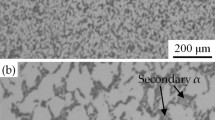
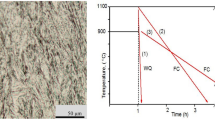
Abstract
Understanding the mechanism of high temperature deformation is important for controlling the forming quality of the titanium alloy forgings. In the present work, the flow softening mechanism in subtransus deformation of titanium alloys with equiaxed structure was investigated by interrupted isothermal compression tests. The results show that limited strain hardening followed by continuous flow softening occurs in high temperature deformation of a two-phase TA15 titanium alloy. The flow softening can not be rationalized by dynamic recrystallization. Instead, the increase of mobile dislocations during deformation is an important reason for flow softening. The grain boundaries (including the α-β interfaces) act as an important source for the generation of mobile dislocations. The continuous flow softening results from the significant deformation heterogeneity in subtransus working.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lütjering G, Williams JC (2007) Titanium, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Yang H, Fan XG, Sun ZC et al (2011) Recent developments in plastic forming technology of titanium alloys. Sci China Tech Sci 54:490–501
Ding R, Guo ZX, Wilson A (2002) Microstructure evolution of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during thermomechanical processing. Mater Sci Eng A 327:233–245
Ding R, Guo ZX (2004) Microstructural evolution of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during β-phase processing: experimental and simulative investigations. Mater Sci Eng A 365:172–179
Bao R, Huang X, Cao C (2006) Deformation behavior and mechanism of Ti-1023 alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 16:274–280
Duan YP, Li P, Xue KM et al (2007) Flow behavior and microstructure evolution of TB8 alloy during hot deformation process. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 17:1199–1204
Furuhara T, Poorganji B, Abe H et al (2007) Dynamic recovery and recrystallization in titanium alloys by hot deformation. JOM 59:64–67
Momeni A, Abbasi SM (2010) Effect of hot working on flow behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy in single phase and two phase regions. Mater Des 31:3599–3604
Zong YY, Shan DB, Lu Y (2006) Microstructural evolution of a Ti-4.5Al-3Mo-1V alloy during hot working. J Mater Sci 41:3753–3760
Sen I, Ramamurty U (2010) High-temperature (1023 K to 1273 K [750 °C to 1000 °C]) plastic deformation behavior of B-modified Ti-6Al-4V alloys: temperature and strain rate effects. Metall Mater Trans A 41:2959–2969
Zhao ZL, Guo HZ, Wang XC et al (2009) Deformation behavior of isothermally forged Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr-4Mo-4Cr powder compact. J Mater Process Technol 209:5509–5513
Jackson M, Dashwood R, Christodoulou L et al (2005) The microstructural evolution of near beta alloy Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al during subtransus forging. Metall Mater Trans A 36:1317–1327
Jackson M, Jones NG, Dye D et al (2009) Effect of initial microstructure on plastic flow behaviour during isothermal forging of Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al. Mater Sci Eng A 501:248–254
Semiatin SL, Seetharaman V, Weiss I (1999) Flow behavior and globularization kinetics during hot working of Ti–6Al–4V with a colony alpha microstructure. Mater Sci Eng A 263:257–271
Miller RM, Bieler TR, Semiatin SL (1999) Flow softening during hot working of Ti-6Al-4V with a lamellar colony microstructure. Scripta Mater 40:1387–1393
Semiatin SL, Bieler TR (2001) The effect of alpha platelet thickness on plastic flow during hot working of Ti-6Al-4V with a transformed microstructure. Acta Mater 49:3565–3573
Semiatin SL, Bieler TR (2001) Effect of texture and slip mode on the anisotropy of plastic flow and flow softening during hot working of Ti-6Al-4V. Metall Mater Trans A 32:1787–1799
Jones NG, Jackson M (2011) On mechanism of flow softening in Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–3Cr. Mater Sci Technol 27:1025–1032
Jones NG, Dashwood RJ, Dye D et al (2009) The flow behavior and microstructural evolution of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr during subtransus isothermal forging. Metall Mater Trans A 40:1944–1954
Song HW, Zhang SH, Cheng M (2010) Subtransus deformation mechanisms of TC11 titanium alloy with lamellar structure. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 20:2168–2173
Seshacharyulu T, Medeiros SC, Frazier WG et al (2002) Microstructural mechanisms during hot working of commercial grade Ti-6Al-4V with lamellar starting structure. Mater Sci Eng A 325:112–125
Seshacharyulu T, Medeiros SC, Morgan JT et al (2000) Hot deformation and microstructural damage mechanisms in extra-low interstitial (ELI) grade Ti–6Al–4V. Mater Sci Eng A 279:289–299
Wanjara P, Jahazi M, Monajati H et al (2005) Hot working behavior of near-α alloy IMI834. Mater Sci Eng A 396:50–60
Wanjara P, Jahazi M, Monajati H et al (2006) Influence of thermomechanical processing on microstructural evolution in near-α alloy IMI834. Mater Sci Eng A 416:300–311
Zhao Y, Li B, Zhu Z et al (2010) The high temperature deformation behavior and microstructure of TC21 titanium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 527:5360–5367
Jones NG, Dashwood RJ, Dye D et al (2008) Thermomechanical processing of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr. Mater Sci Eng A 490:369–377
Majorell A, Srivatsa S, Picu RC (2002) Mechanical behavior of Ti-6Al-4V at high and moderate temperatures—part I: experimental results. Mater Sci Eng A 326:297–305
Seshacharyulu T, Medeiros SC, Frazier WG et al (2000) Hot working of commercial Ti-6Al-4V with an equiaxed α-β microstructure: materials modeling considerations. Mater Sci Eng A 284:184–194
Niu Y, Hou H, Li M et al (2008) High temperature deformation behavior of a near alpha Ti600 titanium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 492:24–28
Huang LJ, Geng L, Li AB et al (2009) Characteristics of hot compression behavior of Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si alloy with an equiaxed microstructure. Mater Sci Eng A 505:136–143
Vo P, Jahazi M, Yue S et al (2007) Flow stress prediction during hot working of near-α titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 447:99–110
Vo P, Jahazi M, Yue S (2008) Recrystallization during thermomechanical processing of IMI834. Metall Mater Trans A 39:2965–2980
Fan XG, Yang H, Gao PF (2011) Deformation behavior and microstructure evolution in multistage hot working of TA15 titanium alloy: on the role of recrystallization. J Mater Sci 46:6018–6028
Zong YY, Shan DB, Xu M et al (2009) Flow softening and microstructural evolution of TC11 titanium alloy during hot deformation. J Mater Process Technol 209:1988–1994
Liu Y, Zhu J, Wang Y et al (2008) Hot compressive deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of Ti-6Al-2Zr-1Mo-1V alloy at 1073 K. Mater Sci Eng A 490:113–116
Jia WJ, Zeng WD, Zhou YG et al (2011) High-temperature deformation behavior of Ti60 titanium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 528:4068–4074
Sun SD, Zong YY, Shan DB et al (2010) Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of TC4 titanium alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 20:2181–2184
Fan XG, Yang H (2011) Internal-state-variable based self-consistent constitutive modeling for hot working of two-phase titanium alloys coupling microstructure evolution. Int J Plast 27:1833–1852
Zeng Z, Zhang Y, Jonsson S (2009) Deformation behaviour of commercially pure titanium during simple hot compression. Mater Des 30:3105–3111
Semiatin SL, Bieler TR (2001) Effect of texture changes on flow softening during hot working of Ti-6Al-4V. Metall Mater Trans A 32:1871–1875
Fan XG, Yang H, Gao PF (2013) Prediction of constitutive behavior and microstructure evolution in hot deformation of TA15 titanium alloy. Mater Des 51:34–42
Zahiri SH, Davies CHJ, Hodgson PD (2005) A mechanical approach to quantify dynamic recrystallization in polycrystalline metals. Scripta Mater 52:299–304
Iza-Mendia A, Piñol-Juez A, Urcola JJ et al (1998) Microstructural and mechanical behavior of a duplex stainless steel under hot working conditions. Metall Mater Trans A 29:2975–2986
Piñol-Juez A, Iza-Mendia A, Gutiérrez I (2000) δ/γ interface boundary sliding as a mechanism for strain accommodation during hot deformation in a duplex stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans A 31:1671–1677
Balancin O, Hoffmann WAM, Jonas JJ (2000) Influence of microstructure on the flow behavior of duplex stainless steels at high temperatures. Metall Mater Trans A 31:1353–1364
Júnior AMJ, Reis GS, Balancin O (2011) Influence of the microstructure on the plastic behaviour of duplex stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng A 528:2259–2264
Hull D, Bacon DJ (2011) Introduction to dislocations, 5th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Burlington, pp 220–227
Johnston WG (1962) Yield points and delay times in single crystals. J Appl Phys 33:2719–2730
Philippart I, Rack HJ (1998) High temperature dynamic yielding in metastable Ti-6.8Mo-4.5F-1.5Al. Mater Sci Eng A 243:196–200
Semiatin SL, Montheillet F, Shen G et al (2002) Self-consistent modeling of the flow behavior of wrought alpha/beta titanium alloys under isothermal and nonisothermal hot-working conditions. Metall Mater Trans A 33:2719–2727
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (50935007, 51205317), the National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB731701), and 111 Project (B08040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Yang, H. & Gao, P. The mechanism of flow softening in subtransus hot working of two-phase titanium alloy with equiaxed structure. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 2859–2867 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0332-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0332-4