Abstract
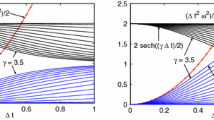
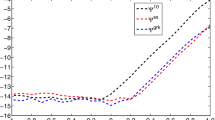
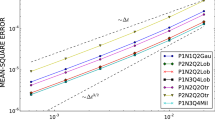
With the natural splitting of a Hamiltonian system into kinetic energy and potential energy, we construct two new optimal thirdorder force-gradient symplectic algorithms in each of which the norm of fourth-order truncation errors is minimized. They are both not explicitly superior to their no-optimal counterparts in the numerical stability and the topology structure-preserving, but they are in the accuracy of energy on classical problems and in one of the energy eigenvalues for one-dimensional time-independent Schrödinger equations. In particular, they are much better than the optimal third-order non-gradient symplectic method. They also have an advantage over the fourth-order non-gradient symplectic integrator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wisdom J. The origin of the Kirkwood gaps - a mapping for asteroidal motion near the 3/1 commensurability. Astron J, 1982, 87: 577–593
Ruth R D. A canonical integration technique. IEEE Tran Nucl Sci, 1983, 30: 2669–2671
Feng K, Qin M Z. The symplectic methods for computation of Hamiltonian equations. In: Zhu Y L, Guo B Y, eds. Proc Conf on Numerical Methods for PDE’s. Berlin: Springer, 1987. 1–37. Lect Notes in Math 1297
Forest E, Ruth R D. Fourth-order symplectic integration. Physica D, 1990, 43: 105–117
Yoshida H. Construction of higher order symplectic integrators. Phys Lett A, 1990, 150: 262–269
Chin S A. Symplectic integrators from composite operator factorizations. Phys Lett A, 1997, 75: 226–344
Chin S A, Chen C R. Fourth order gradient symplectic integrator methods for solving the time-dependent Schrödinger equation. J Chem Phys, 2001, 114: 7338–7341
Chin S A, Chen C R. Forward symplectic integrators for solving gravitational few-body problems. Celest Mech Dyn Astron, 2005, 91: 301–322
Chin S A. Physics of symplectic integrators: Perihelion advances and symplectic corrector algorithms. Phys Rev E, 2007, 75: 036701
Xu J, Wu X. Several fourth order force gradient symplectic algorithms. Res Astron Astrophys, 2010, 10: 173–188
McLachlan R I, Atela P. The accuracy of symplectic integrators. Nonlinearity, 1992, 5: 541–562
Casas F, Murua A. An efficient algorithm for computing the Baker- Campbell-Hausdorff series and some of its applications. J Mathemat Phys, 2009, 50: 033513
Liu F Y, Wu X, Lu B K. On the numerical stability of some symplectic integrators. Chin Astorn Astrophys, 2007, 31: 172–186
Sun Y S, Zhou J L. Global applicability of the symplectic integrator method of Hamiltonian systems. Celest Mech Dyn Astron, 1996, 64: 185–195
Yoshida H. Recent progress in the theory and application of symplectic integration. Celest Mech Dyn Astron, 1993, 56: 27–43
Wisdom J, Holman M. Symplectic maps for the n-body problem. Astron J, 1991, 102: 1520–1538
Mikkola S. Practical symplectic methods with time transformation for the few-body problem. Celest Mech Dyn Astron, 1997, 67: 145–165
Zhong S Y, Wu X. A velocity scaling method with least-squares correction of several constraints. Astrophys Space Sci, 2009, 324: 31–40
Liu X S, Zhou Z Y, Ding P Z, et al. Numerical solution of one-dimensional time-independent Schrödinger equation by using symplectic schemes. Int J Quant Chem, 2000, 79: 343–349
Quarteroni A, Sacco R, Saleri F. Numerical Mathematics. Berlin: Springer Science, 2000. 254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Wu, X. Optimized third-order force-gradient symplectic algorithms. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 53, 1600–1609 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-010-4074-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-010-4074-2