Abstract
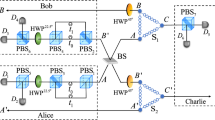
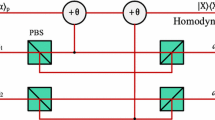
We present two nonlocal entanglement concentration protocols (ECPs) to distill a subset of N-photon systems in a Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) state or a W state from a set of photon systems in a partially entangled GHZ-like pure state or a less-entangled W-like state with known parameter, respectively. Our ECPs have some advantages. First, our ECPs work in a heralded way with linear-optical elements only, without the postselection based on nonlinear optics, far different from the previous ECPs. Second, they require only a copy of the less-entangled photon system in each round of the entanglement concentration process, not two copies, which decreases the difficulty of their implementation in experiment largely. Third, our ECPs avoid checking the photon number in the output modes of linear-optical elements with the sophisticated single-photon detectors. Moreover, all parties can operate the process for concentration simultaneously and independently, which leads to flexible operations and improves the performance greatly in experiment. These advantages make our ECPs useful in practical applications in long-distance quantum communication network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Crépeau C, et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 70: 1895–1899
Bennett C H, Wiesner S J. Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen states. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 69: 2881–2884
Liu X S, Long G L, Tong D M, et al. General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys Rev A, 2002, 65: 022304
Ekert A K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett, 1991, 67: 661–663
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Mermin N D. Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 68: 557–559
Deng F G, Long, G L. Controlled order rearrangement encryption for quantum key distribution. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 042315
Li X H, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel. Phys Rev A, 2008, 78: 022321
Zhang C X, Guo B H, Cheng G M, et al. Spin-orbit hybrid entanglement quantum key distribution scheme. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014, 57: 2043–2048
Long G L, Liu X S. Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys Rev A, 2002, 65: 032302
Deng F G, Long G L, Liu X S. Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 042317
Deng F G, Long, G L. Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 052319
Wang C, Deng F G, Li Y S, et al. Quantum secure direct communication with highdimension quantum superdense coding. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 044305
Gu B, Huang Y G, Fang X, et al. A two-step quantum secure direct communication protocol with hyperentanglement. Chin Phys B, 2011, 20: 100309
Hillery M, Buzek V, Berthiaume A. Quantum secret sharing. Phys Rev A, 1999, 59: 1829–1834
Xiao L, Long G L, Deng F G, et al. Efficient multiparty quantumsecret-sharing schemes. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 052307
Gu B, Xu F, Ding L G, et al. High-capacity three-party quantum secret sharing with hyperentanglement. Int J Theor Phys, 2012, 51: 3559–3566
Gu B, Li C Q, Xu F, et al. High-capacity three-party quantum secret sharing with superdense coding. Chin Phys B, 2009, 18: 4690–4694
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Popescu S, et al. Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channel. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 76: 722–725
Pan J W, Simon C, Brukner Č, et al. Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature, 2001, 410: 1067–1070
Sheng Y B, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Efficient polarization-entanglement purification based on parametric down-conversion sources with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys Rev A, 2008, 77: 042308
Sheng Y B, Deng F G. Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys Rev A, 2010, 81: 032307
Sheng Y B, Deng F G. One-step deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys Rev A, 2010, 82: 044305
Li X H. Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys Rev A, 2010, 82: 044304
Deng F G. One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys Rev A, 2011, 83: 062316
Sheng Y B, Zhou L. Deterministic polarization entanglement purification using time-bin entanglement. Laser Phys Lett, 2014, 11: 085203
Ren B C, Du F F, Deng F G. Two-step hyperentanglement purification with the quantum-state-joining method. Phys Rev A, 2014, 90: 052309
Deng F G. Efficient multipartite entanglement purification with the entanglement link from a subspace. Phys Rev A, 2011, 84: 052312
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jin G S. Polarization-entanglement purification and concentration using cross-kerr nonlinearity. Quantum Inform Comput, 2011, 11: 988–1002
Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhang R. Entanglement purification based on hybrid entangled state using quantum-dot and microcavity coupled system. Opt Express, 2011, 19: 25685–25695
Gu B, Chen Y L, Zhang C Y, et al. Efficient polarization entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Chin Phys Lett, 2010, 27: 100304
Sheng Y B, Zhao S Y, Liu J, et al. Atomic entanglement purification using photonic Faraday rotation. Quantum Inf Process, 2014, 13: 881–893
Bennett C H, Bernstein H J, Popescu S, et al. Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys Rev A, 1996, 53: 2046–2052
Bose S, Vedral V, Knight P L. Purification via entanglement swapping and conserved entanglement. Phys Rev A, 1999, 60: 194–197
Shi B S, Jiang Y K, Guo G C. Optimal entanglement purification via entanglement swapping. Phys Rev A, 2000, 62: 054301
Zhao Z, Pan J W, Zhan M S. Practical scheme for entanglement concentration. Phys Rev A, 2001, 64: 014301
Yamamoto T, Koashi M, Imoto N. Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs. Phys Rev A, 2001, 64: 012304
Sheng Y B, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Nonlocal entanglement concentration scheme for partially entangled multipartite systems with nonlinear optics. Phys Rev A, 2008, 77: 062325
Sheng Y B, Zhou L, Zhao S M, et al. Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs. Phys Rev A, 2012, 85: 012307
Deng F G. Optimal nonlocal multipartite entanglement concentration based on projection measurements. Phys Rev A, 2012, 85: 022311
Ren B C, Du F F, Deng F G. Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys Rev A, 2013, 88: 012302
Ren B C, Deng F G. Hyperentanglement purification and concentration assisted by diamond NV centers inside photonic crystal cavities. Laser Phys Lett, 2013, 10: 115201
Ren B C, Long G L. General hyperentanglement concentration for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins inside optical microcavities. Opt Express, 2014, 22: 6547–6561
Gu B. Single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration of partially entangled multiphoton W states with linear optics. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 29: 1685–1689
Wang H F, Zhang S, Yeon K H. Linear optical scheme for entanglement concentration of two partially entangled three photon W states. Eur Phys J D, 2010, 56: 271–275
Wang H F, Zhang S, Yeon K H. Linear-optics-based entanglement concentration of unknown partially entangled three photon W states. J Opt Soc Am B, 2010, 27: 2159–2164
Xiong W, Ye L. Schemes for entanglement concentration of two unknown partially entangled states with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Opt Soc Am B, 2011, 28: 2030–2037
Sheng Y B, Zhou L, Zhao S M. Efficient two-step entanglement concentration for arbitrary W states. Phys Rev A, 2012, 85: 042302
Du F F, Li T, Ren B C, et al. Single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration of a multiphoton system in a partially entangled W state with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 26: 1399–1405
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jin G S. Entanglement purification and concentration of electron-spin entangled states using quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys Rev A, 2011, 84: 032307
Wang C. Efficient entanglement concentration for partially entangled elctrons using a quantum-dot and microcavity coupled system. Phys Rev A, 2012, 86: 012323
Cao C, Wang C, He L Y, et al. Atomic entanglement purification and concentration using coherent state input-output process in low-Q cavity QED regime. Opt Express, 2013, 21: 4093–4105
Li T, Yang G J, Deng F G. Entanglement distillation for quantum communication network with atomic-ensemble memories. Opt Express, 2014, 22: 23897–23911
Xiong W, Ye L. Schemes for entanglement concentration of two unknown partially entangled states with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Opt Soc Am B, 2011, 28: 2030–2037
Sun L L, Wang H F, Zhang S, et al. Entanglement concentration of partially entangled threephoton W states with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 29: 630–634
Zhou L, Sheng Y B. Efficient single-photon entanglement concentration for quantum communications. Opt Commun, 2014, 313: 217–222
Gu B, Quan D H, Xiao S R. Multi-photon entanglement concentration protocol for partially entangled W states with projection measurement. Int J Theor Phys, 2012, 51: 2966–2973
Zhou L, Sheng Y B, Cheng WW, et al. Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary single-photon multimode W state. J Opt Soc Am B, 2013, 30: 71–78
Zhou L. Efficient entanglement concentration for electron-spin W state with the charge detection. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 2087–2101
Sheng Y B, Zhou L. Quantum entanglement concentration based on nonlinear optics for quantum communications. Entropy, 2013, 15: 1776–1820
Wang T J, Long G L. Entanglement concentration for arbitrary unknown less-entangled three-photon W states with linear optics. J Opt Soc Am B, 2013, 30: 1069–1076
Sheng Y B, Zhou L. Efficient W-state entanglement concentration using quantum-dot and optical microcavities. J Opt Soc Am B, 2013, 30: 678–686
Xu T T, Xiong W, Ye L. Concentrating arbitrary four-photon less-entangled cluster state by single photons. Mod Phys Lett B, 2013, 26: 1250214
Sheng Y B, Zhou L, Wang L, et al. Efficient entanglement concentration for quantum dot and optical microcavities systems. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 1885–1895
Zhao S Y, Liu J, Zhou L, et al. Two-step entanglement concentration for arbitrary electronic cluster state. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 3633–3647
Zhang R, Zhou S H, Cao C. Efficient nonlocal two-step entanglement concentration protocol for three-level atoms in an arbitrary less-entangledW state using cavity input-output process. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014 57: 1511–1518
Sheng Y B, Liu J, Zhao S Y, et al. Multipartite entanglement concentration for nitrogen-vacancy center and microtoroidal resonator system. Chin Sci Bull, 2013, 58: 3507–3513
Fan L L, Xia Y, Song J. Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary less-hyperentanglement multi-photon W states with linear optics. Quantum Inf Process, 2014, 13: 1967–1978
Wang C, Cao C, He L Y, et al. Hybrid entanglement concentration using quantum dot and microcavity coupled system. Quantum Inf Process, 2014, 13: 1025–1034
Zhao S Y, Liu J, Zhou L, et al. Two-step entanglement concentration for arbitrary electronic cluster state. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 3633–3647
Choudhury B S, Dhara A. An entanglement concentration protocol for cluster states. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 2577–2585
Zhou L, Sheng Y B, Cheng WW, et al. Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary less-entangled NOON states. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 1307–1320
Li X H, Ghose S. Hyperconcentration for multipartite entanglement via linear optics. Laser Phys Lett, 2014, 11: 125201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, F., Deng, F. Heralded entanglement concentration for photon systems with linear-optical elements. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 1–8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5638-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5638-3