Abstract
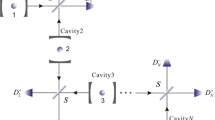
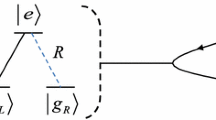
We present an efficient two-step entanglement concentration protocol (ECP) for three-level atoms trapped in one-sided optical micro-cavities in an arbitrary three-particle less-entangled W state, using the coherent state input-output process in low-Q cavity quantum electrodynamics system. In each step of the new proposed protocol, one of the three remote users prepares the auxiliary coherent optical pulses to perform cavity input-output process and then utilizes the standard homodyne measurement to discriminate the final outgoing coherent states. When both of the two steps are successful, remote parties can deterministically concentrate the less-entangled W state atoms to a standard maximally entangled W state. Compared with previous ECPs for W state, this protocol has some advantages and can be widely used in current quantum repeater and some quantum information processing tasks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekert A K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett, 1991, 67: 661–663
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Mermin N D. Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 68: 557–559
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Crepeau C, et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 70: 1895–1899
Bennett C H, Wiesner S J. Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen states. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 69: 2881–2884
Liu X S, Long G L, Tong D M, et al. General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys Rev A, 2002, 65: 022304
Grudka A, Wójcik A. Symmetric scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys Rev A, 2002, 66: 014301
Long G L, Liu X S. Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-keydistribution scheme. Phys Rev A, 2002, 65: 032302
Deng F G, Long G L. Controlled order rearrangement encryption for quantum key distribution. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 042315
Li X H, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel. Phys Rev A, 2008, 78: 022321
Hillery M, Bužek V, Berthiaume A. Quantum secret sharing. Phys Rev A, 1999, 59: 1829–1834
Karlsson A, Koashi M, Imoto N. Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting. Phys Rev A, 1999, 59: 162–168
Xiao L, Long G L, Deng F G, et al. Efficient multiparty quantumsecret-sharing schemes. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 052307
Deng F G, Long G L, Liu X S. Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 042317
Wang C, Deng F G, Li Y S, et al. Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 044305
Li X H, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Improving the security of secure direct communication based on the secret transmitting order of particles. Phys Rev A, 2006, 74: 054302
Briegel H J, Dür W, Cirac J I, et al. Quantum repeaters: The role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81: 5932–5935
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Popescu S, et al. Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 76: 722–725
Bennett C H, Bernstein H J, Popescu S, et al. Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys Rev A, 1996, 53: 2046–2052
Bose S, Vedral V, Knight P L. Purification via entanglement swapping and conserved entanglement. Phys Rev A, 1999, 60: 194–197
Shi B S, Jiang Y K, Guo G C. Optimal entanglement purification via entanglement swapping. Phys Rev A, 2000, 62: 054301
Yamamoto T, Koashi M, Imoto N. Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs. Phys Rev A, 2001, 64: 012304
Zhao Z, Pan J W, Zhan M S. Practical scheme for entanglement concentration. Phys Rev A, 2001, 64: 014301
Sheng Y B, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Nonlocal entanglement concentration scheme for partially entangled multipartite systems with nonlinear optics. Phys Rev A, 2008, 77: 062325
Sheng Y B, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Single-photon entanglement concentration for long-distance quantum communication. Quantum Inf Comput, 2010, 10: 272–281
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jin G S. Polarization-entanglement purification and concentration using cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Quantum Inf Comput, 2011, 11: 988–1002
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jin G S. Dicke state generation using cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Mod Opt, 2011, 58: 21–25
Sheng Y B, Zhou L, Zhao S M, et al. Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs. Phys Rev A, 2012, 85: 012307
Deng F G. Optimal nonlocal multipartite entanglement concentration based on projection measurements. Phys Rev A, 2012, 85: 022311
Feng X L, Kwek L C, Oh C H. Electronic entanglement purification scheme enhanced by charge detections. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 064301
Sheng Y B, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Efficient polarization entanglement concentration for electrons with charge detection. Phys Lett A, 2009, 373, 1823–1825
Yang M, Zhao Y, Song W, et al. Entanglement concentration for unknown atomic entangled states via entanglement swapping. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 044302
Cao Z L, Zhang L H, Yang M. Concentration for unknown atomic entangled states via cavity decay. Phys Rev A, 2006, 73: 014303
Ogden C D, Paternostro M, Kim M S. Concentration and purification of entanglement for qubit systems with ancillary cavity fields. Phys Rev A, 2007, 75: 042325
Cao C, Wang C, He L Y, et al. Atomic entanglement purification and concentration using coherent state input-output process in low-Q cavity QED regime. Opt Express, 2013, 21: 4093–4105
Yang M, Song W, Cao Z L. Entanglement purification for arbitrary unknown ionic states via linear optics. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 012308
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jin G S. Entanglement purification and concentration of electron-spin entangled states using quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys Rev A, 2011, 84: 032307
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jin G S. Entanglement purification based on hybrid entangled state using quantum-dot and microcavity coupled system. Opt Express, 2011, 19: 25685–25695
Wang C. Efficient entanglement concentration for partially entangled electrons using a quantum-dot and microcavity coupled system. Phys Rev A, 2012, 86: 012323
Sheng Y B, Zhou L, Wang L, et al. Efficient entanglement concentration for quantum dot and optical microcavities systems. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 1885–1895
Wang C. Nonlocal entanglement analysis using quantum dot and microcavity coupled system. J Mod Opt, 2012, 59: 962–966
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jin G S, et al. Efficient entanglement purification of separate nitrogen-vacancy centers via coupling to microtoroidal resonators. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 29: 3349–3354
Cao Z L, Yang M. Entanglement distillation for three-particle W class states. J Phys B, 2003, 36: 4245
Zhang L H, Yang M, Cao Z L. Entanglement concentration for unknown W class states. Phys A, 2007, 374: 611–616
Wang H F, Zhang S, Yeon K H. Linear optical scheme for entanglement concentration of two partially entangled three-photon W states. Eur Phys J D, 2010, 56: 271–275
Wang H F, Zhang S, Yeon K H. Linear-optics-based entanglement concentration of unknown partially entangled three-photon Wstates. J Opt Soc Am B, 2010, 27: 2159–2164
Gu B. Single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration of partially entangled multiphoton W states with linear optics. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 29: 1685–1689
Xiong W, Ye L. Schemes for entanglement concentration of two unknown partially entangled states with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Opt Soc Am B, 2011, 28: 2030–2037
Sun L L, Wang H F, Zhang S, et al. Entanglement concentration of partially entangled three-photon W states with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 29: 630–634
Du F F, Li T, Ren B C, et al. Single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration of a multiphoton system in a partially entangled Wstate with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 29: 1399–1405
Sheng Y B, Zhou L, Zhao S M. Efficient two-step entanglement concentration for arbitrary W states. Phys Rev A, 2012, 85: 042302
An J H, Feng M, Oh C H. Quantum-information processing with a single photon by an input-output process with respect to low-Q cavities. Phys Rev A, 2009, 79: 032303
Chen Q, Feng M. Quantum gating on neutral atoms in low-Q cavities by a single-photon input-output process. Phys Rev A, 2009, 79: 064304
Wei H, Deng Z, Zhang X, et al. Transfer and teleportation of quantum states encoded in decoherence-free subspace. Phys Rev A, 2007, 76: 054304
Chen Q, Feng M. Quantum-information processing in decoherencefree subspace with low-Q cavities. Phys Rev A, 2010, 82: 052329
Chen J J, An J H, Feng M, et al. Teleportation of an arbitrary multipartite state via photonic Faraday rotation. J Phys B, 2010, 43: 095505
Bastos W P, Cardoso W B, Avelar A T, et al. Controlled teleportation via photonic Faraday rotations in low-Q cabities. Quantum Inf Process, 2012, 11: 1867–1881
Peng Z H, Zou J, Liu X J, et al. Teleportation of atomic and photonic states in low-Q cavity QED. Opt Commun, 2012, 285: 5558–5563
Bastos W P, Cardoso W B, Avelar A T, et al. A note on entanglement swapping of atomic states through the photonic Faraday Rrotation. Quantum Inf Process, 2011, 10: 395–404
Peng Z H, Zou J, Liu X J, et al. Atomic and photonic entanglement concentration via photonic Faraday rotation. Phys Rev A, 2012, 86: 034305
Mei F, Yu Y F, Feng X L, et al. Quantum entanglement distribution with hybrid parity gate. Phys Rev A, 2010, 82: 052315
Su S L, Guo Q, Zhu L, et al. Atomic quantum information processing in low-Q cavity in the intermediate coupling region. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012, 29: 2827–2833
Nuβmann S, Hijlkema M, Weber B, et al. Submicron positioning of single atoms in a microcavity. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 95: 173602
Fortier K M, Kim S Y, Gibbons M J, et al. Deterministic loading of individual atoms to a high-finesse optical cavity. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 98: 233601
Colombe Y, Steinmetz T, Dubois G, et al. Strong atom-field coupling for Bose-Einstein condensates in an optical cavity on a chip. Nature, 2007, 450: 272–276
Sauer J A, Fortier K M, Chang M S, et al. Cavity QED with optically transported atoms. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 051804
Mundt A B, Kreuter A, Becher C, et al. Coupling a single atomic quantum bit to a high finesse optical cavity. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89: 103001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Zhou, S. & Cao, C. Efficient nonlocal two-step entanglement concentration protocol for three-level atoms in an arbitrary less-entangledW state using cavity input-output process. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 1511–1518 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5308-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5308-x