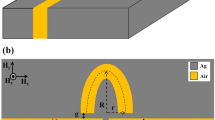
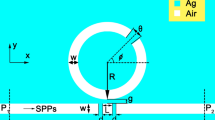
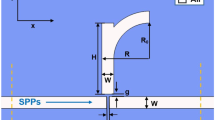
Abstract
Though adding a groove to a plasmonic end-coupled perfect ring (PR) resonator, two additional resonance modes, which can be controlled by the length of the groove, will arise in this proposed ring-groove (RG) joint metal-insulator-metal (MIM) waveguide. By further cascading, the PR resonator and the RG joint resonator, single and dual Fano resonances with asymmetric line shapes are obtained due to the interference effects between the dark modes and the bright modes. High figure of merit and high refractive-index sensitivity are achieved, and thus this structure is suitable for the biochemistry sensing area. Interestingly, normal and abnormal dispersions are also investigated for the Fano peaks and dips, respectively. The performances of the proposed structure are investigated by using the finite-difference time-domain method.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song G, Yu L, Wu C, Duan G, Wang L, Xiao J (2013) Polarization splitter with optical bistability in metal gap waveguide nanocavities. Plasmonics 8(2):943–947
Liu Y, Zhou F, Yao B, Cao J, Mao Q (2013) High-extinction-ratio and low-insertion-loss plasmonic filter with coherent coupled nano-cavity array in a MIM waveguide. Plasmonics 8(2):1035–1041
Chen Z, Song XK, Duan GY, Wang LL, Yu L (2015) Multiple Fano resonances control in MIM side-coupled cavities systems. IEEE Photon J 7(3):2701009
Wen KH, Hu YH, Chen L, Zhou JY, He M, Lei L, Meng ZM (2015) Multiple plasmon-induced transparency responses in a subwavelength inclined ring resonators system. IEEE Photon J 7(6):1–7
Wen KH, Hu YH, Chen L, Zhou JY, Lei L, Meng ZM (2016) Plasmonic bidirectional/unidirectional wavelength splitter based on metal-dielectric-metal waveguides. Plasmonics 11(1):71–77
Nikolajsen T, Leosson K, Bozhevolnyi SI (2004) Surface Plasmon polariton based modulators and switches operating at telecom wavelengths. Appl Phys Lett 85(24):5833–5835
Lu H, Liu XM, Wang L, Gong Y, Mao D (2011) Ultrafast all-optical switching in nanoplasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator. Opt Express 19(4):2910–2915
Wurtz GA, Pollard R, Zayats AV (2006) Optical bistability in nonlinear surface-plasmon polaritonic crystals. Phys Rev Lett 97(5):057402
Randhawa S, González MU, Renger J, Enoch S, Quidant R (2010) Design and properties of dielectric surface plasmon Bragg mirrors. Opt Express 18(14):14496–14510
Bozhevolnyi SI, Volkov VS, Devaux E, Laluet JY, Ebbesen TW (2006) Channel plasmon subwavelength waveguide components including interferometers and ring resonators. Nature 440(7083):508–511
Enoch S, Quidant R, Badenes G (2004) Optical sensing based on plasmon coupling in nanoparticle arrays. Opt Express 12(15):3422–3427
Park J, Kim H, Lee B (2008) High order plasmonic Bragg reflection in the metal-insulator-metal waveguide Bragg grating. Opt Express 16(1):413–425
Hu FF, Yi HX, Zhou ZP (2011) Wavelength demultiplexing structure based on arrayed plasmonic slot cavities. Opt Lett 36(8):1500–1502
Ma FS, Lee C (2013) Optical nanofilters based on meta-atom side-coupled plasmonics metal-insulator-metal waveguides. J Lightwave Technol 31(17):2876–2880
Pu MB, Hu CG, Huang C, Wang CT, Zhao ZY, Wang YQ, Luo XG (2013) Investigation of Fano resonance in planar metamaterial with perturbed periodicity. Opt Express 21(1):992–1001
Pu MB, Li X, Ma XL, Wang YQ, Zhao ZY, Wang CT, Hu CG, Gao P, Huang C, Ren HR, Li XP, Qin F, Yang J, Gu M, Hong MH, Luo XG (2015) Catenary optics for achromatic generation of perfect optical angular momentum. Sci Adv 1(9):e1500396
Luo X, Zou X, Li X, Zhou Z, Pan W, Yan L, Wen KH (2013) High-uniformity multichannel plasmonic filter using linearly lengthened insulators in metal–insulator–metal waveguide. Opt Lett 38(9):1585–1587
Luk’yanchuk B, Zheludev N, Maier S, Halas N, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong C (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9(9):707–715
Chen J, Li Z, Zou Y, Deng Z, Xiao J, Gong Q (2013) Coupled-resonator-induced Fano resonances for plasmonic sensing with ultra-high figure of merits. Plasmonics 8(4):1627–1631
Piao X, Yu S, Koo S, Lee K, Park N (2011) Fano-type spectral asymmetry and its control for plasmonic metal-insulator-metal stub structures. Opt Express 19(11):10907–10912
Qi J, Chen Z, Chen J, Li Y, Qiang W, Xu J, Sun Q (2014) Independently tunable double Fano resonances in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Opt Express 22(12):14688–14695
Paul S, Bera M, Ray M (2015) Parametric analysis of spectral Fano lineshape for plasmonic waveguide-coupled dual nanoresonator. J Lightwave Technol 33(13):2824–2830
Li BX, Li HJ, Zeng LL, Zhan SP, He ZH, Chen ZQ, Xu H (2016) Sensing application in Fano resonance with T-shape structure. J Lightwave Technol 34(14):3342–3347
Zhan S, Peng Y, He Z, Li B, Chen Z, Xu H, Li H (2016) Tunable nanoplasmonic sensor based on the asymmetric degree of Fano resonance in MDM waveguide. Sci Rep 6:22428
Fan C, Shi F, Wu H, Chen Y (2015) Tunable all-optical plasmonic diode based on Fano resonance in nonlinear waveguide coupled with cavities. Opt Lett 40(11):2449–2452
Zhang ZD, Wang HY, Zhang ZY (2013) Fano resonance in a gear-shaped nanocavity of the metal–insulator–metal waveguide. Plasmonics 8(2):797–801
Wen K, Hu Y, Chen L, Zhou J, Lei L, Guo Z (2015) Fano resonance with ultra-high figure of merits based on plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 10(1):27–32
Chen Z, Yu L (2014) Multiple Fano resonances based on different waveguide modes in a symmetry breaking plasmonic system. IEEE Photon J 6(6):1–8
Wen KH, Hu YH, Chen L, Zhou JY, Lei L, Meng ZM (2016) Single/dual Fano resonance based on plasmonic metal-dielectric-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 11(1):315–321
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Dionne JA, Sweatlock LA, Atwater HA (2006) Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys Rev B 73:035407
Becker J, Trügler A, Jakab A, Hohenester U, Sönnichsen C (2010) The optimal aspect ratio of gold nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5(2):161–167
Lu H, Liu X, Mao D, Wang G (2012) Plasmonic nanosensor based on Fano resonance in waveguide-coupled resonators. Opt Lett 37(18):3780–3782
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 61405039 and No. 61475037, Science and Technology Planning Projects of Guangdong Province, China under Grant No. 2016A020223013, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China, under Grant No. 2014A030310300, the State Key Lab of Optical Technologies for Micro-Engineering and Nano-Fabrication of China, the Foundation for Distinguished Young Talents in Higher Education of Guangdong, China, under Grant No. 2014KQNCX066, Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China under Grant No. 20134407110008, Guangzhou Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province, China under Grant No. 2016201604030027, Research Project of Guangdong Province under Grant No. 2013B090500035, and the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou under Grant No. 2014 J4100202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, K., Hu, Y., Chen, L. et al. Fano Resonance Based on End-Coupled Cascaded-Ring MIM Waveguides Structure. Plasmonics 12, 1875–1880 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0457-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0457-1