Abstract
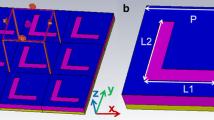
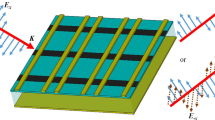
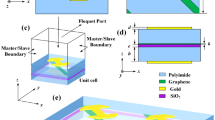
We have proposed two designs of graphene-enabled cross polarization converters, which are capable of high-efficiency polarization conversion rate and can work equally well for a wide range of incident wave angles. The first type is carefully constructed by an ellipse-shaped graphene sheet printed on a dielectric material backed up by a gold ground plane, while the second one comprises a graphene ring embedded an ellipse resonator. Numerical results demonstrate that the polarization conversion rate of the first polarizer reaches 99.38 % at 22.541 THz when the Fermi energy is fixed at 0.9 eV. The second one can simultaneously work at two frequencies with its polarization conversion rate being 96.74 and 95.88 %, respectively. Therefore, for two devices, the incident linearly polarized beams are almost completely rotated to its orthogonal counterpart after reflection in the mid-infrared spectral range. More importantly, the cross polarization amplitude and resonant frequencies can be dynamically tuned by shifting the Fermi energy without changing the nanostructure, which will exhibit enormous potential applications in photonics field.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanna L, Jari T, Jani T (2005) Design of polarization gratings for broadband illumination. Opt Express 13(8):3055–3067
Du GX, Saito S, Takahashi M (2011) Tailoring the Faraday effect by birefringence of two dimensional plasmonic nanorod array. Appl Phys Lett 99(19):191107
Feng M, Wang J, Ma H, et al. (2013) Broadband polarization rotator based on multi-order plasmon resonances and high impedance surface. J Appl Phys 114(7):074508
Huang L, Chen X, Mühlenbernd H, et al. (2012) Dispersionless phase discontinuities for controlling light propagation. Nano Lett 12(11):5750–5755
Francesco A, Patrice G, Mikhail K, et al. (2013) Aberrations of flat lenses and aplanatic metasurfaces. Opt Express 21(21):31530–31539
Wei Ting C, Kuang-Yu Y, Chih-Ming W, et al. (2014) High-efficiency broadband meta-hologram with polarization-controlled dual images. Nano Lett 14(1):225
Yang B, Ye WM, Yuan XD, et al. (2013) Design of ultrathin plasmonic quarter-wave plate based on period coupling. Opt Lett 38(5):679–681
Yang Y, Wang W, Moitra P, et al. (2014) Dielectric meta-reflectarray for broadband linear polarization conversion and optical vortex generation. Nano Lett 14(3):1394–1399
Li R, Guo Z, Wang W, et al. (2015a) High-efficiency cross polarization converters by plasmonic metasurface. Plasmonics 10(5):1–6
Song Z, Zhang L, Liu QH (2015) High-efficiency broadband cross polarization converter for near-infrared light based on anisotropic meta-surface. Plasmonics 1:4
Liu W, Chen S, Li Z, et al. (2015) Realization of broadband cross-polarization conversion in transmission mode in the terahertz region using a single-layer metasurface. Opt Lett 40(13):3185–3188
Xi C (2013) Terahertz angle-insensitive 90° polarization rotator using chiral metamaterial. Phys B Condens Matter 422(422):83–86
Bao Q, Loh KP (2012) Graphene photonics, plasmonics, and broadband optoelectronic devices. ACS Nano 6(5):3677–3694
Fang Z, Wang Y, Liu Z, et al. (2012) Plasmon-induced doping of graphene. ACS Nano 6(11):10222–10228
Ishikawa A, Tanaka T (2013) Plasmon hybridization in graphene metamaterials. Appl Phys Lett 102(25):253110
Li J, Yu P, Cheng H, et al. (2016) Optical polarization encoding using graphene-loaded plasmonic metasurfaces. Adv Opt Mater 4(1):91–98
Li Z, Yao K, Xia F, et al (2015b) Graphene plasmonic metasurfaces to steer infrared light. Sci Rep 5
Cheng H, Chen S, Yu P, et al. (2015) Dynamically tunable broadband infrared anomalous refraction based on graphene metasurfaces. Adv Opt Mater 3(12):1744–1749
Chen PY, Soric J, Padooru YR, et al. (2013) Nanostructured graphene metasurface for tunable terahertz cloaking. New J Phys 5(12):919–926
Fal’kovskii LA (2008) Optical properties of graphene. J Exp Theor Phys 115(3):496–508
Ashkan V, Nader E (2011) Transformation optics using graphene. Science 332(6035):1291–1294
Menzel C, Rockstuhl C, Lederer F (2010) An advanced Jones calculus for the classification of periodic metamaterial. Phys Rev A 82(5):3464–3467
Hao JM, Ren QJ, An ZH et al (2009) Optical metamaterial for polarization control. Phys Rev A 80(2):92–92
Yao G, Ling F, Yue J et al (2015) Dynamically tunable terahertz cross polarization amplitude based on graphene metamaterial. Optoelectronic Devices and Integration. doi:10.1364/OEDI.2015.JW3A.38
Hsiao-Kuan Y, Chettiar UK, Wenshan C, et al. (2007) A negative permeability material at red light. Opt Express 15(3):1076–1083
Minovkoppensich FHL, Chang DE, Thongrattanasiri S, et al. (2011) Graphene plasmonics: a platform for strong light-matter interactions. Nano Lett 11(8):3370–3377
Furchi M, Urich A, Pospischil A, et al. (2012) Microcavity-integrated graphene photodetector. Nano Lett 12(6):2773–2777
Ding J, Arigong B, Ren H, et al. (2014) Mid-infrared tunable dual-frequency cross polarization converters using graphene-based L-shaped nanoslot array. Plasmonics 10(2):351–356
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ming Chen and Wei Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Sun, W., Cai, J. et al. Frequency-Tunable Mid-Infrared Cross Polarization Converters Based on Graphene Metasurface. Plasmonics 12, 699–705 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0316-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0316-0