Abstract
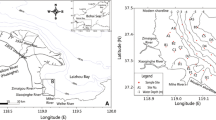
There are 71 surface sediment samples collected from the eastern Beibu Gulf. The moment parameters (i.e. mean size, sorting and skewness) were obtained after applying grain size analysis. The geostatistical analysis was then applied to study the spatial autocorrelation for these parameters; while range, a parameter in the semivariogram that meters the scale of spatial autocorrelation, was estimated. The results indicated that the range for sorting coefficient was physically meaningful. The trend vectors calculated from grain size trend analysis model were consistent with the annual ocean circulation patterns and sediment transport rates according to previous studies. Therefore the range derived from the semivariogram of mean size can be used as the characteristic distance in the grain size trend analysis, which may remove the bias caused by the traditional way of basing on experiences or testing methods to get the characteristic distance. Hence the results from geostatistical analysis can also offer useful information for the determination of sediment sampling density in the future field work.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caeiro S, Painho M, Goovaerts P et al., 2003. Spatial sampling design for sediment quality assessment in estuaries. Environmental Modelling & Software, 18: 853–859.
Cai S Q, Long X M, Liu H L et al., 2006. Tide model evaluation under different conditions. Continental Shelf Research, 26: 104–112.
Cao D M, Fang G H, 1990. The numerical simulation of tides and currents in the Beibu Gulf. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 21(2): 105–113. (in Chinese)
Chappell A, Warren A, 2003. Spatial scales of 137Cs-derived soil flux by wind in a 25 km2 arable area of eastern England. Catena, 52: 209–234.
Chen L R, Zhang X R. Mineral assemblages and their distribution pattern of the sediments from the Beibu Gulf. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1986, 8(3): 340–346. (in Chinese)
Duman M, Avci M, Duman S et al., 2004. Surficial sediment distribution and net sediment transport pattern in Izmir Bay, western Turkey. Continental Shelf Research, 24: 965–981.
Fang G H, Kwok Y K, Yu K J et al., 1999. Numerical simulation of principal tidal constituents in the South China Sea, Gulf of Tonkin and Gulf of Thailand. Continental Shelf Research, 19: 845–869.
Felletti F, Bersezio R, Giudici M, 2006. Geostatistical simulation and numerical upscaling, to model ground-water flow in a sandy-gravel, braided river, aquifer analogue. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 76: 1215–1229.
Gao S, Collins M, 1991. A critique of the “McLaren Method” for defining sediment transport paths: Discussion. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 61(1): 143–146.
Gao S, Collins M, 1992. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain-size trends, based upon definition of “transport vectors”. Sedimentary Geology, 80: 47–60.
Gao S, Cheng P, Wang Y P et al., 2000. Characteristics of suspended sediment concentrations over the areas adjacent to Changjiang River Estuary, the summer of 1998. Marine Science Bulletin, 2(1): 14–24.
Gao S., Collins M, 2001. The use of grain size trends in marine sediment dynamics: A review. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 19: 265–271.
Gao S, Fang G H, Yu K J et al., 2001. Methodology for evaluating the stability of sandy seabed controlled by sediment movement, with an example of application. Studia Marina Sinica, 43: 25–37. (in Chinese)
Li S H, 1987a. Preliminary study on the Eulerian current in the Beibu Gulf. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 3: 8–14. (in Chinese)
Li S H, 1987b. Preliminary study on the tidal current in the Beibu Gulf. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 2(1): 22–29. (in Chinese)
Li Z H, Ke X K, 2000. Preliminary study on tidally-induced sediment fluxes of the Qiongzhou Strait. Marine Science Bulletin, 19(6): 42–49. (in Chinese)
Liu F S, Yu T C, 1980. Preliminary study on the current in the Beibu Gulf. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1: 9–14 (in Chinese)
Ma R H, Pu Y X, Ma X D, 2007. Mining Spatial Association Patterns from GIS Database. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese)
Maren D S, Hoekstra P, 2005. Dispersal of suspended sediments in the turbid and highly stratified Red River plume. Continental Shelf Research, 25: 503–519.
Matheron G, 1963. Principles of geostatistics. Economic Geology, 58: 1246–1266.
McLaren P, Bowles D, 1985. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distributions. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 55: 457–470.
Mear Y, Poizot E, Murata A et al., 2006. Fine-grained sediment spatial distribution on the basis of a geostatistical analysis: Example of the eastern Bay of the Seine (France). Continental Shelf Research, 26: 2335–2351.
Murraya C J, Leeb H J, Hampton M A, 2002. Geostatistical mapping of effluent-affected sediment distribution on the Palos Verdes shelf. Continental Shelf Research, 22: 881–897.
Poizot E, Mear Y, Thomas M et al., 2006. The application of geostatistics in defining the characteristic distance for grain size trend analysis. Computers & Geosciences, 32: 360–370.
Roux J P, O’Brien R D, Rios F et al., 2002. Analysis of sediment transport paths using grain-size parameters. Computers & Geosciences, 28: 717–721.
Sun H L, Huang W M, 2001. Three dimensional numerical simulation for tide and tidal current in the Beibu Gulf. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 23(2): 1–8. (in Chinese)
Sun H L, Huang W M, Zhao J S, 2001. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of tide-induced, wind-driven and thermohaline residual currents in the Beibu Gulf. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 32(5): 561–568. (in Chinese)
Tang D L, Kawamura H S, Lee M A et al., 2003. Seasonal and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a concentrations and water conditions in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea. Remote Sensing of Environment, 85: 475–483.
Tang T, Cai Q H, Pan W B, 2000. Application of geostatistics in freshwater ecology. Journal of Lake Sciences, 12(3): 280–288. (in Chinese)
Wang W J, 2000. Propagation of tidal waves and development of sea-bottom sand ridges and sand ripples in northern South China Sea. Tropic Oceanology, 19(1): 1–7. (in Chinese)
Wang Y P, Gao S, Jia J J, 2000. Sediment distribution and transport patterns in Jiaozhou Bay and adjoining areas. Acta Geographica Sinica, 55(4): 449–458. (in Chinese)
Xia H Y, Li S H, Shi M C, 2001. A 3-D numerical simulation of wind-driven currents in the Beibu Gulf. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 23(6): 11–23. (in Chinese)
Yang O, Liu C Z, 2002. Analysis on sediment transport patterns and sediment sources of north branch of Changjiang estuary. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2: 79–84. (in Chinese)
Zhao B R, Zhuang G W, Cao D M et al., 1995. Circulation, tidal residual currents and their effects on the sedimentations in the Bohai Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 26(5): 466–473. (in Chinese)
Zhao J S, Wang G Y, Chen Z S et al., 2001. A Research on the Efficient Application of the Marine Environment: On Beibu Gulf and the Seacoast of Guangxi. Beijing: China Ocean Press. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: Chinese Offshore Investigation and Assessment Project, No.908-01-ST09; State Student Innovation Training Project, No.SIT-05; Program for New Century Excellent Talents, No.NCET-06-0446; National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.J0630535
Author: Ma Fei (1987–), undergraduate student, specialized in geographical science.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, F., Wang, Y., Li, Y. et al. The application of geostatistics in grain size trend analysis: A case study of eastern Beibu Gulf. J. Geogr. Sci. 20, 77–90 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-010-0077-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-010-0077-1