Abstract
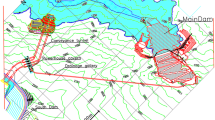
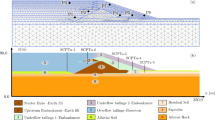
Seepage is a vital reason that may bring many adverse consequences such as subsidence, inclination and fracture to the channel, and is harmful to the safety and stability of the channel. Thus, a 3D visualization model is established for the engineering geological information of the research channel section by using NURBS-TIN-BRep hybrid data structure. Coupled with the VOF (volume of fluid) method, the N-S (Navier-Stokes) equations are applied to seepage simulation of the research channel section. Then the stability of the channel is studied coupled with the seepage simulation results, to comprehensively analyze the stress and displacement conditions of the channel under the impact of different factors such as seepage and underground goafs. The results of this study illustrate that the channel seepage has great influence on its stability, especially on the displacement field: it will lead to a significant sedimentation to the foundation. Therefore, during the practical construction, it is suggested that the certain part of the channel should be reinforced and effective seepage control measures should be taken.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie J B, Fan J, Liu W L, et al. Dynamic stability of the tailings dam under high intensity seismic load coupled with the effect of seepage. Disast Adv, 2012, 5: 816–821
Vandamme J, Zou Q P. Investigation of slope instability induced by seepage and erosion by a particle method. Comput Geotech, 2013, 48: 9–20
Zheng H K, Zhang F, Li Y, et al. Simulation and assessment of seepage control effects at dam site in Kala hydropower project (in Chinese). Rock Soil Mech, 2012, 33: 2743–2748
Chen S K, Yan J, Li J M. Seepage field 3D finite element simulation of concrete faced rockfill dam under failure condition of vertical fracture (in Chinese). Rock Soil Mech, 2011, 32: 3473–3478, 3486
Graziani A, Boldini D. Influence of hydro-mechanical coupling on tunnel response in clays. J Geotech Geoenviron, 2012, 138: 415–418
Samimi S, Pak A. Three-dimensional simulation of fully coupled hydro-mechanical behavior of saturated porous media using Element Free Galerkin (EFG) method. Comput Geotech, 2012, 46: 75–83
Jia C H, Wang X, Wang Y. Research on the deformation of foundation pit considering couple effect of seepage and stress (in Chinese). J Wuhan Univ Technol, 2010, 32: 119–122
Zhou C B, Chen Y F, Jiang Q H, et al. On generalized multi-field coupling for fractured rock masses and its application to rock engineering(in Chinese). Chin J Rock Mech Eng, 2008, 27: 1329–1340
Chai J R, Xu W S. Coupling analysis of unsteady seepage and stress fields in discrete fractures network of rock mass in dam foundation. Sci China Tech Sci, 2011, 54(Suppl 1): 133–139
Jiang Y Z, Ren Q W, Xu W, et al. Definition of the general initial water penetration fracture criterion for concrete and its engineering application. Sci China Tech Sci, 2011, 54: 1575–1580
Zhang C H, Ma Z Y, Zhou S D, et al. Analysis of fluid-solid interaction vibration characteristics of large-scale hydropower house (in Chinese). J Hydroelectr Eng, 2012, 31: 192–197
Bathe K J, Khoshgoftaar M R. Finite element free surface seepage analysis without mesh iteration. Int J Numer Anal Met, 1979, 3: 13–22
Desai C S. Finite element residual schemes for unconfined flow. Int J Numer Meth Eng, 1976, 10: 1415–1418
Zhang Y T, Chen P, Wang L. Initial flow method for seepage analysis with free surface (in Chinese). J Hydrau Eng, 1988, 8: 18–26
Pun S L, Wang Q F, Yu J. Improvement of analysis of free surface seepage problem by using initial flow method (in Chinese). Chin J Geotech Eng, 2012, 34: 202–209
Jiang Q H, Ye Z Y, Yao C, et al. A new variational inequality formulation for unconfined seepage flow through fracture networks. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 3090–3101
Ren H L, Ma T B, Yao X H. Numerical studies of penetration problems by an improved particle method. Sci China Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 55: 2273–2283
Wu Y, Chen X, She Z S, et al. Incorporating boundary constraints to predict mean velocities in turbulent channel flow. Sci China Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 55: 1691–1695
Wang S Z, Gao Z X, Lee C H. Numerical investigation of compressibility effects in turbulent channel flows using large eddy simulation. Sci China Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 55: 305–315
Hirt C W, Niehols B D. Volume of Fluid (VOF) method for the study of free boundaries. J Comput Phys. 1981, 39: 201–225
Zhong D H, Li M C, Liu J. 3D integrated modeling approach to geo-engineering objects of hydraulic and hydroelectric projects. Sci China Tech Sci, 2007, 03: 329–342
Gambolati G, Allan F R. Mathematical simulation of the subsidence of Venice. Water Resour Res, 1973, 9: 721–733
Mao X M, Yao L Q, Feng S Y, et al. Numerical simulation on canal seepage and soil water distribution for concrete lining canal with layered soil structure (in Chinese). J Hydraul Eng, 2011, 08: 949–955
Li X Y, Li J P, Zhou C B, et al. Comparative study on numerical simulation and similarity simulation of overburden deformation in abandoned stope (in Chinese). Rock Soil Mech, 2005, 12: 1907–1912
Zhang L Y, Zheng Y R, Zhao S Y, et al. The feasibility study of strength-reduction method with FEM for calculating safety factors of soil slope stability (in Chinese). J Hydraul Eng, 2003, 1: 21–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, D., Zhang, X., Ao, X. et al. Study on coupled 3D seepage and stress fields of the complex channel project. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 56, 1906–1914 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5284-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5284-4