Abstract
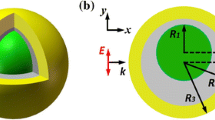
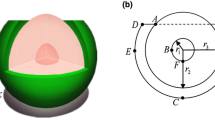
In this work, we have demonstrated that the perforated Au-SiO2-Si multilayer nanoshells can support additional magnetic response besides electric response, where Si core provides additional magnetic response, unlike regular metal-dielectric-metal multilayer nanoshells exhibiting pure electric response. Dipole radiative enhancement is used to analyze magnetic and electric responses of the perforated Au-SiO2-Si multilayer nanoshells and the spectral features of nanoshells can be used to quantitatively characterize by the coupled oscillator model. The magnetic and electric responses of the perforated Au-SiO2-Si multilayer nanoshells are dependent sensitively on the incident angles of light due to the symmetry breaking and can be easily tuned by means of varying the geometry. The unique capability of the perforated Au-SiO2-Si multilayer nanoshells exhibiting magnetic-electric responses can provide various applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hess O, Pendry JB, Maier SA, Oulton RF, Hamm JM, Tsakmakidis KL (2012) Active nanoplasmonic metamaterials. Nat Materials 11:573–584
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10:2342–2348
Huang Y, Xiao JJ, Gao L (2015) Antiboding and bonding lasing modes with low gain threshold in nonlocal metallic nanoshell[J]. Opt Express 23:8818–8828
Huang ML, Zhang YF, Du CL, Peng S, Shi DN (2016) Plasmon peak sensitivity investigation of individual Cu and Cu@Cu2O core–shell nanoparticle sensors[J]. Plasmonics 11:1197–1200
Hu Y, Noelck SJ, Drezek RA (2010) Symmetry breaking in gold-silica-gold multilayer nanoshells. ACS Nano 4:1521–1528
Hao F, Sonnefraud Y, Halas NJ, Nordlander P (2008) Symmetry breaking in plasmonic nanocavities: subradiant LSPR sensing and a tunable Fano resonance. Nano Lett 8:3983–3988
Mukherjee S, Sobhani H, Lassiter JB, Bardhan R, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2010) Fanoshells: nanoparticles with built-in Fano resonances. Nano Lett 10:2694–2701
Qian J, Wang WD, Li YD, Xu JJ, Sun Q (2012) Optical extinction properties of perforated gold-silica-gold multilayer nanoshells. J Phys Chem C 116:10349–10355
Ma YW, Zhang LH, Wu ZW, Yi MF, Zhang J, Jian GS (2015) The study of tunable local surface plasmon resonances on Au-Ag and Ag-Au core-chell alloy nanostructure particles with DDA method. Plasmonics 10:1791–1800
Chern RL (2008) Magnetic and surface plasmon resonances for periodic lattices of plasmonic split-ring resonators. Phys Rev B 78:085116
Zhou J, Koschny, Kafesaki M, Economou EN, Pendry JB, Soukoulis CM (2005) Saturation of the magnetic response of split-ring resonators at optical frequencies. Phys Rev Lett 95:223902
Yang ZJ, Zhang ZS, Hao ZH, Wang QQ (2012) Strong bonding magnetic plasmon hybridizations in double split-ring resonators. Opt Lett 37:3675–3677
Liu N, Liu H, Zhu S, Giessen H (2009) Stereometamaterials. Nat Photonics 3:157–162
Shafiei F, Monticone F, Hartsfield T, Alù A, Li XQ (2013) A subwavelength plasmonic metamolecule exhibiting magnetic-based optical Fano resonance. Nat Nanotech 8:95–99
Nazir A, Panaro S, Zaccaria RP, Liberale C, Angelis FD, Toma A (2014) Fano coil-type resonance for magnetic hot-spot generation. Nano Lett 14:3166–3171
Sheikholeslami SN, Garcíaetxarri A, Dionne JA (2011) Controlling the interplay of electric and magnetic modes via Fano-like plasmon resonances. Nano Lett 11:3927–3934
Jia ZX, Shuai Y, Xu SD, Tan HP (2015) Optical coherent thermal emission by excitation of magnetic polariton in multilayer nanoshell trimer. Opt Express 23:1096–1110
Yuan HF, Kuznetsov AI, Miroshnichenko AE, Ye FY, Lukyanchuk B (2013) Directional visible light scattering by silicon nanoparticles. Nat Commun 4:66–78
Moreno F, Nietovesperinas M, Saenz JJ (2011) Electric and magnetic dipolar response of germanium nanospheres: interference effects; scattering anisotropy; and optical forces. Physics 5:30–32
Yan JH, Liu P, Lin ZY, Wang H, Chen HJ, Wang CX, Yang GW (2015) Directional Fano resonance in a silicon nanosphere dimer. ACS Nano 9:2968–2980
Naraghi RR, Sukhov S, Dogariu A (2015) Directional control of scattering by all-dielectric core-shell spheres. Opt Lett 40:585–588
Albella P, Moreno F, Aizpurua J (2013) Low-loss electric and magnetic field-enhanced spectroscopy with subwavelength silicon dimers. J Phys Chem C 117:13573–13584
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Palik ED (1985) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic Press 33:189
Ci XT, Wu BT, Liu Y, Chen GG, Wu E, Zeng HP (2014) Magnetic-based Fano resonance of hybrid silicon-gold nanocavities in the near-infrared region. Optn 22:23749–23758
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61275057), the Basal Research Fund Project of the Liaoning Education Department (71600160), and the College Students’Innovative Training Program of Dalian Polytechnic University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhao, X., Zheng, L. et al. Highly-Tunable Magnetic and Electric Responses in the Perforated Au-SiO2-Si Multilayer Nanoshells. Plasmonics 13, 259–264 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0507-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0507-3