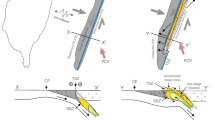
Abstract
Although tectonic models were presented for exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks during the continental collision, there is increasing evidence for the decoupling between crustal slices at various depths within deeply subducted continental crust. This lends support to the multi-slice successive exhumation model of the UHP metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogen. The available evidence is summarized as follows: (1) the low-grade metamorphic slices, which have geotectonic affinity to the South China Block and part of them records the Triassic metamorphism, occur in the northern margin of the Dabie-Sulu UHP metamorphic zone, suggesting decoupling of the upper crust from the underlying basement during the initial stages of continental subduction; (2) the Dabie and Sulu HP to UHP metamorphic zones comprise several HP to UHP slices, which have an increased trend of metamorphic grade from south to north but a decreased trend of peak metamorphic ages correspondingly; and (3) the Chinese Continental Science Drilling (CCSD) project at Donghai in the Sulu orogen reveals that the UHP metamorphic zone is composed of several stacked slices, which display distinctive high and low radiogenic Pb from upper to lower parts in the profile, suggesting that these UHP crustal slices were derived from the subducted upper and middle crusts, respectively. Detachment surfaces within the deeply subducted crust may occur either along an ancient fault as a channel of fluid flow, which resulted in weakening of mechanic strength of the rocks adjacent to the fault due to fluid-rock interaction, or along the low-viscosity zones which resulted from variations of geotherms and lithospheric compositions at different depths. The multi-slice successive exhumation model is different from the traditional exhumation model of the UHP metamorphic rocks in that the latter assumes the detachment of the entire subducted continental crust from the underlying mantle lithosphere and its subsequent exhumation as a whole. This also reveals the difference between the continental subduction and oceanic subduction. In addition, several important proposals concerning the multi-slice successive exhumation model are made for further studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chopin C. Coesite and pure pyrope in high grade blueschists of the western Alps: A first record and some consequences. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 1984, 86: 107–118
Smith D C. Coesite in clinopyroxene in the Caledonides and its implications for geodynamics. Nature, 1984, 310: 641–644
Xu Z Q. Etude tectonique et microtectonique de la chaine paleozoique et triasique des Qinlings (Chine).These de doctorat, Univ Sci Tech Languedoc, Montpeuier, 1987
Okay A I, Xu S, Sengor A M C. Coesite from the Dabie Shan eclogites, central China. Eur J Mineral, 1989, 1: 595–598
Wang X, Liou J G, Mao H K. Coesite-bearing eclogites from the Dabie Mountains in central China. Geology, 1989, 17: 1085–1088
Sobolev N V, Shatsky V S. Diamond inclusions in garnets from metamorphic rocks: a new environment for diamond formation. Nature, 1990, 343: 742–746
Xu S T, Okay A.I., Ji S., et al. Diamonds from the Dabie Shan metamorphic rocks and its implication for tectonic setting. Science, 1992, 256: 80–82
Okay A I, Sengör A M C. Evidence for intracontinental thrust-related exhumation of the ultrahigh-pressure rocks in China. Geology, 1992, 20: 411–414
Chemenda A I, Mattauer M, Bokun A N. Continental subduction and a mechanism for exhumation of high-pressure metamorphic rocks: new modelling, field data from Oman. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1996, 143: 173–182
Maruyama S, Liou J G, Zhang R. Tectonic evolution of the ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) and high-pressure (HP) metamorphic belts from central China. The Island Arc, 3: 112–121
Faure M, Lin W, Shu L, et al. Tectonics of the Dabieshan (eastern China) and possible exhumation mechanism of ultra high-pressure rocks. Terra Nova, 1999, 11: 251–258
Zhong Z Q, Suo S T, You Z D. Extensional tectonic framework of post high and ultrahigh pressure metamorphism in Dabieshan, China (in Chinese). Earth Sci-J China Univ Geosci, 1998, 23(3): 225–229
Suo S T, Zhong Z Q, You Z D. Extensional deformation of post ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and exhumation process of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks in the Dabie massif, China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2000, 43(3): 225–236
Ernst W G, Maruyama S, Wallis S. Buoyancy-driven, rapid exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphosed continental crust. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 1997, 94: 9532–9537
Dong S W, Chen J, Huang D. Differential exhumation of tectonic units and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Dabie Mountains, China. The Island Arc, 1998, 7: 174–183
Wang Q C, Cong B L. Exhumation of UHP Terranes: A case study from the Dabie Mountains, eastern China. Int Geol Rev, 1999, 41: 994–1004
Hacker B R, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, et al. Exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in east central China: Late Triassic-Early Jurassic tectonic unroofing. J Geophys Res, 2000, 105(B6): 13339–13364
Ratschbacher L, Hacker B R, Webb L E, et al. Exhumation of the ultrahigh-pressure continental crust ineast-central China: Cretaceous and Cenozoic unroofing and the Tan-Lu fault. J Geophys Res, 2000, 105: 13303–13338
Liu X C, Jahn B M., Liu D, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of a metagabbro and eclogites from western Dabieshan (Hong’an Block), China, and its tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 2004, 394: 171–192
Chemenda A I, Mattauer M, Malavieille J, et al. A mechanism for syn-collisional rock exhumation and associated normal faulting: Results from physical modeling. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1995, 132: 225–232
Massonne H J. Involvement of crustal material in delamination of the lithosphere after continent-continent collision. Internat Geol Rev, 2005, 47: 792–804
Zuber M T. Folding a jelly sandwich. Nature, 1994, 371: 650–651
Li S G, Huang F, Zhou H, et al. U-Pb isotopic compositions of the ultrahigh pressure metamorphic (UHPM) rocks from Shuanghe and gneisses from Northern Dabie zone in the Dabie Mountains, central China: Constraint on the exhumation mechanism of UHPM rocks. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2003, 46: 200–209
Li S G, Li Q L, Hou Z, et al. Cooling history and exhumation mechanism of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Dabie Mountains, central China (in Chinese). Acta Petrol Sin, 2005, 21: 1117–1124
Liu Y and Li S. Lower crustal rocks from the Dabie Mountains and their deep subduction (in Chinese). Acta Petrol Sin, 2005, 21(4): 1059–1066
Xu Z Q, Zeng L S, Liang F H, et al. A dynamic model for sequential subduction and exhumation of acontinental slab: Age constraints on the timing of exhumation of the Sulu HP-UHP metamorphic terrane (in Chinese). Acta Petrol et Mineral, 2005, 24: 357–368
Xu Z Q, Zeng L S, Liu F L, et al. Polyphase subduction and exhumation of the Sulu high-pressure-ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terrane. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2006, 403: 792–113
Liu Y C, Li S G, Xu S T. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating for gneiss in northern Dabie high T/P metamorphic zone, central China: Implication for decoupling within subducted continental crust. Lithos, 2007, 96: 170-185
Zheng Y F, Zhou J B, Wu Y B, et al. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: a passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction. Int Geol Rev, 2005, 47: 851–871
Tang J, Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating, C and O isotopes for impure marbles from the Jiaobei terrane in the Sulu orogen: Implication for tectonic affinity. Precambrian Res, 2006, 144: 1–18
Liu, Y C, Li S G, Gu X F, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating for olivine gabbro at Wangmuguan in the Beihuaiyang zone and its geological significance. Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51: 2500–2506
Zhou J B, Zheng Y F, Li L, et al. Accretionary wedge of the subduction of the Yangtze plate (in Chinese). Acta Geol Sin, 2001, 75: 338–352
Zhou J B, Zheng Y F, Wu Y B. Zircon U-Pb ages for Wulian granites in northwest Sulu and their tectonic implications. Chin Sci Bull, 2003, 48(4): 379–384
Zhou J B, Liu J, Zheng C. Geological Genesis and Tectonic Implications of Low-grade Metamorphic Rocks in Sulu Orogenic Belt (in Chinese). Acta Geol Sin, 2005, 79(4): 475–486
Xie Z, Chen J, Zhang X, et al. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in North Huaiyang region (in Chinese). Acta Geosci Sin, 2002, 23: 517–520
Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, Zhao Z F, et al. Finding of Neoproterozoic low-18O igneous rocks in the northern margin of the Dabie orogen. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(14): 1536–1538
Jiang L L, Wolfgang S, Chen F, et al. U-Pb zircon ages for the Luzhenguan Complex in northern part of the eastern Dabie orogen. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2005, 48: 1357–1367
Wu Y B, Zheng Y F, Tang J, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating of water-rock interaction during Neoproterozoic rift magmatism in South China. Chem Geol, 2007, 246: 65–86
Zhou J B, Wilde S A, Zhao G C, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Wulian Complex: defining the boundary between the North and South China Cratons in the Sulu Orogenic Belt, China. Precambrian Res, 2008, 162: 559–576
Chu X L, Wolfgang Todt, Zhang Q R, et al. U-Pb zircon age for the Nanhua-Sinian boundary. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50: 716–718
Condon D, Zhu M, Bowring S, et al. U-Pb Ages from the Neoproterozoic Doushantuo Formation, China. Science, 2005, 308: 98–98
Yin C Y, Tang F, Liu Y, et al. U-Pb zircon age from the base of the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation in the Yangtze Gorges, South China: constraint on the age of Marinoan glaciation. Episodes, 2005, 28: 48–49
Rowley D B, Xue F, Tucker R D, et al. Ages of ultrahigh pressure metamorphism and protolith orthogneisses from the eastern Dabie Shan: U/Pb zircon geochronology. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1997, 151: 191–203
Hacker B R, Ratschbacher L, Webb L E, et al. Zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie orogen, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1998, 161: 215–230
Zheng Y F, Fu B, Gong B, et al. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth Sci Rev, 2003, 62: 105–161
Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, Chen F K, et al. Zircon U-Pb and oxygen isotope evidence for a large-scale 18O depletion event in igneous rocks during the Neoproterozoic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2004, 68: 4145–4165
Chen L, Ma C, She Z, et al. Liulin gabbro in the Beihuaiyang tectonic belt of the Dabie orogen:A witness of the Late Neoproterozoic rifting event (in Chinese). Earth Sci-J China Univ Geosci, 2006, 31: 578–584
Ye B D, Jian P, Xu J, et al. The Sujiahe Terrene Collage Belt and Its Constitution and Evolutionalong the North Hillslope of the Tongbai-Dabie Orogenic Belt (in Chinese). Wuhan: Press of China University of Geosciences, 1993. 1–81
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Jiang L L, et al. Architecture and Kinematics of the Dabie Mountains Orogen (in Chinese). Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2002. 1–133
Chen J, Dong S, Deng Y, et al. Interpretation of K-Ar ages of the Dabie orogen — A differential uplifted block. Geol Rev (in Chinese), 1993, 39(1): 17–22
Ratschbacher L, Franz L, Enkelmann E, et al. The Sino-Korean-Yangtze suture, the Huwan detachment, and the Paleozoic-Tertiary exhumation of (ultra) high-pressure rocks along the Tongbai-Xinxian-Dabie Mountains. In eds. Hacker B R, McClelland W C, Liou J G, Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic: Deep continental subduction. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2006, 403: 45–77
Dong S W, Wang X and Huang D. Discovery of low-grade metavolcanic rock sheets within UHP belt in Dabieshan and its implications. Chin Sci Bull, 1997, 42: 1199–1203
Cliff R A. Isotopic dating in metamorphic belt. J Geol Soc London, 1985, 142: 97–110
Mezger K and Krogstad E J. Interpretation of discordant U-Pb zircon ages: A evaluation. J Metamorph Geol, 1997, 15: 127–140
Liu Y C, Li S G, Gu X F, et al. Ultrhigh-pressure eclogite transformed from mafic granulite in the Dabie orogen. J Metamorph Geol, 2007, 25: 975–989
Li S G, Huang F, Nie Y, et al. Geochemical and geochronological constrains on the suture location between the North and South China Blocks in the Dabie orogen, central China. Phys Chem the Earth (A), 2001, 26: 655–672
Zhong Z Q, Suo S T, Zhang H, et al. Major constituents and texture of the Tongbai-Dabie collisional orogenic belt. Earth Sci-J Chin Univ Geosc (in Chinese), 2001, 26(6): 560–567
Li X P, Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, et al. Low-T eclogite in the Dabie terrane of China: petrological and isotopic constrains on fluid activity and radiometric dating. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 2004, 148: 443–470
Liu Y C, Li S G, Xu S T, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of eclogites from the northern Dabie Mountains, central China. J Asian Earth Sci, 2005, 25: 431–443
Li S G, Liu D L, Chen Y, et al. The Sm-Nd isotopic age of coesitebearing eclogite from the Southern Dabie Mountains. Chin Sci Bull, 1992, 37: 1638–1641
Li S G, Xiao Y L, Liu D, et al. Collision of the North China and Yangtze blocks and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites: Timing and processes. Chem Geol, 1993, 109: 89–111
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Su W, et al. Discovery of the eclogite and its petrography in the Northern Dabie Mountains. Chin Sci Bull, 2000, 45(3): 273–278
Liu Y C, Xu S T, Li S G, et al. Distribution and metamorphic P-T condition of the eclogites from the mafic-ultramafic belt in the northern part of the Dabie Mountains (in Chinese). Acta Geol Sin, 2001, 75: 385–395
Tsai C H, Liou J G. Eclogite-facies relics and inferred ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the North Dabie Complex, central-eastern China. Am Mineral, 2000, 85: 1–8
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Chen G, et al. New finding of micro-diamonds in eclogites from Dabie-Sulu region in central-eastern China. Chin Sci Bull, 2003, 48: 988–994
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Chen G, et al. Microdiamonds, their classification and tectonic implications for the host eclogites from the Dabie and Su-Lu regions in central eastern China. Mineral Mag, 2005, 69: 509–520
Malaspina N, Hermann J, Scambelluri M, et al. Multistage metasomatism in ultrahigh-pressure mafic rocks from the North Dabie Complex (China). Lithos, 2006, 90: 19–42
Liu Y C, Li S G, Xu S T, et al. U-Pb zircon ages of the eclogite and tonalitic gneiss from the northern Dabie Mountains, China and multiovergrowths of metamorphic zircons (in Chinese). Geol J Chin Univ, 2000, 6: 417–423
Xie Z, Chen J F, Zhang X, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating of gneiss from Shizhuhe in North Dabie and its geologic implications (in Chinese). Acta Petrol Sin, 2001, 17(1): 139–144
Ge N J, Xia Q K, Wu Y, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages of Yanzihe gneiss from northern Dabie, China: evidence for Triassic metamorphism (in Chinese). Acta Petrol Sin, 2003, 19(3): 513–516
Xie H, Dong S, Liu X. Geochemical characteristics and U-Pb zircon daying of Dashanken monzonitic granitic gneiss in northeastern Dabie Mountains (in Chinese). Adv Earth Sci, 2003, 18(2): 192–197
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Jiang L L, et al. Tectonic Regime and Evolution of Dabie Mountains (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1994. 1–175
Cong B L. Ultrahigh-pressure Metamorphic Rocks in the Dabieshan-Sulu Region of China. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. 1–224
Castelli D, Rolfo F, Compagnoni R, et al. Metamorphic veins with kyanite, zoisite and omphacite in the Zhu-Jia-Chong eclogite Dabie Shan, China. The Island Arc, 1998, 7: 159–173
Xiao Y L, Hoefs J, van den Kerkhof A M, et al. Geochemical constraints of the eclogite and granulite facies metamorphism as recognized in the Raobazhai complex from North Dabie Shan, China. J Metamorph Geol, 2001, 19: 3–19
Xiao Y L, Hoefs J, van den Kerkhof A M, et al. Fluid History during HP and UHP Metamorphism in Dabie Shan, China: Constraints from Mineral Chemistry, Fluid Inclusions, and Stable Isotopes. J Petrol, 2002, 43: 1505–1527
Liu Y C, Xu S T, Li S G, et al. Tectonic affinity, T-t path and uplift trajectory of eclogites from northern Dabie Mountains, centraleastern China. J Chin Univ Geosci, 2003, 14: 28–33
Liu Y C, Xu S T, Li S G, et al. Eclogite from the subducted lower crust of the Yangtze plate within the Luotian dome and its geological implication (in Chinese). Earth Sci-J Chin Univ of Geosci, 2005, 30(1): 71–77
Wang X M, Liou J G, Maruyama S. Coesite-bearing eclogites from the Dabie Mountains, central China: petrogenesis, P-T path and implications for regional tectonics. J Geol, 1992, 100: 231–250
Okay A I. Petrology of diamond and coesite-bearing metamorphic terrane: Dabie Shan, China. Eur J Mineral, 1993, 5: 659–676
Zhai M G, Cong B L, Zhao Z Y, et al. Petrologic-tectonic units in the coesite-bearing metamorphic terrain of the Dabie Mountains, central China and their geotectonic implication. J SE Geosci, 1995, 11(1): 1–13
Rolfo F, Compagnoni R, Xu S, et al. First report of felsic whiteschist in the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt of Dabie Shan, China. Eur J Mineral, 2000, 12: 883–898
Rolfo F, Compagnoni R, Wu W, et al. A coherent lithostratigraphic unit in the coesite-eclogite complex of Dabie Shan, China: geologic and petrologic evidence. Lithos, 2004, 73: 71–94
Okay A I, Sengör A M C. Tectonics of an ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terrane: the Dabie Shan/Tongbai orogen, China. Tectonics, 1993, 12: 1320–1334
Zartman R E. Plumbotectonics—the model. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75: 135–162
Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical geodynamics. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci, 1986, 14: 493–571
Zhang H F, Gao S, Zhang B, et al. Pb isotopic study on crustal structure of Dabie Mountains, central China (in Chinese). Geochmica, 2001, 30: 395–401
Li S G, Jagoutz E, Chen Y, et al. Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotope chronology of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks and their country rocks at Shuanghe in the Dabie Mountains, central China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2000, 64: 1077–1093
Ames L, Zhou G, Xiong B. Geochronology and isotopic character of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism with implications for the collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtze cratons, central China. Tectonics, 1996, 15: 472–489
Li S G, Li H, Chen Y, et al. Chronology of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the Dabie mountains and Su-Lu terrane: II. U-Pb isotope system of zircons (in Chinese). Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 1997, 27: 200–206
Chen D G, Isachen C, Zhi X, et al. Zircon U/Pb ages for gniess from Qianshan, Anhui. Chin Sci Bull, 2000, 45(8): 764–767
Ayers J C, Dunkle S, Gao S, et al. Constraints on timing of peak and retrograde metamorphism in the Dabie Shan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, east-central China, using U-Th-Pb dating of zircon and monazite. Chem Geol, 2002, 186: 315–331
Wan Y S, Li R W, Wilde S A, et al. UHP metamorphism and exhumation of the Dabie Orogen, China: Evidence from SHRIMP dating of zircon and monazite from a UHP granitic gneiss cobble from the Hefei Basin. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2005, 69: 4333–4348
Liu D Y, Jian P, Kröner A, et al. Dating of prograde metamorphic events deciphered from episodic zircon growth in rocks of the Dabie-Sulu UHP complex, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2006, 250: 650–666
Liu F L, Gerdes A, Liou J G, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating from Sulu-Dabie dolomitic marble, eastern China: constraints on prograde, ultrahigh-pressure and retrograde metamorphic ages. J Metamorph Geol, 2006, 24: 569–589
Wu Y B, Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F, et al. U-Pb, Hf and O isotope evidence for two episodes of fluid-assisted zircon growth in marble-hosted eclogites from the Dabie orogen. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2006, 70: 3743–3761
Wu Y B, Gao S, Zhang H, et al, Yuan H. Timing of UHP metamorphism in the Hong’an area, western Dabie Mountains, China: evidence from zircon U-Pb age, trace element and Hf isotope composition. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 2008, 155: 123–133
Zheng Y F, Gao T S, Wu Y B, et al. Fluid flow during exhumation of deeply subducted continental crust: zircon U-Pb age and O-isotope studies of a quartz vein within ultrahigh-pressure eclogite. J Metamorph Geol, 2007, 25: 267–283
Li Q L, Li S G, Hou Z H, et al. A combined study of SHRIMP U-Pb dating, trace element and mineral inclusions on high-pressure metamorphic overgrowth zircon in eclogite from Qinglongshan in the Sulu terrane. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50: 459–465
Liu F L, Xu Z, Liou J G, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb ages of ultrahigh-pressure and retrograde metamorphism of gneisses, south-western Sulu terrane, eastern China. J Metamorph Geol, 2004, 22: 315–326
Li Q L, Li S G, Zheng Y F, et al. A high precision U-Pb age of metamorphic rutile in coesite-bearing eclogite from the Dabie Mountains in central China: a new constraint on the cooling history. Chem Geol, 2003, 200: 255–265
Li S G, Wang S S, Chen Y Z, et al. Wxcess argon in phengite from eclogite: Evidence from dating of eclogite minerals by Sm-Nd, Rb-Sr and 40Ar/39Ar methods. Chem Geol, 1994, 112: 343–350
Yang J S, Wooden J L, Wu C L, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of coesitebearing zircon from the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks, Sulu terrane, east China. J Metamorph Geol, 2003, 21: 551–560
Li J Y, Yang T N, Chen W, et al. 40Ar/39Ar dating of deformation events and reconstruction of exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in Donghai, East China. Acta Geol Sin, 2003, 77: 155–168
Dong S W, Gao R, Cong B L, et al. Crustal structure of the Southern Dabie ultrahigh-pressure orogen and Yangtze foreland from deep seismic reflection profiling. Terra Nova, 2004, 16: 319–324
Dong F, Li S G, Li Q L, et al. Preliminary study of common Pb of UHP metamorphic rocks from CCSD (100 to 200 m): Evidence for decoupling within subducting continental crust. Acta Petrol Sin (in Chinese), 2006, 22: 1791–1798
Xiao Y L, Zhang Z M, Hoefs J, et al. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling Project: II. Oxygen isotope and fluid inclusion distributions through vertical sections. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 2006, 152: 443–458
Chen R X, Zheng Y F, Gong B, et al. Oxygen isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from 200–4000 m core samples of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling. Chem Geol, 2007, 242: 51–75
Meissner R, Mooney W. Weakness of the lower continental crust: a condition for delamination, uplift, and escape. Tectonophysics, 1998, 296: 47–60
Oxburg E R. Flake tectonics and continental collision. Nature, 1972, 239: 202–204
Hsü K J. Thin-skinned plate-tectonic model for collision-type orogenesis. Sci China Ser A-Math, 1981, 24: 100–110
Gerya T V, Yuen D A, Maresh W V. Thermomechanical modeling of slab detachment. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2004, 226: 101–116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. kzcx2-yw-131) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40572035, 40634023 and 40773013).
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, S. Detachment within subducted continental crust and multi-slice successive exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks: Evidence from the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 3105–3119 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0387-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0387-1