Abstract
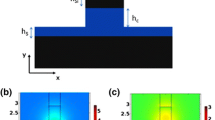
Propagation properties of hybrid plasmonic slab waveguides are studied in detail using transfer matrix method considering structural and material aspects. Hybrid metal–insulator, hybrid metal–insulator–metal, and hybrid insulator–metal–insulator waveguides are considered. Propagation length (L p), spatial length (L s), and mode length (L m) are utilized as three common figures of merit to compare and optimize the waveguides according to the layer thicknesses and metal/dielectric materials. The effect of constituting materials including metals (such as silver, gold, copper, and aluminum) and dielectrics (common dielectric materials used in photonic integrated circuit technologies such as silicon and silicon compounds, III–V compounds, and polymers) are discussed. It is found that hybrid waveguides are partially to completely superior to conventional plasmonic waveguides, providing a better balance between confinement and loss.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarid D (1981) Long-range surface-plasma waves on very thin metal films. Phys Rev Lett 47(26):1927–1930
Berini P (2001) Plasmon-polariton waves guided by thin lossy metal films of finite width: bound modes of asymmetric structures. Phys Rev B63:125417
Lamprecht B, Krenn JR, Schider G, Ditlbacher H, Salerno M, Félidj N, Leitner A, Aussenegg FR, Weeber JC (2001) Surface plasmon propagation in microscale metal stripes. Appl Phys Lett 79:51–53
Zia R, Selker MD, Catrysse PB, Brongersma MI (2004) Geometries and materials for subwavelength surface plasmon modes. J Opt Soc 21:2442–2446
Zia R, Selker MD, Brongersma MI (2005) Leaky and bound modes of surface plasmon waveguides. Physical Rev B 71:165431
Veronis G, Fan S (2005) Guided subwavelength plasmonic mode supported by a slot in a thin metal film. Opt Lett 30:3359–3361
Breukelaar I, Charbonneau R, Berini P (2006) Long-range surface plasmon-polariton mode cutoff and radiation. Appl Phys Lett 88:051119
Bozhevolnyi SI, Volkov VS, Devaux E, Laluet JY, Ebbesen TW (2007) Channeling surface plasmons. Applied Physics A 89:225–231
HolmgaardT BS (2007) Theoretical analysis of dielectric-loaded surface plasmon-polariton waveguides. Physical Rev B 75:1–12
Krasavin AV, Zayats AV (2007) Passive photonic elements based on dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polariton waveguides. Appl Phys Lett 90:211101
Oulton RF, Sorger VJ, Genov DA, Pile DFP, Zhang X (2008) A hybrid plasmonic waveguide for subwavelength confinement and long-range propagation. Nature Photonics 2:496–500
Mart A, Garc C, Mart J (2008) Analysis of hybrid dielectric plasmonic waveguides. J Selec Topics Quantum Elec 14:1496–1501
Fujii M, Leuthold J, Freude W (2009) Dispersion relation and loss of subwavelength confined mode of metal-dielectric-gap optical waveguides. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 21:362–364
Dai D, He S (2009) A silicon-based hybrid plasmonic waveguide with a metal cap for a nano-scale light confinement. Opt Express 17:16646–16653
Chu HS, Li EP, Bai P, Hegde R (2010) Optical performance of single-mode hybrid dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguide-based components. Appl Phys Lett 96:1–3
Wu M, Van V (2010) Subwavelength silicon hybrid plasmonic waveguides and components. OSA Conf 2:5–6
Song Y, Wang J, Li Q, Yan M, Qiu M (2010) Broadband coupler between silicon waveguide and hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Opt Express 18:13173–13179
Bian Y, Zheng Z, Liu Y, Zhu J, Zhou T (2011) Fabrication-error-tolerant, hybrid wedge plasmon polariton waveguides for ultra-deep-subwavelength mode confinement at 1550 nm wavelength. OSA Conf 2–4
Chu HS, Bai P, Li EP, Hoefer WRJ (2011) Hybrid dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguide-based power splitter and ring resonator: compact size and high optical performance for nanophotonic circuits. Springer Plasmonics 6:591–597
Dai D, He S (2010) Low-loss hybrid plasmonic waveguide with double low-index nano-slots. Opt Express 18:2133–2135
Kim JT (2011) CMOS-compatible hybrid plasmonic waveguide for subwavelength light confinement and on-chip integration. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 23:206–208
Bian Y, Zheng Z, Zhao X, Zhu J, Zhou T (2009) Symmetric hybrid surface plasmon polariton waveguides for 3D photonic integration. Opt Express 17:21320–21325
Kim JT, Ju JJ, Park S, Kim MS, Park SK (2010) Hybrid plasmonic waveguide for low-loss lightwave guiding. Opt Express 18:2808–2813
Kou Y, Ye F, Chen X (2011) Low-loss hybrid plasmonic waveguide for compact and high-efficient photonic integration. Opt Express 19:11746–11752
Ruschin S, Marom E (1984) Coupling effects in symmetrical three-guide structures. J Opt Soc Amer A 1:1120–1128
Schlereth KH, Tacke M (1990) The complex propagation constant of multilayer waveguides: an algorithm for a personal computer. IEEE J Quantum Electron 26:626–630
Sun L, Marhic E (1991) Numerical study of attenuation in multilayer infrared waveguides by the circle-chain convergence method. J Opt Soc Amer B 8:478–483
Ghatak AK, Thyagarajan K, Shanoy MR (1987) Numerical analysis of planar optical waveguides using matrix approach. J Light Technol 5:660–667
Anemogiannis E, Member S, Glytsis EN, Member S (1992) Multilayer waveguides: efficient numerical analysis of general structures. J Light Technol 10:1344–1351
Maier SA (2006) Plasmonic field enhancement and SERS in the effective mode volume picture. Opt Express 14:1957–1964
Ruppin R (2002) Electromagnetic energy density in a dispersive and absorptive material. Physics Letters A 299:309–312
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Physical Rev B 6:4370–4379
Weber MJ (2003) Handbook of optical materials. CRC, Boca Raton
Barnes WL (2006) Surface plasmon–polariton length scales: a route to sub-wavelength optics. J Optics A: Pure Applied Optics 8:S87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talafi Noghani, M., Vadjed Samiei, M.H. Analysis and Optimum Design of Hybrid Plasmonic Slab Waveguides. Plasmonics 8, 1155–1168 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9526-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9526-x