:6–18
Hesse LM, von Moltke LL, Shader RI, Greenblatt DJ (2001) Ritonavir, efavirenz, and nelfinavir inhibit CYP2B6 activity in vitro: potential drug interactions with bupropion. Drug Metab Dispos 29:100–102
Horberg M, Klein D, Hurley L, Silverberg M, Towner W, Antoniskis D, Kovach D, Mogyoros M, Blake W, Dobrinich R, Dodge W (2008) Efficacy and safety of ritonavir-boosted and unboosted atazanavir among antiretroviral-naive patients. HIV Clin Trials 9:367–374
Hukkanen J, Hakkola J, Anttila S, Piipari R, Karjalainen A, Pelkonen O, Raunio H (1997) Detection of mRNA encoding xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450s in human bronchoalveolar macrophages and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mol Carcinog 20:224–230
Hukkanen J, Pelkonen O, Hakkola J, Raunio H (2002) Expression and regulation of xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes in human lung. Crit Rev Toxicol 32:391–411
Johnson M, Grinsztejn B, Rodriguez C, Coco J, DeJesus E, Lazzarin A, Lichtenstein K, Rightmire A, Sankoh S, Wilber R (2005) Atazanavir plus ritonavir or saquinavir, and lopinavir/ritonavir in patients experiencing multiple virological failures. Aids 19:685–694
Kabanov AV, Gendelman HE (2007) Nanomedicine in the diagnosis and therapy of neurodegenerative disorders. Progress in Polymer Science 32:1054–1082
Kalter DC, Greenhouse JJ, Orenstein JM, Schnittman SM, Gendelman HE, Meltzer MS (1991) Epidermal Langerhans cells are not principal reservoirs of virus in HIV disease. J Immunol 146:3396–3404
Kraft-Terry SD, Buch SJ, Fox HS, Gendelman HE (2009) A coat of many colors: neuroimmune crosstalk in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Neuron 64:133–145
Kumagai AK, Eisenberg JB, Pardridge WM (1987) Absorptive-mediated endocytosis of cationized albumin and a beta-endorphin-cationized albumin chimeric peptide by isolated brain capillaries. Model system of blood–brain barrier transport. J Biol Chem 262:15214–15219
Kumar GN, Dykstra J, Roberts EM, Jayanti VK, Hickman D, Uchic J, Yao Y, Surber B, Thomas S, Granneman GR (1999) Potent inhibition of the cytochrome P-450 3A-mediated human liver microsomal metabolism of a novel HIV protease inhibitor by ritonavir: a positive drug–drug interaction. Drug Metab Dispos 27:902–908
Mascolini M, Larder BA, Boucher CA, Richman DD, Mellors JW (2008) Broad advances in understanding HIV resistance to antiretrovirals: report on the XVII International HIV Drug Resistance Workshop. Antivir Ther 13:1097–1113
Meade CS, Hansen NB, Kochman A, Sikkema KJ (2009) Utilization of medical treatments and adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-positive adults with histories of childhood sexual abuse. AIDS Patient Care STDS 23:259–266
Metzner KJ, Giulieri SG, Knoepfel SA, Rauch P, Burgisser P, Yerly S, Gunthard HF, Cavassini M (2009) Minority quasispecies of drug-resistant HIV-1 that lead to early therapy failure in treatment-naive and -adherent patients. Clin Infect Dis 48:239–247
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Murri R, Lepri AC, Cicconi P, Poggio A, Arlotti M, Tositti G, Santoro D, Soranzo ML, Rizzardini G, Colangeli V, Montroni M, Monforte AD (2006) Is moderate HIV viremia associated with a higher risk of clinical progression in HIV-infected people treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy: evidence from the Italian cohort of antiretroviral-naive patients study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 41:23–30
Nowacek A, Gendelman HE (2009) NanoART, neuroAIDS and CNS drug delivery. Nanomed 4:557–574
Nowacek A, Kosloski LM, Gendelman HE (2009a) Neurodegenerative disorders and nanoformulated drug development. Nanomed 4:541–555
Nowacek AS, Miller RL, McMillan J, Kanmogne G, Kanmogne M, Mosley RL, Ma Z, Graham S, Chaubal M, Werling J, Rabinow B, Dou H, Gendelman HE (2009b) NanoART synthesis, characterization, uptake, release and toxicology for human monocyte-macrophage drug delivery. Nanomed 4:903–917
Paterson DL, Swindells S, Mohr J, Brester M, Vergis EN, Squier C, Wagener MM, Singh N (2000) Adherence to protease inhibitor therapy and outcomes in patients with HIV infection. Ann Intern Med 133:21–30
Perry VH, Bell MD, Brown HC, Matyszak MK (1995) Inflammation in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:636–641
Piipari R, Savela K, Nurminen T, Hukkanen J, Raunio H, Hakkola J, Mantyla T, Beaune P, Edwards RJ, Boobis AR, Anttila S (2000) Expression of CYP1A1, CYP1B1 and CYP3A, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adduct formation in bronchoalveolar macrophages of smokers and non-smokers. Int J Cancer 86:610–616
Raunio H, Hakkola J, Hukkanen J, Lassila A, Paivarinta K, Pelkonen O, Anttila S, Piipari R, Boobis A, Edwards RJ (1999) Expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing CYPs in human pulmonary tissue. Exp Toxicol Pathol 51:412–417
Royal SW, Kidder DP, Patrabansh S, Wolitski RJ, Holtgrave DR, Aidala A, Pals S, Stall R (2009) Factors associated with adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy in homeless or unstably housed adults living with HIV. AIDS Care 21:448–455
Valcour V, Paul R (2006) HIV infection and dementia in older adults. Clin Infect Dis 42:1449–1454
Varatharajan L, Thomas SA (2009) The transport of anti-HIV drugs across blood-CNS interfaces: summary of current knowledge and recommendations for further research. Antiviral Res 82:A99–109
Xu L, Desai MC (2009) Pharmacokinetic enhancers for HIV drugs. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 10:775–786
Zeldin RK, Petruschke RA (2004) Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor therapy in HIV-infected patients. J Antimicrob Chemother 53:4–9
Zolopa AR (2009) The evolution of HIV treatment guidelines: current state-of-the-art of ART. Antiviral Res 85(1):241–244
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Janice A. Taylor and James R. Talaska of the Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Core Facility at the University of Nebraska Medical Center for providing assistance with confocal microscopy, the Nebraska Research Initiative, and the Eppley Cancer Center for their support of the Core Facility. We also thank Ms. Robin Taylor for the critical reading of the manuscript and outstanding graphic and literary support.
Financial and competing interests disclosures
The work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants 2R01 NS034239, 2R37 NS36126, P01 NS31492, P20RR 15635, P01MH64570, and P01 NS43985 (to H.E.G.) and from a research grant from Baxter Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental 1
3D reconstruction of nanoART laden MDM. MDM were incubated with 100 µM each of ATV-H1045 (purple) labeled with Vybrant DiO cell-labeling solution, RTV-H1025 (green) labeled with Vybrant DiD cell-labeling solution, and EFV-P1044 (red) with rhodamine B 1,2-dihexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-ethanolamine, triethylammonium salt. Images were acquired after 2 h of incubation with nanoART combination. Z-Stack was constructed from 25 individual fluorescent microscopy images of 1.0-μm thickness each. A 3D reconstruction of the Z-Stack was made using Zeiss LSM510 software (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging Inc., Thornwood, NY). The 3D reconstruction rotates 360° in 16 frames. All three nanoART were taken up by MDM. Overlay (white) represents colocalization of all three formulations to cytoplasmic vesicles. (GIF 117 kb; GIF 117 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowacek, A.S., McMillan, J., Miller, R. et al. Nanoformulated Antiretroviral Drug Combinations Extend Drug Release and Antiretroviral Responses in HIV-1-Infected Macrophages: Implications for NeuroAIDS Therapeutics. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 5, 592–601 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-010-9198-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-010-9198-7