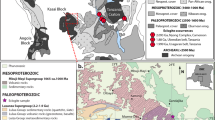
Abstract
High-temperature (HT; >850°C) metamorphism in continental collision orogens, particularly for those ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks, has become one of the remarkable topics in Earth science. It has bearing on the element and isotope behaviors of UHP rocks, their partial melting and related geodynamic effects during exhumation. In this paper, five representative continental collision orogens with typical HT/UHP rocks, including the Dabie orogen in China, the Kokchetav in Kazakhstan, the Caledonides in Greenland, the Rhodope in Greece, and the Erzgebirge in Germany are introduced, and their HT/UHP metamorphism and evolution processes are summarized. In addition, metamorphic P-T-t paths, multistage exhumation processes, and partial melting and preservation and retrogression of UHP index minerals during exhumation and their possible mechanisms are discussed. On this basis, the forthcoming key fields and scientific subjects of HT/UHP rocks within continental subduction channel are proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auzanneau E, Vielzeuf D, Schmidt M W. 2006. Experimental evidence of decompression melting during exhumation of subducted continental crust. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 152: 125–148
Babeyko A Y, Sobolev S V, Trumbull R B, et al. 2002. Numerical models of crustal scale convection and partial melting beneath the Altiplano-Puna plateau. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 199: 373–388
Baldwin J A, Brown M, Schmitz M D. 2007. First application of titanium-in-zircon thermometry to ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism. Geology, 35: 295–298
Baziotis I, Mposkos E, Perdikatsis V. 2008. Geochemistry of amphibolitized eclogites and cross-cutting tonalitic-trondhjemitic dykes in the Metamorphic Kimi Complex in East Rhodope (N.E. Greece): Implications for partial melting at the base of a thickened crust. Int J Earth Sci, 97: 459–477
Bourdon B, Tipper E T, Fitoussi C, et al. 2010. Chondritic Mg isotope composition of the Earth. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 74: 5069–5083
Braun I, Raith M, Kumar G R R. 1996. Dehydration-melting phenomena in leptynitic gneisses and the generation of leucogranites: A case study from the Kerala Khondalite belt, southern India. J Petrol, 37: 1285–1305
Brown M. 2004. The mechanism of melt extraction from lower continental crust of orogens. Trans R Soc Edinb-Earth Sci, 95: 35–48
Brown M. 2010. Melting of the continental crust during orogenesis: The thermal, rheological, and compositional consequences of melt transport from lower to upper continental crust. Can J Earth Sci, 47: 655–694
Brown M, Korhonen F J, Siddoway C S. 2011. Organizing melt flow through the crust. Element, 7: 261–266
Burg J P, Gerya T V. 2005. The role of viscous heating in Barrovian metamorphism of collisional orogens: Thermomechanical models and application to the Lepontine Dome in the Central Alps. J Metamorphic Geol, 23: 75–95
Carswell D A, Compagnoni R. 2003. Ultra-high pressure metamorphism. Eur Mineral Union Notes Mineral, 5: 1–508
Chopin C. 1984. Coesite and pure pyrope in high-grade blueschists of the western Alps: A first record and some consequence. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 86: 107–118
Chopin C. 2003. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism: Tracing continental crust into the mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 212: 1–14
Chopin C, Henry C, Michard A. 1991. Geology and petrology of the coesite-bearing terrane, Dora Maira massif, Western Alps. Eur J Mineral, 3: 263–291
Coleman R G, Wang X M. 1995. Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1–528
Cloos M, Shreve R. 1988a. Subduction-channel model of prism accretion, mélange formation, sediment subduction, and subduction erosion at convergent plate margins: 1. Background and Description. Pure Appl Geophys, 128: 455–500
Cloos M, Shreve R. 1988b. Subduction-channel model of prism accretion, mélange formation, sediment subduction, and subduction erosion at convergent plate margins: 2. Implications and Discussion. Pure Appl Geophys, 128: 501–544
Davies J, von Blankenburg F. 1995. Slab breakoff: A model of lithosphere detachment and its test in the magmatism and deformation of collisional orogens. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 129: 85–102
Dobrzhinetskaya L, Schweinehage R, Massonne H J, et al. 2002. Silica precipitates in omphacite from eclogite at Alpe Arami, Switzerland: Evidence of deep subduction. J Metamorph Geol, 20: 481–492
Dobretsov N L, Sobolev N V, Shatsky V S, et al. 1995. Geotectonic evolution of diamondiferous paragneisses, Kokchetav Complex, northern Kazakhstan: The geologic enigma of ultrahigh-pressure crustal rocks within a Paleozoic foldbelt. Island Arc, 4: 267–279
England P C, Thompson A. 1986. Some thermal and tectonic models for crustal melting in continental collision zones. In: Coward M P, Ries A C, eds. Collision Tectonics. Geol Soc Spec Publ, 19: 83–94
Ernst W G, Liou J G. 2008. High- and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism: Past results and future prospects. Am Mineral, 93: 1771–1786
Faure M, Lin W, Shu L, et al. 1999. Tectonics of the Dabieshan (Eastern China) and possible exhumation mechanism of ultra high-pressure rocks. Terra Nova, 11: 251–258
Ferry J M, Watson E B. 2007. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 154: 429–437
Galy A, Bar-Matthews M, Halicz L, et al. 2002. Mg isotope composition of carbonate: Insight from speleothem formation. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 201: 105–115
Gayk T, Kleinschrodt R, Langosch A, et al. 1995. Quartz exsolution in clinopyroxene of high-pressure granulite from the Munchberg Massif. Eur J Mineral, 7: 1217–1220
Ghiribelli B, Frezzotti M L, Palmeri R. 2002. Coesite in eclogites of the Lanterman range (Antarctica): Evidence from textural and Raman studies. Eur J Mineral, 14: 355–360
Gilotti J A, Ravna E K. 2002. First evidence for ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the North-East Greenland Caledonides. Geology, 30: 551–554
Gilotti J A, Nutman A P, Brueckner H K. 2004. Devonian to Carboniferous collision in the Greenland Caledonides: U-Pb zircon and Sm-Nd ages of high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 148: 216–235
Gilotti J A, McClelland W C. 2007. Characteristics of, and a tectonic model for, ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the overriding plate of the Caledonian Orogen. Int Geol Rev, 47: 777–797
Gilotti J A, Jones K A, Elvevold S. 2008. Caledonian metamorphic patterns in Greenland. In: Higgins A K, Gilotti J A, Smith M P, eds. The Greenland Caledonides: Evolution of the Northeast Margin of Laurentia. Geol Soc Am Mem, 202: 201–225
Gilotti J A, McClelland W C. 2011. Geochemical and geochronological evidence that the North-East Greenland ultrahigh-pressure terrane is Laurentian crust. J Geol, 119: 439–456
Gilotti J A. 2013. The realm of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism. Elements, 9: 255–260
Gilotti J A, McClelland W C, Wooden J L. 2014. Zircon captures exhumation of an ultrahigh-pressure terrane, North-East Greenland Caledonides. Gondwana Res, 25: 235–256
Groppo C, Rubatto D, Rolfo F, et al. 2010. Early Oligocene partial melting in the Main Central Thrust Zone (ArunValley, eastern Nepal Himalaya). Lithos, 118: 287–301
Groppo C, Rolfo F, Indares A. 2012. Partial melting in the Higher Himalayan Crystallines of Eastern Nepal: The effect of decompression and implications for the’ channel flow’ model. J Petrol, 53: 1057–1088
Groppo C, Rolfo F, Liu Y C, et al., 2015. P-T evolution of elusive UHP eclogites from the Luotian dome (North Dabie Zone, China): How far can the thermodynamic modeling lead us? Lithos, doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.11.013
Grove T L, Chatterjee N, Parman S W, et al. 2006. The influence of H2O on mantle wedge melting. Earth Plan Sci Lett, 249: 74–89
Gu X F, Liu Y C, Deng L P. 2013. Geochronology and petrogenesis of eclogite from the Luotian dome, North Dabie complex zone (central China), and their element and isotope behavior during exhumation (in Chinese). Chin Sci Bull, 22: 2132–2137
Guillot S, Hattori K, Agard P, et al. 2009. Exhumation processes in oceanic and continental subduction contexts: A review. In: Lallemand S, Funiciello F, eds. Subduction Zone Geodynamics. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. 175–205
Hacker B R, Liou J G. 1998. When Continent Collide: Geodynamics and Geochemistry of Ultrahigh-Pressure Rocks. Dordrecht: Kluw Acad Publ. 1–323
Hacker B R, Calvert A, Zhang R Y, et al. 2003. Ultrarapid exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure diamond-bearing metasedimentary rocks of the Kokchetav Massif, Kazakhstan? Lithos, 70: 61–75
He Y S, Li S G, Jochen Hoefs, et al. 2013. Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Early Cretaceous granitoids from the Dabie orogen: Constraints on the recycled lower continental crust. Lithos, 156–159: 204–217
Hemingway B S, Bohlen S R, Hankins W B, et al. 1998. Heat capacity and thermodynamic properties for coesite and jadeite: Reexamination of the quartz-coesite equilibrium boundary. Am Mineral, 83: 409–418
Hermann J, Green D H. 2001. Experimental constraints on high pressure melting in subducted crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 188: 149–168
Hermann J, Rubatto D, Korsakov A V, et al. 2001. Multiple zircon growth during fast exhumation of diamondiferous, deeply subducted continental crust (Kokchetav Massif, Kazakhstan). Contrib Mineral Petrol, 141: 66–82
Holland T J B. 1980. The reaction albite=jadeite+quartz determined experimentally in the range 600–1200°C. Am Mineral, 65: 129–134
Huerta A D, Royden L H, Hodges K V. 1998. The thermal structure of collisional orogens as a response to accretion, erosion, and radiogenic heating. J Geophys. Res, 103: 15287–15302
Hwang S L, Shen P, Chu H T, et al. 2001. Genesis of microdiamonds from melt and associated multiphase inclusions in garnet of ultrahigh-pressure gneiss from Erzgebirge, Germany. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 188: 9–15
Kalsbeek F, Thrane K, Higgins A K, et al. 2008. Polyorogenic history of the East Greenland Caledonides. In: Higgins A K, Gilotti J A, Smith M P, eds. The Greenland Caledonides—Evolution of the Northeast Margin of Laurentia. Geol Soc Am Mem, 202: 55–72
Katayama I, Parkinson C D, Okamoto K, et al. 2000a. Supersilicic clinopyroxene and silica exsolution in UHPM eclogite and politic gneiss from the Kokchetav massif, Kazakhstan. Am Mineral, 85: 1368–1374
Katayama I, Zayachkovsky A A, Maruyama S. 2000b. Prograde pressure-temperature records from inclusions in zircons from ultrahigh-pressure-high-temperature rocks of the Kokchetav Massif, northern Kazakhstan. Island Arc, 9: 417–427
Kelsey D E, Hand M. 2015. On ultrahigh temperature crustal metamorphism: Phase equilibria, trace element thermometry, bulk composition, heat sources, timescales and tectonic settings. Geosci Front, doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2014.09.006
Kennedy C S, Kennedy G G. 1976. The equilibrium boundary between graphite and diamond. J Geophys Res, 81: 2467–2470
Kincaid C, Silver P. 1996. The role of viscous dissipation in the orogenic process. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 142: 271–288
Kooijman E, Upadhyay D, Mezger K, et al. 2011. Response of the U-Pb chronometer and trace elements in zircon to ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism: The Kadavur anorthosite complex, southern India. Chem Geol, 290: 177–188
Kostopoulos D K, Ioannidis N M, Sklavounos S A. 2000. A new occurrence of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism, central Macedonia, Norther Greece: Evidence from graphitized diamonds? Int Geol Rev, 42: 545–554
Krohe A, Mposkos E. 2002. Multiple generations of extensional detachments in the Rhodope Mountains (northern Greece): Evidence of episodic exhumation of high-pressure rocks. In: Blundell D J, Neubauer F, Von Quadt A, eds. The Timing and Location of Major Ore Deposits in an Evolving Orogen. London Geol Soc Spec Pub, 204: 151–178
Kunz B E, Johnson T E, White R W, et al. 2014. Partial melting of metabasic rocks in Val Strona di Omegna, Ivrea Zone, northern Italy. Lithos, 190–191: 1–12
Kylander-Clark A R C, Hacker B R, Mattinson C G. 2012. Size and exhumation rate of ultrahigh-pressure terranes linked to orogenic stage. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 321–322: 115–120
Labrousse L, Jolivet L, Agard P, et al. 2002. Crustal-scale boudinage and migmatization of gneiss during their exhumation in the UHP province of western Norway. Terra Nova, 14: 263–270
Labrousse L, Prouteau G, Ganzhorn A C. 2011. Continental exhumation triggered by partial melting at ultrahigh pressure. Geology, 39: 1171–1174
Lathe C, Koch-Müller M, Wirth R, et al. 2005. The influence of OH in coesite on the kinetics of the coesite-quartz phase transition. Am Mineral, 90: 36–43
Leloup P H, Ricard Y, Battaglia J, et al. 1999. Shear heating in continental strike-slip zones: Model and field examples. Geophys J Int, 136: 19–40
Li S G, Xiao Y, Liu D, et al. 1993. Collision of the North China and Yangtze blocks and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites: Timing and processes. Chem Geol, 109: 89–111
Li S G, Li Q, Hou Z, et al. 2005. Cooling history and exhumation of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Dabie Mountains, central China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Petrol Sin, 21: 1117–1124
Li S G, He Y, Wang S. 2013. Process and mechanism of mountain-root removal of the Dabie Orogen—Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of post-collisional igneous rocks. Chin Sci Bull, 58: 4411–4417
Li W Y, Teng F Z, Xiao Y L, et al. 2011. High-temperature inter-mineral magnesium isotope fractionation in eclogite from the Dabie orogen, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 304: 224–230
Li Z X, Li X H, Kinny P D, et al. 2003. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents: Evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia. Precambrian Res, 122: 85–109
Liati A, Gebauer D. 1999. Constraining the prograde and retrograde P-T-t path of Eocene HP rocks by SHRIMP dating of different zircon domains: Inferred rates of heating, burial, cooling and exhumation for central Rhodope, northern Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 135: 340–354
Liati A, Gebauer D, Wysoczanski R. 2002. U-Pb SHRIMP-dating of zircon domains from UHP garnet-rich mafic rocks and late pegmatoids in the Rhodope zone (N Greece): Evidence for Early Cretaceous crystallization and Late Cretaceous metamorphism. Chem Geol, 184: 281–299
Liu F L, Robinson P T, Liu P H. 2012. Multiple partial melting events in the Sulu UHP terrane: Zircon U-Pb dating of granitic leucosomes within amphibolite and gneiss. J Metamorph Geol, 30: 887–906
Liu Y C, Li S G, Xu S T, et al. 2000. U-Pb zircon ages of the eclogite and tonalitic gneiss from the northern Dabie Mountains, China and multi-overgrowths of metamorphic zircons (in Chinese with English abstract). Geol J Chin Univ, 6: 417–423
Liu Y C, Xu S T, Li S G, et al. 2001. Distribution and metamorphic P-T condition of the eclogites from the mafic-ultramafic belt in the northern part of the Dabie Mountains (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Geol Sin, 75: 385–395
Liu Y C, Li S, Xu S, et al. 2005. Geochemistry and geochronology of eclogites from the northern Dabie Mountains, central China. J Asian Earth Sci, 25: 431–443
Liu Y C, Li S G, Gu X F, et al. 2007a. Ultrahigh-pressure eclogite transformed from mafic granulite in the Dabie orogen, east-central China. J Metamorph Geol, 25: 975–989
Liu Y C, Li S G, Xu S T. 2007b. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating for gneiss in northern Dabie high T/P metamorphic zone, central China: Implication for decoupling within subducted continental crust. Lithos, 96: 170–185
Liu Y C, Li S G. 2008. Detachment within subducted continental crust and multi-plate successive exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks: Evidence from the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt. Chin Sci Bull, 53: 3105–3119
Liu Y C, Gu X F, Li S G, et al. 2011a. Multistage metamorphic events in granulitized eclogites from the North Dabie complex zone, central China: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age, trace element and mineral inclusion. Lithos, 122: 107–121
Liu Y C, Gu X F, Rolfo F, et al. 2011b. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and multistage exhumation of eclogite of the Luotian dome, North Dabie Complex Zone (central China): Evidence from mineral inclusions and decompression textures. J Asian Earth Sci, 42: 607–617
Liu Y C, Deng L P, Gu X F, et al. 2014. Multistage high temperature metamorphism and partial melting in the North Dabie complex zone and the geodynamic process and tectonic significance (in Chinese with English abstract). Chin J Geol, 49: 355–367
Liu Y C, Deng L P, Gu X F, et al. 2015. Application of Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers to constrain high-temperature metamorphism in eclogites from the Dabie orogen, central China. Gondwana Res, 27: 410–423
Malaspina N, Hermann J, Scambelluri M, et al. 2006. Multistage metasomatism in ultrahigh-pressure mafic rocks from the North Dabie Complex (China). Lithos, 90: 19–42
Maruyama S, Liou J G, Zhang R. 1994. Tectonic evolution of the ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) and high-pressure (HP) metamorphic belts from central China. Island Arc, 3: 112–121
Maruyama S, Liou J G, Terabayashi M. 1996. Blueschists and eclogites of the world, and their exhumation. Int Geol Rev, 38: 485–594
Maruyama S, Parkinson C D. 2000. Overview of the geology, petrology and tectonic framework of the high-pressure-ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt of the Kokchetav Massif, Kazakhstan. Island Arc, 9: 439–455
Massonne H J. 2001. First find of coesite in the ultrahighpressure metamorphic region of the Central Erzgebirge, Germany. Eur J Mineral, 13: 565–570
Massonne H J. 2003. A comparison of the evolution of diamondiferous quartz-rich rocks from the Saxonian Erzgebirge and the Kokchetav Massif: Are so-called diamondiferous gneisses magmatic rocks? Earth Planet Sci Lett, 216: 347–364
Massonne H J, O’Brien P J. 2003. The Bohemian Massif and the NW Himalaya. In: Carswell D A, Compagnoni R, eds. Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphism. EMU Notes Mineral, 5: 145–187
Massonne H J. 2013. Constructing the pressure-temperature path of ultrahigh-pressure rocks. Elements, 9: 267–272
Massonne H J, Czambor A. 2007. Geochemical signatures of Variscan eclogites from the Saxonian Erzgebirge, central Europe. Chem der Erde Geochem, 67: 69–83
McClelland W C, Power S E, Gilotti J A, et al. 2006. U-Pb SHRIMP geochronology and trace element geochemistry of coesite-bearing zircons, North-East Greenland Caledonides. In: Hacker B R, McClelland W C, Liou J G, eds. Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism: Deep Continental Subduction. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap, 403: 23–43
Miller J A, Buick I S, Cartwright I, et al. 2002. Fluid processes during the exhumation of high-P metamorphic belts. Mineral Mag, 66: 93–119
Mosenfelder J L, Bohlen S R. 1997. Kinetics of the coesite to quartz transformation. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 153: 133–147.
Mosenfelder J L, Schertl H P, Smyth J R, et al. 2005. Factors in the preservation of coesite: The importance of fluid infiltration. Am Mineral, 90: 779–789
Mposkos E D. 2002. Petrology of the ultra-high pressure metamorphic Kimi complex in Rhodope (N.E. Greece): A new insight into the Alpine geodynamic evolution of the Rhodope. Bull Geol Soc Greece, 34: 2169–2188
Mposkos E D, Baziotis I, Palikari S et al. 2004. Alpine UHP metamorphism in the Kimi complex of the Rhodope HP province N.E. Greece: Mineralogical and textural indicators. In: Proceedings of the 32rd International Geological Congress. Florence. 18–28: 108
Mposkos E D, Kostopoulos D K. 2001. Diamond, former coesite and supersilicic garnet in metasedimentary rocks from the Greek Rhodope: A new ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic province established. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 192: 497–506
Mposkos E D, Krohe A. 2006. Pressure-temperature-deformation paths of closely associated ultra-high-pressure (diamond-bearing) crustal and mantle rocks of the Kimi complex: Implications for the tectonic history of the Rhodope Mountains, northern Greece. Can J Earth Sci, 43: 1755–1776
Mposkos E D, Wawrzenitz N. 1995. Metapegmatites and pegmatites bracketing the time of HP-metamorphism in polymetamorphic rocks of the E-Rhodope: Petrological and geochronological constraints. Geol Soc Grec Spec Publ, 2: 602–608
Nakamura D, Svojtka M, Naemura K, et al. 2004. Very high-pressure (>4 GPa) eclogite associated with the Moldanubian Zone garnet peridotite (Nové Dvory, Czech Republic). J metamorph Geol, 22: 593–603
Nakano N, Osanai Y, Owada M. 2007. Multiple breakdown and chemical equilibrium of silicic clinopyroxene under extreme metamorphic conditions in the Kontum Massif, central Vietnam. Am Mineral, 92: 1844–1855
Nasdala L, Massonne H J. 2000. Microdiamonds from the Saxonian Erzgebirge, Germany: In situ micro-Raman characterisation. Eur J Mineral, 12: 495–498
Ogasawara Y, Fukasawa K, Maruyama S. 2002. Coesite exsolution from supersilicic titanite in UHP marble from the Kokchetav Massif, northern Kazakhstan. Am Mineral, 87: 454–461
Okamoto K, Liou J G, Ogasawara Y. 2000. Petrology of the diamond-grade eclogite in the Kokchetav Massif, northern Kazakhstan. Island Arc, 9: 379–399
Patiño Douce A E. 2005. Vapor-absent melting of tonalite at 15–32 kbar. J Petrol, 46: 275–290
Perraki M, Proyer A, Mposkos E, et al. 2006. Raman micro-spectroscopy on diamond, graphite and other carbon polymorphs from the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic Kimi Complex of the Rhodope Metamorphic Province, NE Greece. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 241: 672–685
Ragozin A L, Liou J G, Shatsky V S, et al. 2009. The timing of the retrograde partial melting in the Kumdy-Kol region (Kokchetav Massif, Northern Kazakhstan). Lithos, 109: 274–284
Rötzler J, Kroner U. 2012. The Erzgebirge. In: Romer R L, Förster H J, Kroner U, et al., eds. Granites of the Erzgebirge: Relation of magmatism to the metamorphic and tectonic evolution of the Variscan Orogen, chapter 4, 53–71. Scientific Technical Report 12/15, GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences
Rowley D B, Xue F, Tucker R D, et al. 1997. Ages of ultrahigh pressure metamorphism and protolith orthogneisses from the eastern Dabie Shan: U/Pb zircon geochronology. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 151: 191–203
Rüpke L H, Morgan J P, Hort M, et al. 2004. Serpentine and the subduction zone water cycle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 223: 17–34
Sawyer E W, Cesare B, Brown M. 2011. When the continental crust melts. Elements, 7: 229–234
Shatsky V S, Jagoutz E, Sobolev N V, et al. 1999. Geochemistry and age of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Kokchetav massif (Northern Kazakhstan). Contrib Mineral Petrol, 137: 185–205
Shreve R L, Cloos M. 1986. Dynamics of sediment subduction, melánge formation, and prism accretion. J Geophys Res, 91: 10229–10245
Sisson T W, Grove T L. 1993a. Experimental investigations of the role of H2O in calc-alkaline differentiation and subduction zone magmatism. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 113: 143–166
Sisson T W, Grove T L. 1993b. Temperatures and H2O contents of low-MgO high-alumina basalts. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 113: 167–184
Skjerlie K P, Patiño Douce A E. 2002. The fluid-absent partialmelting of a zoisite-bearing quartz eclogite from 1.0 to 3.2 GPa; implications formelting in thickened continental crust and for subduction-zone processes. J Petrol, 43: 291–314
Smith D C. 1984. Coesite in clinopyroxene in the Caledonides and its implications for geodynamics. Nature, 310: 641–644
Sobolev N V, Shatsky V S. 1990. Diamond inclusions in garnet from metamorphic rocks: A new environment for diamond formation. Nature, 343: 742–746
Stüwe K. 1998. Heat sources of Cretaceous metamorphism in the Eastern Alps—A discussion. Tectonophisics, 287: 251–269
Teng F Z, Wadhwa M, Helz R T. 2007. Investigation of magnesium isotope fractionation during basalt differentiation: Implications for a chondritic composition of the terrestrial mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 261: 84–92
Timms N E, Kinny P D, Reddy S M, et al. 2011. Relationship among titanium, rare earth elements, U-Pb ages and deformation microstructures in zircon: Implications for Ti-in-zircon thermometry. Chem Geol, 280: 33–46
Tipper E T, Galy A, Bickle M J. 2006. Riverine evidence for a fractionated reservoir of Ca and Mg on the continents: Implications for the oceanic Ca cycle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 247: 267–279
Tomkins H S, Powell R, Ellis D J. 2007. The pressure dependence of the zirconium-in-rutile thermometer. J metamorph Geol, 25: 703–713
Tsai C H, Liou J G. 2000. Eclogite-facies relics and inferred ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the North Dabie complex, central China. Am Mineral, 85: 1–8
Vanderhaeghe O, Teyssier C. 2001. Partial melting and flow of orogens. Tectonophysics, 342: 451–472
von Blankenburg F, Davies J. 1995. Slab breakoff: A model for syncollisional magmatism and tectonics in the Alps. Tectonics, 14: 120–131
Wallis S, Tsuboi M, Suzuki K, et al. 2005. Role of partial melting in the evolution of the Sulu (eastern China) ultrahigh-pressure terrane. Geology, 33: 129–132
Wang Q, Cong B. 1999. Exhumation of UHP Terranes: A case study from the Dabie Mountains, eastern China. Int Geol Rev, 41: 994–1004
Wang S J, Li S G, Chen L J, et al. 2013. Geochronology and geochemistry of leucosomes in the North Dabie Terrane, East China: Implication for post-UHPM crustal melting during exhumation. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 165: 1009–1029
Warren C J, Beaumont C, Jamieson R A. 2008. Deep subduction and rapid exhumation: Role of crustal strength and strain weakening in continental subduction and ultrahigh-pressure rock exhumation. Tectonics, 27, doi: 10.1029/2008TC002292
Watson E B, Harrison T M. 2005. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest earth. Science, 308: 841–844
Watson E B, Wark D A, Thomas J B. 2006. Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 151: 413–433
Wei C J, Zhou X W. 2003. Progresses in metamorphic phase equilibrium research (in Chinese with English abstract). Earth Sci Front, 10: 341–351
Whitney D L, Teyssier C, Rey P F. 2009. The consequences of crustal melting in continental subduction. Lithosphere, 1: 323–327
Whittington A G, Treloar P J. 2002. Crustal anatexis and its relation to the exhumation of collisional orogenic belts, with particular reference to the Himalaya. Mineral Mag, 66: 53–91
Whittington A G, Hofmeister A M, Nabelek P I. 2009. Temperature-dependent thermal diffusivity of the Earth’s crust and implications for magmatism. Nature, 458: 319–321
Wu Y B, Zheng Y F, Zhang S, et al. 2007. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of migmatite from the North Dabie terrane in China: Constraints on partial melting. J Metamorph Geol, 25: 991–1009
Xia Q X, Zheng Y F, Zhou L G. 2008. Dehydration and melting during continental collision: Constraints from element and isotope geochemistry of low-T/UHP granitic gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Chem Geol, 247: 36–65
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Su W, et al. 2000. Discovery of the eclogite and its petrography in the Northern Dabie Mountains. Chin Sci Bull, 45: 273–278
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Chen G B, et al. 2003. New finding of microdiamonds in eclogites from Dabie-Sulu region in central-eastern China. Chin Sci Bull, 48: 988–994
Xu S T, Liu Y C, Chen G B, et al. 2005. Microdiamonds, their classification and tectonic implications for the host eclogites from the Dabie and Su-Lu regions in central eastern China. Mineral Mag, 69: 509–520
Xu S T, Okay A I, Ji S C, et al. 1992. Diamonds from the Dabie Shan metamorphic rocks and its implication for tectonic setting. Science, 256: 80–82
Ye K, Cong B, Ye D. 2000. The possible subduction of continental material to depths greater than 200 km. Nature, 407: 734–736
Zen E. 1988. Thermal modelling of stepwise anatexis in a thrust-thickened sialic crust. Trans R Soc Edinb-Earth Sci, 79: 223–235
Zhang R Y, Liou J G, Ernst W G, et al. 1997. Metamorphic evolution of diamond-bearing and associated rocks from the Kokchetav Massif, Northern Kazakhstan. J Metamorph Geol, 15: 479–496
Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Chen R X, et al. 2007. Element mobility in mafic and felsic ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 71: 5244–5266
Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. 2008. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf and O isotopes constrain the crustal architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Dabie orogen in China. Chem Geol, 253: 222–242
Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Zhang J, et al. 2012. Syn-exhumation magmatism during continental collision: Evidence from alkaline intrusives of Triassic age in the Sulu orogen. Chem Geol, 328: 70–88
Zheng Y F, Fu B, Gong B, et al. 2003. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth Sci Rev, 62: 105–161
Zheng Y F, Zhou J B, Wu Y B, et al. 2005. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: A passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction. Int Geol Rev, 47: 851–871
Zheng Y F, Chen R X, Zhao Z F. 2009. Chemical geodynamics of continental subduction-zone metamorphism: Insights from studies of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD) core samples. Tectonophysics, 475: 327–358
Zheng Y F, Xia Q X, Chen R X, et al. 2011. Partial melting, fluid supercriticality and element mobility in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision. Earth Sci Rev, 107: 342–374
Zheng Y F. 2012. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones. Chem Geol, 328: 5–48
Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F, Chen Y X. 2013. Continental subduction channel processes: Plate interface interaction during continental collision. Chin Sci Bull, 58: 4371–4377
Zheng Y F, Hermann J. 2014. Geochemistry of continental subduction-zone fluids. Earth Planet Space, 66: 93
Zhong Z, Suo S, You Z, et al. 2001. Major constituents of the Dabie collisional orogenic belt and partial melting in the ultrahigh-pressure unit. Int Geol Rev, 43: 226–236
Zong K, Liu Y, Hu Z, et al. 2010. Melting-induced fluid flow during exhumation of gneisses of the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane. Lithos, 120: 490–510
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Deng, L. & Gu, X. Multistage exhumation and partial melting of high-T ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in continental subduction-collision zones. Sci. China Earth Sci. 58, 1084–1099 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-015-5067-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-015-5067-9