Abstract
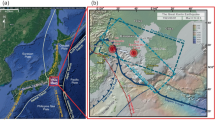
At GMT time 13:19, August 8, 2017, an Ms7.0 earthquake struck the Jiuzhaigou region in Sichuan Province, China, causing severe damages and casualties. To investigate the source properties, seismogenic structures, and seismic hazards, we systematically analyzed the tectonic environment, crustal velocity structure in the source region, source parameters and rupture process, Coulomb failure stress changes, and 3-D features of the rupture plane of the Jiuzhaigou earthquake. Our results indicate the following: (1) The Jiuzhaigou earthquake occurred on an unmarked fault belonging to the transition zone of the east Kunlun fault system and is located northwest of the Huya fault. (2) Both the mainshock and aftershock rupture zones are located in a region where crustal seismic velocity changes dramatically. Southeast to the source region, shear wave velocity at the middle to lower crust is significantly low, but it rapidly increases northeastward and lies close to the background velocity across the rupture fault. (3) The aftershock zone is narrow and distributes along the northwest-southeast trend, and most aftershocks occur within a depth range of 5–20 km. (4) The focal mechanism of the Jiuzhaigou earthquake indicates a left-lateral strike-slip fault, with strike, dip, and rake angles of 152°, 74° and 8°, respectively. The hypocenter depth measures 20 km, whereas the centroid depth is about 6 km. The co-seismic rupture mainly concentrates at depths of 3–13 km, with a moment magnitude (Mw) of 6.5. (5) The co-seismic rupture also strengthens the Coulomb failure stress at the two ends of the rupture fault and the east segment of the Tazang fault. Aftershocks relocation results together with geological surveys indicate that the causative fault is a near vertical fault with notable spatial variations: dip angle varies within 66°–89° from northwest to southeast and the average dip angle measures ~84°. The results of this work are of fundamental importance for further studies on the source characteristics, tectonic environment, and seismic hazard evaluation of the Jiuzhaigou earthquake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai D, Unsworth M J, Meju M A, Ma X, Teng J, Kong X, Sun Y, Sun J, Wang L, Jiang C, Zhao C, Xiao P, Liu M. 2010. Crustal deformation of the eastern Tibetan Plateau revealed by magnetotelluric imaging. Nat Geosci, 3: 358–362
Burchfiel B C, Zhiliang C, Yupinc L, Royden L H. 1995. Tectonics of the Longmen shan and adjacent regions, central China. Int Geol Rev, 37: 661–735
Burchfiel B C, Royden L H, van der Hilst R D, Hager B H, Chen Z, King R W, Li C, Lü J, Yao H, Kirby E. 2008. A geological and geophysical context for the Wenchuan earthquake of 12 May 2008, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China. Gsa Today, 18: 4
Chen S F, Wilson C J L, Deng Q D, Zhao X L, Luo Z L. 1994. Active faulting and block movement associated with large earthquakes in the Min Shan and Longmen Mountains, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res, 99: 24025–24038
Deng Q D, Chen S F, Zhao X L. 1994. Tectonics, seismicity and dynamics of Longmenshan mountains and its adjacent regions (in Chinese with English abstract). Seismol Geol, 16: 389–403
Department of Earthquake Disaster Prevention, China Earthquake Administration. 1995. The Catalogue of Chinese Historical Strong Earthquakes (23Century BC−1911AD) (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press
Department of Earthquake Disaster Prevention, China Earthquake Administration. 1999. The Catalogue of Modern Earthquakes of China (1912AD−1990AD) (in Chinese). Beijing: Science and Technology Press
Harkins N, Kirby E, Shi X, Wang E, Burbank D, Chun F. 2010. Millennial slip rates along the eastern Kunlun fault: Implications for the dynamics of intracontinental deformation in Asia. Lithosphere, 2: 247–266
Huang Z, Xu M, Wang L, Mi N, Yu D, Li H. 2008. Shear wave splitting in the southern margin of the Ordos Block, north China. Geophys Res Lett, 35: L19301
Hubbard J, Shaw J H, Klinger Y. 2010. Structural Setting of the 2008Mw7.9Wenchuan, China, Earthquake. Bull Seismological Soc Am, 100: 2713–2735
Ji C, Wald D J, Helmberger D V. 2002. Source description of the 1999 Hector Mine, California, Earthquake, Part I: Wavelet domain inversion theory and resolution analysis. Bull Seismological Soc Am, 92: 1192–1207
Jiang C, Yang Y, Zheng Y. 2014. Penetration of mid-crustal low velocity zone across the Kunlun Fault in the NE Tibetan Plateau revealed by ambient noise tomography. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 406: 81–92
Jones L M, Han W, Hauksson E, Jin A, Zhang Y, Luo Z. 1984. Focal mechanisms and aftershock locations of the Songpan earthquakes of August 1976 in Sichuan, China. J Geophys Res, 89: 7697–7707
Kirby E, Harkins N, Wang E, Shi X, Fan C, Burbank D. 2007. Slip rate gradients along the eastern Kunlun fault. Tectonics, 26: TC2010
Kirby E, Whipple K X, Tang W, Chen Z. 2003. Distribution of active rock uplift along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Inferences from bedrock channel longitudinal profiles. J Geophys Res, 108: 2217
Laske G, Masters G, Ma Z, Pasyanos M. 2013. Update on CRUST1.0—A 1° Global Model of Earth’s Crust. Geophys Res Abstracts, 15, Abstract EGU2013–2658
Li C X, Xu X W, Wen X Z, Zheng R Z, Chen G H, Yang H, An Y F, Gao X. 2011. Rupture segmentation and slip partitioning of the mid-eastern part of the Kunlun Fault, north Tibetan Plateau. Sci China Earth Sci, 54: 1730–1745
Li C X, Yuan D Y, Yang H, Xu X W. 2016. The tectonic activity characteristics of Awancang fault in the late quaternary, the sub-strand of the eastern Kunlun fault (in Chinese with English abstract). Seismol Geol, 38: 44–64
Li H B, Van der Woerd J, Tapponnier P, Klinger Y, Qi X X, Yang J S, Zhu Y T. 2005. Slip rate on the Kunlun fault at Hongshui Gou, and recurrence time of great events comparable to the 14/11/2001, Mw~7.9 Kokoxili earthquake. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 237: 285–299
Li Y, Zhou R J, Densmore A L, Ellis M A. 2006. The Geology of the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Beijing: Geological Publishing House
Li Y, Gao M, Wu Q. 2014. Crustal thickness map of the Chinese mainland from teleseismic receiver functions. Tectonophysics, 611: 51–60
Lin A, Guo J. 2008. Nonuniform slip rate and millennial recurrence interval of large earthquakes along the eastern segment of the Kunlun fault, northern Tibet. Bull Seismological Soc Am, 98: 2866–2878
Liu C, Zheng Y, Xiong X, Wang R. 2015. Rupture process of the 23O ctober 2011Mw7.1 Van earthquake in eastern Turkey by joint inversion of teleseismic, GPS and strong-motion data. Pure Appl Geophys, 172: 1383–1396
Liu Q Y, van der Hilst R D, Li Y, Yao H J, Chen J H, Guo B, Qi S H, Wang J, Huang H, Li S C. 2014. Eastward expansion of the Tibetan Plateau by crustal flow and strain partitioning across faults. Nat Geosci, 7: 361–365
Luo Y, Zeng X F, Ni S D. 2013. Progress on the determination of focal depth (in Chinese with English abstract). Progr Geophys, 28: 309–2321
Molnar P, Tapponnier P. 1975. Cenozoic Tectonics of Asia: Effects of a Continental Collision: Features of recent continental tectonics in Asia can be interpreted as results of the India-Eurasia collision. Science, 189: 419–426
Ren J, Xu X, Yeats R S, Zhang S. 2013a. Latest Quaternary paleoseismology and slip rates of the Longriba fault zone, eastern Tibet: Implications for fault behavior and strain partitioning. Tectonics, 32: 216–238
Ren J, Xu X, Yeats R S, Zhang S. 2013b. Millennial slip rates of the Tazang fault, the eastern termination of Kunlun fault: Implications for strain partitioning in eastern Tibet. Tectonophysics, 608: 1180–1200
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, Wang E, Chen Z L, Shen F, Liu Y P. 1997. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet. Science, 276: 788–790
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, van der Hilst R D. 2008. The geological evolution of the Tibetan plateau. Science, 321: 1054–1058
Shan B, Xiong X, Wang R, Zheng Y, Yadav R B S. 2015. Stress evolution and seismic hazard on the Maqin-Maqu segment of East Kunlun Fault zone from co-, post- and interseismic stress changes. Geophys J Int, 200: 244–253
Shan B, Xiong X, Zheng Y, Jin B K, Liu C L, Xie Z J, Hsu H T. 2013. Stress changes on major faults caused by 2013 Lushan earthquake and its relationship with 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Sci China Earth Sci, 56: 1169–1176
Shan B, Zheng Y, Liu C L, Xie Z J, Kong J. 2017. Coseismic Coulomb failure stress changes caused by the 2017 M7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake, and its relationship with the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Sci China Earth Sci, 60: 2181–2189
Shen W, Ritzwoller M H, Kang D, Kim Y H, Lin F C, Ning J, Wang W, Zheng Y, Zhou L. 2016. A seismic reference model for the crust and uppermost mantle beneath China from surface wave dispersion. Geophys J Int, 206: 954–979
Tan Y, Zhu L, Helmberger D V, Saikia C K. 2006. Locating and modeling regional earthquakes with two stations. J Geophys Res, 111: B01306
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y, Armijo R, Cobbold P. 1982. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology, 10: 611–616
Van der Woerd J, Ryerson F J, Tapponnier P, Meriaux A S, Gaudemer Y, Meyer B, Finkel R C, Caffee M W, Zhao G G, Xu Z Q. 2000. Uniform slip-rate along the Kunlun Fault: Implications for seismic behaviour and large-scale tectonics. Geophys Res Lett, 27: 2353–2356
Van der Woerd J, Tapponnier P, Ryerson F J, Meriaux A S, Meyer B, Gaudemer Y, Finkel R C, Caffee M W, Zhao G G, Xu Z Q. 2002. Uniform postglacial slip-rate along the central 600 km of the Kunlun Fault (Tibet), from 26Al, 10Be, and 14C dating of riser offsets, and climatic origin of the regional morphology. Geophys J Int, 148: 356–388
Waldhauser F, Ellsworth W L. 2000. A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: Method and application to the northern Hayward fault, California. Bull Seismological Soc Am, 90: 1353–1368
Wang M, Jia D, Shaw J H, Hubbard J, Plesch A, Li Y, Liu B. 2014. The 2013 Lushan earthquake: Implications for seismic hazards posed by the Range Front blind thrust in the Sichuan Basin, China. Geology, 42: 915–918
Wells D L, Coppersmith K J. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull Seismol Soc Amer, 84: 974–1002
Wen X Z, Du F, Zhang P Z, Long F. 2011. Correlation of major earthquake sequences on the northern and eastern boundaries of the Bayan Har block, and its relation to the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake (in Chinese with English abstract). Chin J Geophys, 54: 706–716
Wen X, Yi G, Xu X. 2007. Background and precursory seismicities along and surrounding the Kunlun fault before the Ms8.1, 2001, Kokoxili earthquake, China. J Asian Earth Sci, 30: 63–72
Xie Z J, Jin B K, Zheng Y, Ge C, Xiong X, Xiong C, Hsu H T. 2013. Source parameters inversion of the 2013 Lushan earthquake by combining teleseismic waveforms and local seismograms. Sci China Earth Sci, 56: 1177–1186
Xie Z, Zheng Y, Liu C, Xiong X, Li Y, Zheng X. 2015. Source Parameters of the 2014 Ms6.5 Ludian Earthquake Sequence and Their Implications on the Seismogenic Structure. Seismological Res Lett, 86: 1614–1621
Xiong X, Shan B, Zheng Y, Wang R. 2010. Stress transfer and its implication for earthquake hazard on the Kunlun Fault, Tibet. Tectonophysics, 482: 216–225
Xu X W, Wen X Z, Han Z J, Chen G H, Li C Y, Zheng W J, Zhnag S M, Ren Z Q, Xu C, Tan X B, Wei Z Y, Wang M M, Ren J J, He Z T, Liang M J. 2013. Lushan Ms7.0 earthquake: A blind reserve-fault event. Chin Sci Bull, 58: 3437–3443
Xu X, Wen X, Yu G, Chen G, Klinger Y, Hubbard J, Shaw J. 2009. Coseismic reverse- and oblique-slip surface faulting generated by the 2008 Mw7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China. Geology, 37: 515–518
Xu X W, Yu G H, Ma W T, Chen W B, Wen X Z. 2003. Model of latest crustal tectonic motion of the central tectonic zone on the mainland of China (in Chinese with English abstract). Earth Science Frontiers, 10 (Suppl): 160–167
Xu X W, Zhang P Z, Wen X Z, Qin Z L, Chen G H, Zhu A L. 2005. Features of active tectonics and recurrence behaviors of strong earthquakes in the western Sichuan province and its adjacent regions (in Chinese with English abstract). Seimol Geol, 27: 446–461
Yang Y, Ritzwoller M H, Zheng Y, Shen W, Levshin A L, Xie Z. 2012. A synoptic view of the distribution and connectivity of the mid-crustal low velocity zone beneath Tibet. J Geophys Res, 117: B04303
Yao H. 2012. Lithospheric structure and deformation in SE Tibet revealed by ambient noise and earthquake surface wave tomography: Recent advances and perspectives. Earthq Sci, 25: 371–383
Yao H, van der Hilst R D, Montagner J P. 2010. Heterogeneity and anisotropy of the lithosphere of SE Tibet from surface wave array tomography. J Geophys Res, 115: B12307
Yeats R S. 2012. Active Faults of the World. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Zhang J L. 2017. On fault evidence for a large earthquake in the late fifteenth century, Eastern Kunlun fault, China. J Seismol, 21: 1397–1405
Zhang P Z. 2013. A review on active tectonics and deep crustal processes of the Western Sichuan region, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics, 584: 7–22
Zhang P Z, Molnar P, Xu X. 2007. Late Quaternary and present-day rates of slip along the Altyn Tagh Fault, northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics, 26: TC5010
Zhang P Z, Wen X Z, Shen Z K, Chen J H. 2010. Oblique, high-angle, listric-reverse faulting and associated development of strain: The Wenchuan earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci, 38: 353–382
Zhang Y Q, Yang N, Shi W, Dong S W. 2008. Neotectonics of eastern Tibet and its control on the Wenchuan earthquake (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Geolog Sin, 82: 1668–1678
Zhao G, Unsworth M J, Zhan Y, Wang L, Chen X, Jones A G, Tang J, Xiao Q, Wang J, Cai J, Li T, Wang Y, Zhang J. 2012. Crustal structure and rheology of the Longmenshan and Wenchuan Mw7.9 earthquake epicentral area from magnetotelluric data. Geology, 40: 1139–1142
Zhao L S, Helmberger D V. 1994. Source estimation from broadband regional seismograms. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 84: 91–104
Zheng W J, Yuan D Y, He W G, Min W, Ren Z K, Liu X W, Wang A G, Xu C, Ge W P, Li F. 2013. Geometric pattern and active tectonics in Southeastern Gansu province: Discussion on seismogenic mechanism of the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms6.6 earthquake on July 22, 2013 (in Chinese with English abtract). Chin J Geophys, 56: 4058–4071
Zheng X F, Yao Z X, Liang J H, Zheng J. 2010. The role played and opportunities provided by IGP DMC of China National Seismic Network in Wenchuan earthquake disaster relief and researches. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 100: 2866–2872
Zheng Y, Ge C, Xie Z J, Yang Y J, Xiong X, Hsu H T. 2013. Crustal and upper mantle structure and the deep seismogenic environment in the source regions of the Lushan earthquake and the Wenchuan earthquake. Sci China Earth Sci, 56: 1158–1168
Zheng Y, Li J, Xie Z, Ritzwoller M H. 2012. 5Hz GPS seismology of the El Mayor-Cucapah earthquake: Estimating the earthquake focal mechanism. Geophys J Int, 190: 1723–1732
Zheng Y, Ma H S, Lü J, Ni S D, Li Y C, Wei S J. 2009. Source mechanism of strong aftershocks (Ms5.6) of the 2008/05/12 Wenchuan earthquake and the implication for seismotectonics. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 52: 739–753
Zheng Y, Ni S, Xie Z, Lv J, Ma H, Sommerville P. 2010a. Strong aftershocks in the northern segment of the Wenchuan earthquake rupture zone and their seismotectonic implications. Earth Planet Sp, 62: 881–886
Zheng Y, Yang Y, Ritzwoller M H, Zheng X, Xiong X, Li Z. 2010b. Crustal structure of the northeastern Tibetan plateau, the Ordos block and the Sichuan basin from ambient noise tomography. Earthq Sci, 23: 465–476
Zhu L P, Helmberger D V. 1996. Advancement in source estimation techniques using broadband regional seismograms. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 86: 1634–1641
Zhu L, Rivera L A. 2002. A note on the dynamic and static displacements from a point source in multilayered media. Geophys J Int, 148: 619–627
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the associate editor Prof. Ling Chen, and two anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions that greatly improved the manuscript. We gratefully acknowledge the support by the Monitoring and Forecasting Department, CEA. All regional seismic waveform data used in this study were provided by the Data Management Centre of China National Seismic Network at Institute of Geophysics (doi: 10.11998/SeisDmc/SN), China National Seismic Network, CEA and Sichuan Earthquake Administration. Teleseismic data were obtained from the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology Data Management Center (IRIS-DMC). The figures were drawn by GMT software. The work was jointly funded by the Seismological Bureau Spark Program Project (Grant No. XH15007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41604058, 41574057, 41621091), and the Sichuan-Yunnan National Seismological Monitoring and Prediction Experimental Station Project (Grant No. 2016CESE0204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Zheng, Y., Yao, H. et al. Preliminary analysis on the source properties and seismogenic structure of the 2017 Ms7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake. Sci. China Earth Sci. 61, 339–352 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9161-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9161-y