Abstract
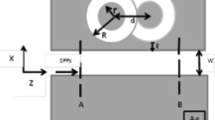
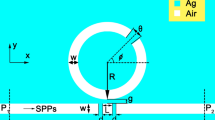
A metal-insulator-metal (MIM) waveguide consisting of two stub resonators and a ring resonator is proposed, which can be used as refractive index sensor and stop-band filter at the same time. The transmission characteristics of the MIM waveguide structure is studied by the finite element method (FEM). The simulation results show that the typical Fano profile and multiple Fano resonances can be achieved. According to the analysis, the range of stop-band and the multiple Fano resonance positions can be adjusted flexibly and independently by adjusting the aggregate parameters of the MIM waveguide structure. Moreover, it is also found that the two Fano resonances at both ends of the stop band can be determined by the two stubs, and the other two Fano resonances are regulated by the ring resonator. In addition, the spectral position of multi-Fano resonances is highly sensitive to the radius of the ring resonator and the refractive index of the filled medium. The maximum sensitivity and the figure of merit (FOM) of the MIM waveguide structure are 1650 nm/RIU and 117.8 in magnitude, respectively. These results provide a reference for implementing high-sensitivity sensors and large-bandwidth stop-band filter in MIM waveguide coupling systems based on multi-Fano resonance effect.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the plots within this paper can be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
There is no code in this paper.
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424:824–830
Kano H, Mizuguchi S, Kawata S (1998) Excitation of surface-plasmon polaritons by a focused laser beam. Josa B 15:1381–1386
Hooper IR, Sambles JR (2002) Dispersion of surface plasmon polaritons on short-pitch metal gratings. Phys Rev B 65:165432
Zhang T, Wang J, Liu Q, Zhou JZ, Dai J, Han X, Li JQ, Zhou Y, Xu K (2019) Efficient spectrum prediction and inverse design for plasmonic waveguide systems based on artificial neural networks. Photonics Res 7:368
Dickson RM, Lyon LA (2000) Unidirectional plasmon propagation in metallic nanowires. J Phys Chem B 104:6095–6098
Gramotnev DK, Pile DFP (2004) Single-mode subwavelength waveguide with channel plasmon-ploartons in triangular grooves on a metal surface. Appl Phys Lett 85:6323–6325
Nikolajsen T, Leosson K, Bozhevolnyi SI (2005) In-line extinction modulator based on long-range surface plasmon polaritons. Opt Commun 244:455–459
Han Z, Forsberg E, He S (2007) Surface plasmon Bragg gratings formed in metal-insulator-metal waveguides. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 19:91–93
Nikolajsen T, Leosson K, Bozhevolnyi S (2004) Surface plasmon polariton based modulators and switches operating at telecom wavelengths. Appl Phys Lett 85:5833–5835
Lin XS, Huang XG (2009) Numerical modeling of a teeth-shaped nano-plasmonic waveguide filter. J Opt Soc Am B 26:1263–1268
Zhai X, Wang L, Wang LL, Li XF, Huang WQ, Wen SH, Fan DY (2013) Tuning bandgap of a double-tooth-shaped MIM waveguide filter by control widths of the teeth. J Opt 15:055008
Zhu JH, Q. Wang J, Shum P, (2011) A nanoplasmonic high-pass wavelength filter based on a metal-insulator-metal circuitous waveguide. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 10:1357–1361
Zafar R, Salim M (2014) Wideband slow light achievement in MIM plasmonic waveguide by controlling Fano resonance. Infrared Phys Technol 67:25–29
Yang ZJ, Hao ZH, Lin HQ, W QQ, (2014) Plasmonic Fano resonances in metallic nanorod complexes. Nanoscale 6:4985–4997
Chen F, Yao DZ (2016) Realizing of plasmon Fano resonance with a metal nanowall moving along MIM waveguide. Opt Commun 369:72–78
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kastel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8:758–762
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Sonnichsen C, Giessen H (2010) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10:1103–1107
Guo ZC, Wen KH, Hu QY, Lai WH, Fang YH (2018) Plasmonic multichannel refractive index sensor based on subwavelength tangent-ring metal–insulator–metal waveguide. Sensors 18:1348
Luk’Yanchuk B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials[J]. Nat Mater 9:707–715
Hu F, Yi H, Zhou Z (2011) Band-pass plasmonic slot filter with band selection and spectrally splitting capabilities. Opt Express 19:4848–4855
Kwon SH (2013) Deep subwavelength-scale metal–insulator–metal plasmonic disk cavities for refractive index sensors. IEEE Photonics J 5:4800107
Shi XL, Ma LJ, Zhang ZD, Tang Y, Zhang YJ, Han JQ, Sun YQ (2018) Dual Fano resonance control and refractive index sensors based on a plasmonic waveguide-coupled resonator system. Opt Commun 427:326–330
Zhang Y, Cui M (2019) Refractive index sensor based on the symmetric MIM waveguide structure. J Electron Mater 48:1005–1010
Li SL, Zhang YY, Song XK, Wang YL, Yu L (2016) Tunable triple Fano resonances based on multimode interference in coupled plasmonic resonator system. Opt Express 24:15351–15361
Zhang ZD, Wang RB, Zhang ZY, Tang J, Wang WD, Xue CY, Yan SB (2017) Electromagnetically induced transparency and refractive index sensing for a plasmonic waveguide with a stub coupled ring resonator. Plasmonics 12:1007–1013
Luo SW, Li B, Xiong DS, Zuo DL, Wang XB (2016) A high performance plasmonic sensor based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide coupled with a double-cavity structure. Plasmonics 12:223–227
Zhan ZD, Luo L, Xue CY, Zhang WD, Yan SB (2016) Fano resonance based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide-coupled double rectangular cavities for plasmonic nanosensors. Sensors 16:642
Zhu JH, Wang QJ, Shum P, Huang XJ (2011) A simple nanometeric plasmonic narrow-band filter structure based on metal–insulator–metal waveguide. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 10:1371–1376
Maxime C, Brulé T, Stacey L, Wenli C, Mitradeep S, Benjamin C, Karen F, Wei P, Michael C, Jean-Francois M (2017) High figure of merit (FOM) of Bragg modes in Au-coated nanodisk arrays for plasmonic sensing. Small 13:1700908
Yan ZD, Wen XG, Gu P, Zhong H, Zhan P, Chen Z, Wang ZL (2017) Double Fano resonances in individual metallic nanostructure for high sensing sensitivity. Nanotechnology 28:475203
Zhang Y, Zhen YR, Neumann O, Day JK, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2014) Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering with single-molecule sensitivity using a plasmonic Fano resonance. Nat Commun 5:4424
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Foundation of China (Grant No. 11604198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology: Chen Zhou, Yiping Huo*. Review and editing: Yiyuan Guo and Qiqiang Niu. Writing—original draft preparation: Chen Zhou. Review, editing, supervision. Funding acquisition: Yiping Huo*. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Huo, Y., Guo, Y. et al. Tunable Multiple Fano Resonances and Stable Plasmonic Band-Stop Filter Based on a Metal-Insulator-Metal Waveguide. Plasmonics 16, 1735–1743 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01437-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01437-2