Abstract
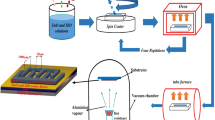
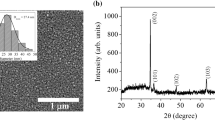
Techniques for fabricating solution-processed zinc oxide (ZnO)-based thin-film transistors (TFTs) are feasible with solution using various routes. Here, ZnO TFTs were fabricated via sol-gel method using zinc acetate as the starting reagent with different modifiers and solvents. The ZnO thin-film semiconductors with well-controlled, preferential crystal orientation and densely packed ZnO crystals can be prepared with the optimized fabrication conditions, exhibiting excellent field-effect far exceeding those of hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H). However, the field-effect characteristics of ZnO TFTs were different for different precursor systems which were constituted by zinc acetate, modifiers and solvents. The co-modification of acetoin and monoethanolamine for the precursor system exhibited higher extent of crystal orientation and field-effect. The maximum mobility of 7.65 cm2V−1s−1 and current on-to-off ratio of ∼105–106 have been obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schroder D K. Semiconductor Material and Device Characterization. New York: Wiley, 1998
Yang A L, Yang Y, Zhang Z Z, et al. Photoluminescence and defect evolution of nano-ZnO thin films at low temperature annealing. Sci China Tech Sci, 2013, 56: 25–31
Li X, Jiang Y D, Tai H L, et al. The fabrication and optimization of OTFT formaldehyde sensors based on Poly(3-hexythiophene)/ZnO composite films. Sci China Tech Sci, 2013, 56: 1877–1882
Howard W E. Thin Film Transistors. New York: Dekker, 2003
Cui J B, Soo Y C, Kandel H, et al. Investigations of ZnO thin films deposited by a reactive pulsed laser ablation. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2009, 52: 99–103
Zhao L, Xu C S, Liu Y X, et al. Effects of temperature and pressure on the structural and optical properties of ZnO films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Sci China Tech Sci, 2010, 53: 317–321
Su G, Song M Q, Sun W Z, et al. Electrodeposition in organic system and properties of NiO electrochromic films. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 1545–1550
Chen Y Y, Chen S G, Chen Y, et al. Surface analysis and electrochemical behaviour of the self-assembled polydopamine/dodecanethiol complex films in protecting 304 stainless steel. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 1527–1534
Wang L H, Shu Y H, Fan J. Effect of humidity on microstructure and properties of YBCO films prepared by Electron Beam Coevaporation. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 2291–2294
Lei J X, Ma F Z, Shi Y, et al. Synthesis of polycrystalline gamma-AlON powders by novel wet chemical processing. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 3405–3410
Bu X B, Wang L B, Li H S, et al. Preparation of composite adsorbent of sawdust and CaCl2 by carbonization method for creating pore. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 2404–2408
Frenzel H, Lajn A, Wenckstern H V, et al. Recent progress on ZnO-based metal-semiconductor field-effect transistors and their application in transparent integrated circuits. Adv Mater, 2010, 22: 5332–5349
Fortunato E, Barquinha P, Martins R. Oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors: a review of recent advances. Adv Mater, 2012, 24: 2945–2986
Obrien P, Saeed T, Knowlcs J. Speciation and the nature of ZnO thin films from chemical bath deposition. J Mater Chem, 1996, 6: 1135–1139
Ohyama M, Kozuka H, Yoko T. Sol-gel preparation of ZnO films with extremely preferred orientation along (002) plane from zinc acetate solution. Thin Solid Films, 1997, 306: 78–85
Yamabi S, Imai H. Growth conditions for wurtzite zinc oxide films in aqueous solutions. J Mater Chem, 2002, 12: 3773–3778
Sirringhaus H. Device physics of solution-processed organic fieldeffect transistors. Adv Mater, 2005, 17: 2411–2425
Klauk H. Organic Electronics: Materials, Manufacturing, and Applications. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2006
Subramanian V, Bakhishev T, Redinger D. Solution-processed zinc oxide transistors for low-cost electronics applications. J Display Technol, 2009, 5: 525–530
Han S Y, Lee D H, Herman G S, et al. Inkjet-printed high mobility transparent-oxide semiconductors. J Display Technol, 2009, 5: 520–524
Wang H, Ji Z Y, Liu M, et al. Advances in organic field-effect transistors and integrated circuits. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2009, 52: 3105–3116
Ryu M K, Park K B, Seon J B, et al. Solution-processed oxide semiconductors for low-cost and high-performance thin-film transistors and fabrication of organic light-emitting-diode displays. J Soc Inf Disp, 2010, 18: 734–744
Jeong S, Moon J. Low-temperature, solution-processed metal oxide thin film transistors. J Mater Chem, 2012, 22: 1243–1250
Li Y, Liu Q, Wang X Z, et al. Pentacene thin film transistor with low threshold voltage and high mobility by inserting a thin metal phthalocyanines interlayer. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 417–420
Park J S, Maeng W-J, Kim H-S, et al. Review of recent developments in amorphous oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor devices. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520: 1679–1693
Shimoda T, Matsuki Y, Furusawa M, et al. Solution-processed silicon films and transistors. Nature, 2006, 440: 783–786
Ridley B A, Nivi B, Jacobson J M. All-inorganic field effect transistors fabricated by printing. Science, 1999, 286: 746–749
Byrne P D, Facchetti A, Marks T J. High-performance thin-film transistors from solution-processed cadmium selenide and a self-assembled multilayer gate dielectric. Adv Mater, 2008, 20: 2319–2324
Mitzi D B, Copel M, Chey S J. Low-voltage transistor employing a high-mobility spin-coated chalcogenide semiconductor. Adv Mater, 2005, 17: 1285–1289
Mitzi D B, Copel M, Murray C E. High-mobility p-type transistor based on a spin-coated metal telluride semiconductor. Adv Mater, 2006, 18: 2448–2452
Mitzi D B. Solution-processed inorganic semiconductors. J Mater Chem, 2004, 14: 2355–2365
Subramanian V, Fréchet J M J, Chang P C, et al. Progress towards development of all-printed RFID tags: Materials, Processes, and Devices. Proc IEEE, 2005, 93: 1330–1338
Faber H, Burkhardt M, Jedaa A, et al. Low-temperature solution-processed memory transistors based on zinc oxide nanoparticles. Adv Mater, 2009, 21: 3099–3104
Schneider J J, Hoffmann R C, Engstler J, et al. Synthesis, characterization, defect chemistry, and FET properties of microwave-derived nanoscaled zinc oxide. Chem Mater, 2010, 22: 2203–2212
Richter T V, Stelzl F, Schulz-Gericke J, et al. Room temperature vacuum-induced ligand removal and patterning of ZnO nanoparticles: from semiconducting films towards printed electronics. J Mater Chem, 2010, 20: 874–879
Sun B, Sirringhaus H. Solution-processed zinc oxide field-effect transistors based on self-assembly of colloidal nanorods. Nano Lett, 2005, 5: 2408–2413
Huang X, Coffer J L. Emissive Er/ZnO/GeOx(SiO2) oxide nanofibers derived from anelectrospinning process. Cryst Growth Des, 2012, 12: 2362–2366
Sun B, Peterson R L, Sirringhaus H, et al. Low-temperature sintering of in-plane self-assembled ZnO nanorods for solution-processed high-performance thin film transistors. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111: 18831–18835
Sun B, Sirringhaus H. Surface tension and fluid flow driven self-assembly of ordered ZnO nanorod films for high-performance field effect transistors. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 16231–16237
Ohya Y, Niwa T, Ban T, et al. Thin film transistor of ZnO fabricated by chemical solution deposition. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2001, 40: 297–298
Zhang X, Huang X, Li C, et al. Dye-sensitized solar cell with energy storage function through PVDF/ZnO nanocomposite counter electrode. Adv Mater, 2013, 25: 4093–4096
Li C S, Li Y N, Wu Y L, et al. ZnO field-effect transistors prepared by aqueous solution-growth ZnO crystal thin film. J Appl Phys, 2007, 102: 076101
Redinger D, Subramanian V. High-performance chemical-bath-deposited zinc oxide thin-film transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54: 1301–1307
Sun K, Wei W, Ding Y. Crystalline ZnO thin film by hydrothermal growth. Chem Commun, 2011, 47: 7776–7778
Li C S, Qiao Y J, Li Y M. Decorating multiwalled carbon nanotubes with zinc oxide nano-crystallines through hydrothermal growth process. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 1365–1370
Wang C X, Zhang X D, Wang D F, et al. Synthesis of nanostructural ZnO using hydrothermal method for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sci China Tech Sci, 2010, 53: 1146–1149
Cheng H C, Chen C F, Tsay C Y. Transparent ZnO thin film transistor fabricated by sol-gel and chemical bath deposition combination method. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 012113
Ong B S, Li C S, Li Y N, et al. Stable, solution-processed, high-mobility ZnO thin-film transistors. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129: 2750–2751
Li C S, Li Y N, Wu Y L, et al. Performance improvement for solution-processed high-mobility ZnO thin-film transistors. J Phys D-Appl Phys, 2008, 41: 125102
Li C S, Li Y N, Wu Y L, et al. Fabrication conditions for solution-processed high-mobility ZnO thin-film transistors. J Mater Chem, 2009, 19: 1626–1634
Hwang Y H, Seo S-J, Bae B-S. Fabrication and characterization of sol-gel-derived zinc oxide thin-film transistor. J Mater Res, 2010, 25: 695–700
Tsay C-Y, Fan K-S, Wang Y-W. Transparent semiconductor zinc oxide thin films deposited on glass substrates by sol-gel process. Ceram Intern, 2010, 36: 1791–1795
Sengupta J, Sahoo R K, Bardhan K K. Influence of annealing temperature on the structural, topographical and optical properties of sol-gel derived ZnO thin films. Mater Lett, 2011, 65: 2572–2574
Tsay C-Y, Fan K-S, Chen S-H, et al. Preparation and characterization of ZnO transparent semiconductor thin films by sol-gel method. J Alloy Compd, 2010, 495: 126–130
Singh S, Chakrabarti P. Simulation, fabrication and characterization of sol-gel deposited ZnO based thin film transistors. Sci Technol Adv Mater, 2012, 4: 199–203
Takahashi Y, Ohsugi A, Arafuka T, et al. Development of new modifiers for titanium alkoxide-based sol-gel process. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol, 2000, 17: 227–238
Ohya T, Kabata M, Ban T, et al. Effect of a-Hydroxyketones as chelate ligands on dip-coating of zirconia thin films. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol, 2002, 25: 43–50
Yutaka O, Takatomo O, Takayuki B, et al. Microstructure of sol-gel ZnO thin films fabricated using ethanolamine and hydroxyketone modifiers. J Ceram Soc Japan, 2005, 113: 220–225
Ohyama M, Kozuka H, Ypko T, et al. Preparation of ZnO films with preferential orientation by sol-gel method. J Ceram Soc Japan, 1996, 104: 296–300
Ohya Y, Saiki H, Tanaka T, et al. Microstructure of TiO2 and ZnO films fabricated by the sol-gel method. J Am Ceram Soc, 1996, 79: 825–830
Kozuka H, Takenaka S, Tokita H, et al. Stress and cracks in gelderived ceramic coatings and thick film formation. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol, 2003, 26: 681–686
Horowitz G. Organic thin film transistors: from theory to real devices. J Mater Res, 2004, 19: 1946–1962
Carcia P F, Mclean R S, Reilly M H, et al. Transparent ZnO thin-film transistor fabricated by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82: 1117–1119
Barquinha P, Pimentel A, Marques A, et al. Influence of the semiconductor thickness on the electrical properties of transparent TFTs based on indium zinc oxide. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2006, 352: 1749–1752
Fortunato E, Barquinha P, Pimentel A, et al. Recent advances in ZnO transparent thin film transistors. Thin Solid Films, 2005, 487: 205–211
Hossain F M, Nishii J, Takagi S, et al. Modeling of grain boundary barrier modulation in ZnO invisible thin film transistors. Physica E, 2004, 21: 911–915
Kumar A, Nathan A, Jabbour G E. Does TFT mobility impact pixel size in AMOLED backplanes? IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52: 2386–2394
Tang M, Guo Y Q, Yuan J, et al. Review of some recent progress on materials science researches in China. Sci China Chem, 2012, 55: 2497–2502
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Tang, D. & Li, C. The impact of solvent and modifier on ZnO thin-film transistors fabricated by sol-gel process. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 2153–2160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5684-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5684-0