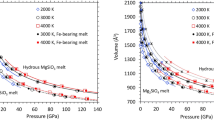
Abstract
Water plays a crucial role in the melting of Earth’s mantle. Mantle magmatisms mostly occur at plate boundaries (including subduction zones and mid-ocean ridges) and in some intraplate regions with thermal anomaly. At oceanic subduction zones, water released by the subducted slab may induce melting of the overlying mantle wedge or even the slab itself, giving rise to arc magmatism, or may evolve into a supercritical fluid. The physicochemical conditions for the formation of slab melt and supercritical fluid are still under debate. At mid-ocean ridges and intraplate hot zones, water and CO2 cause melting of the upwelling mantle to occur at greater depths and in greater extents. Low degree melting of the mantle may occur at boundaries between Earth’s internal spheres, including the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB), the upper mantletransition zone boundary, and the transition zone-lower mantle boundary, usually attributed to contrasting water storage capacity across the boundary. The origin for the stimulating effect of water on melting lies in that water as an incompatible component has a strong tendency to be enriched in the melt (i.e., with a mineral-melt partition coefficient much smaller than unity), thereby lowering the Gibbs free energy of the melt. The partitioning of water between melt and mantle minerals such as olivine, pyroxenes and garnet has been investigated extensively, but the effects of hydration on the density and transport properties of silicate melts require further assessments by experimental and computational approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam J, Locmelis M, Afonso J C, Rushmer T, Fiorentini M L. 2014. The capacity of hydrous fluids to transport and fractionate incompatible elements and metals within the Earth’s mantle. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 15: 2241–2253
Anderson D L, Sammis C. 1970. Partial melting in the upper mantle. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 3: 41–50
Anderson D L. 1989. Theory of the Earth. Blackwell Scientific Publications. 366
Aubaud C, Hauri E H, Hirschmann M M. 2004. Hydrogen partition coefficients between nominally anhydrous minerals and basaltic melts. Geophys Res Lett, 31: L20611, doi: 10.1029/2004GL021341
Aubaud C, Hirschmann M M, Withers A C, Hervig R L. 2008. Hydrogen partitioning between melt, clinopyroxene, and garnet at 3 GPa in a hydrous MORB with 6 wt% H2O. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 156: 607–625
Audétat A, Keppler H. 2004. Viscosity of fluids in subduction zones. Science, 303: 513–516
Bell D R, Rossman G R. 1992. Water in Earth’s mantle: The role of nominally anhydrous minerals. Science, 255: 1391–1397
Beran A, Libowitzky E. 2006. Water in natural mantle minerals II: Olivine, garnet and accessory minerals. Rev Mineral Geochem, 62: 169–191
Bercovici D, Karato S I. 2003. Whole-mantle convection and the transition- zone water filter. Nature, 425: 39–44
Bolfan-Casanova N, Keppler H, Rubie D C. 2003. Water partitioning at 660 km depth and evidence for very low water solubility in magnesium silicate perovskite. Geophys Res Lett, 30: 1905, doi: 10.1029/2003GL-017182
Bolfan-Casanova N, Mackwell S, Keppler H, McCammon C, Rubie D C. 2002. Pressure dependence of H solubility in magnesiowüstite up to 25 GPa: Implications for the storage of water in the Earth’s lower mantle. Geophys Res Lett, 29: 1449, doi: 10.1029/2001GL014457
Dasgupta R. 2013. Ingassing, storage, and outgassing of terrestrial carbon through geologic time. Rev Geophys Res, 75: 183–229.
Dasgupta R, Mallik A, Tsuno K, Withers A C, Hirth G, Hirschmann M M. 2013. Carbon-dioxide-rich silicate melt in the Earth’s upper mantle. Nature, 493: 211–215
Defant M J, Drummond M S. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347: 662–665
Dixon J E, Leist L, Langmuir C, Schilling J G. 2002. Recycled dehydrated lithosphere observed in plume-influenced mid-ocean-ridge basalt. Nature, 420: 385–389
Evans R L. 2014. Geophysics: Making the Earth move. Nature, 509: 40–41
Evans R L, Hirth G, Baba K, Forsyth D, Chave A, Mackie R. 2005. Geophysical evidence from the MELT area for compositional controls on oceanic plates. Nature, 437: 249–252
Ferot A, Bolfan-Casanova N. 2012. Water storage capacity in olivine and pyroxene to 14 GPa: Implications for the water content of the Earth’s upper mantle and nature of seismic discontinuities. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 349: 218–230
Gaillard F. 2004. Laboratory measurements of electrical conductivity of hydrous and dry silicic melts under pressure. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 218: 215–228
Green D H, Hibberson W O, Kovács I, Rosenthal A. 2010. Water and its influence on the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. Nature, 467: 448–451
Green D H, Hibberson W O, Rosenthal A, Kovács I, Yaxley G M, Falloon T J, Brink F. 2014. Experimental study of the influence of water on melting and phase assemblages in the upper mantle. J Petrol, 55: 2067–2096
Grove T L, Chatterjee N, Parman S W, Médard E. 2006. The influence of H2O on mantle wedge melting. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 249: 74–89
Guo X, Chen Q, Ni H. 2016. Electrical conductivity measurement of hydrous silicate melts and water-rich fluid: Implications for melt/fluid in the Earth interior. Sci China Earth Sci, doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5267-y
Hack A C, Thompson A B, Aerts M. 2007. Phase relations involving hydrous silicate melts, aqueous fluids, and minerals. Rev Mineral Geochem, 65: 129–185
Hauri E H, Gaetani G A, Green T H. 2006. Partitioning of water during melting of the Earth’s upper mantle at H2O-undersaturated conditions. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 248: 715–734
Hermann J, Spandler C, Hack A, Korsakov A V. 2006. Aqueous fluids and hydrous melts in high-pressure and ultra-high pressure rocks: Implications for element transfer in subduction zones. Lithos, 92: 399–417
Hirschmann M M. 2000. Mantle solidus: experimental constraints and the effects of peridotite composition. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 1, doi: 10.1029/2000GC000070
Hirschmann M M. 2006. Water, melting, and the deep Earth H2O cycle. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci, 34: 629–653
Hirschmann M M, Aubaud C, Withers A C. 2005. Storage capacity of H2O in nominally anhydrous minerals in the upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 236: 167–181
Hirschmann M M, Tenner T, Aubaud C, Withers A C. 2009. Dehydration melting of nominally anhydrous mantle: The primacy of partitioning. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 176: 54–68
Hodges F. 1974. The solubility of H2O in silicate melts. Year Book Carneg Inst Washington, 73: 251–255
Hui H, Zhang Y. 2007. Toward a general viscosity equation for natural anhydrous and hydrous silicate melts. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 71: 403–416
Jing Z, Karato S I. 2012. Effect of H2O on the density of silicate melts at high pressures: Static experiments and the application of a modified hard-sphere model of equation of state. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 85: 357–372
Johnson E A. 2006. Water in nominally anhydrous crustal minerals: speciation, concentration, and geologic significance. Rev Mineral Geochem, 62: 117–154
Karato S I. 2012. On the origin of the asthenosphere. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 321–322: 95–103
Katz R F, Spiegelman M, Langmuir C H. 2003. A new parameterization of hydrous mantle melting. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 4: 1073, doi: 10.1029/2002GC000433
Kawakatsu H, Kumar P, Takei Y, Shinohara M, Kanazawa T, Araki E, Suyehiro K. 2009. Seismic evidence for sharp lithosphere-asthenosphere boundaries of oceanic plates. Science, 324: 499–502
Keppler H. 2013. Volatiles under High Pressure. Phys Chem Deep Earth, 3–37
Keppler H, Bolfan-Casanova N. 2006. Thermodynamics of water solubility and partitioning. Rev Mineral Geochem, 62: 193–230
Kessel R, Ulmer P, Pettke T, Schmidt M W, Thompson A B. 2005a. The water-basalt system at 4 to 6 GPa: Phase relations and second critical endpoint in a K-free eclogite at 700 to 1400°C. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 237: 873–892
Kessel R, Schmidt M W, Ulmer P, Pettke T. 2005b. Trace element signature of subduction-zone fluids, melts and supercritical liquids at 120–180 km depth. Nature, 437: 724–727
Kimura J I, Nakajima J. 2014. Behaviour of subducted water and its role in magma genesis in the NE Japan arc: A combined geophysical and geochemical approach. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 143: 165–188
Koga K, Hauri E H, Hirschmann M M, Bell D. 2003. Hydrogen concentration analyses using SIMS and FTIR: comparison and calibration for nominally anhydrous minerals. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 4: 1019, doi: 10.1029/2002GC000378
Kohlstedt D, Keppler H, Rubie D. 1996. Solubility of water in the α, β and γ phases of (Mg, Fe)2SiO4. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 123: 345–357
Lambert I B, Wyllie P J. 1972. Melting of a gabbro (qtz eclogite) with excess H2O to 35 kbars with geological applications. J Geol, 80: 693–708
Litasov K, Ohtani E, Langenhorst F, Yurimoto H, Kubo T, Kondo T. 2003. Water solubility in Mg-perovskites and water storage capacity in the lower mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 211: 189–203
Liu X, O’Neill H S C, Berry A J. 2006. The effects of small amounts of H2O, CO2 and Na2O on the partial melting of spinel lherzolite in the system CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2±H2O±CO2±Na2O at 1.1 GPa. J Petrol, 47: 409–434
Malfait W J, Xue X. 2010. The nature of hydroxyl groups in aluminosilicate glasses: Quantifying Si-OH and Al-OH abundances along the SiO2-NaAlSiO4 join by 1H, 27Al-1H and 29Si-1H NMR spectroscopy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 74: 719–737
Manning C E. 2004. The chemistry of subduction-zone fluids. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 223: 1–16
Matsukage K N, Jing Z, Karato S I. 2005. Density of hydrous silicate melt at the conditions of Earth’s deep upper mantle. Nature, 438: 488–491
Mibe K, Kawamoto T, Matsukage K N, Fei Y, Ono S. 2011. Slab melting versus slab dehydration in subduction-zone magmatism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108: 8177–8182
Michael P. 1995. Regionally distinctive sources of depleted MORB: Evidence from trace elements and H2O. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 131: 301–320
Mierdel K, Keppler H, Smyth J R, Langenhorst F. 2007. Water solubility in aluminous orthopyroxene and the origin of Earth’s asthenosphere. Science, 315: 364–368
Mookherjee M, Stixrude L, Karki B B. 2008. Hydrous silicate melt at high pressure. Nature, 452: 983–986
Murakami M, Hirose K, Yurimoto H, Nakashima S, Takafuji N. 2002. Water in Earth’s lower mantle. Science, 295: 1885–1887
Naif S, Key K, Constable S, Evans R L. 2013. Melt-rich channel observed at the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. Nature, 495: 356–359
Ni H, Keppler H, Behrens H. 2011. Electrical conductivity of hydrous basaltic melts: implications for partial melting in the upper mantle. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 162: 637–650
Ni H, Xu Z, Zhang Y. 2013. Hydroxyl and molecular H2O diffusivity in a haploandesitic melt. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 103: 36–48
Ni H. 2013. Advances and application in physicochemical properties of silicate melts (in Chinese). Chin Sci Bull 58: 865–890
Novella D, Frost D J, Hauri E H, Bureau H, Raepsaet C, Roberge M. 2014. The distribution of H2O between silicate melt and nominally anhydrous peridotite and the onset of hydrous melting in the deep upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 400: 1–13
O’Leary J A, Gaetani G A, Hauri E H. 2010. The effect of tetrahedral Al3+ on the partitioning of water between clinopyroxene and silicate melt. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 297: 111–120
Ochs F A, Lange R A. 1999. The density of hydrous magmatic liquids. Science, 283: 1314–1317
Pearson D, Brenker F, Nestola F, McNeill J, Hutchison M T, Matveev K, Mather K, Silvermit G, Schmitz S, Vekemans B, Vincze L. 2014. Hydrous mantle transition zone indicated by ringwoodite included within diamond. Nature, 507: 221–224
Poli S, Schmidt M W. 2002. Petrology of subducted slabs. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci, 30: 207–235
Prouteau G, Scaillet B, Pichavant M, Maury R. 2001. Evidence for mantle metasomatism by hydrous silicic melts derived from subducted oceanic crust. Nature, 410: 197–200
Revenaugh J, Sipkin S. 1994. Seismic evidence for silicate melt atop the 410-km mantle discontinuity. Nature, 369: 474–476
Richet P, Lejeune A M, Holtz F, Roux J. 1996. Water and the viscosity of andesite melts. Chem Geol, 128: 185–197
Rumble D, Liou J G, Jahn B M. 2003. Continental crust subduction and ultrahigh pressure metamorphism. Treat Geochem, 3: 293–319
Sakamaki T, Suzuki A, Ohtani E. 2006. Stability of hydrous melt at the base of the Earth’s upper mantle. Nature, 439: 192–194
Salters V J M, Hart S R. 1989. The hafnium paradox and the role of garnet in the source of mid-ocean-ridge basalts. Nature, 342: 420–422
Salters V J M, Stracke A. 2004. Composition of the depleted mantle. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 5: Q05004, doi: 10.1029/2003GC000597
Schmandt B, Jacobsen S D, Becker T W, Liu Z, Dueker K G. 2014. Dehydration melting at the top of the lower mantle. Science, 344: 1265–1268
Shen A H, Keppler H. 1997. Direct observation of complete miscibility in the albite-H2O system. Nature, 385: 710–712
Sifré D, Gardés E, Massuyeau M, Hashim L, Hier-Majumder S, Gaillard F. 2014. Electrical conductivity during incipient melting in the oceanic low-velocity zone. Nature, 509: 81–85
Skogby H. 2006. Water in natural mantle minerals I: Pyroxenes. Rev Mineral Geochem, 62: 155–167
Smyth J R. 2006. Hydrogen in high pressure silicate and oxide mineral structures. Rev Mineral Geochem, 62: 85–115
Stern R J. 2002. Subduction zones. Rev Geophys, 40: 1012, doi: 10.1029/2001RG000108
Stolper E M. 1982. The speciation of water in silicate melts. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 46: 2609–2620
Tauzin B, Debayle E, Wittlinger G. 2010. Seismic evidence for a global low-velocity layer within the Earth’s upper mantle. Nature Geosci, 3: 718–721
Tenner T J, Hirschmann M M, Withers A C, Ardia P. 2012. H2O storage capacity of olivine and low-Ca pyroxene from 10 to 13 GPa: Consequences for dehydration melting above the transition zone. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 163: 297–316
Tenner T J, Hirschmann M M, Withers A C, Hervig R L. 2009. Hydrogen partitioning between nominally anhydrous upper mantle minerals and melt between 3 and 5 GPa and applications to hydrous peridotite partial melting. Chem Geol, 262: 42–56
Till C B, Grove T L, Withers A C. 2012. The beginnings of hydrous mantle wedge melting. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 163: 669–688
Toffelmier D A, Tyburczy J A. 2007. Electromagnetic detection of a 410-km-deep melt layer in the southwestern United States. Nature, 447: 991–994
Watson E B. 1981. Diffusion in magmas at depth in the earth: the effects of pressure and dissolved H2O. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 52: 291–301
Workman R K, Hart S R. 2005. Major and trace element composition of the depleted MORB mantle (DMM). Earth Planet Sci Lett, 231: 53–72
Yang X. 2013. The origin of electrical anomalies in the uppermost mantle. Acta Petrol Mineral, 32: 663–679
Yoshino T, Katsura T. 2013. Electrical conductivity of mantle minerals: Role of water in conductivity anomalies. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci, 41: 605–628
Yoshino T, Matsuzaki T, Yamashita S, Katsura T. 2006. Hydrous olivine unable to account for conductivity anomaly at the top of the asthenosphere. Nature, 443: 973–976
Zhang L, Meng Y, Yang W, Wang L, Mao W L, Zeng Q S, Jeong J S, Wagner A J, Mkhoyam A, Liu W, Xu R, Mao H-K. 2014. Disproportionation of (Mg, Fe) SiO3 perovskite in Earth’s deep lower mantle. Science, 344: 877–882
Zhang Y X, Ni H, Chen Y. 2010. Diffusion data in silicate melts. Rev Mineral Geochem, 72: 311–408
Zhang Y X, Stolper E M, Wasserburg G. 1991. Diffusion of water in rhyolitic glasses. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 55: 441–456
Zheng Y F, Fu B, Gong B, Li L. 2003. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth Sci Rev, 62: 105–161
Zheng Y F, Xia Q X, Chen R X, Gao X Y. 2011. Partial melting, fluid supercriticality and element mobility in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision. Earth Sci Rev, 107: 342–374
Zheng Y F. 2012. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones. Chem Geol, 328: 5–48
Zheng Y F, Hermann J. 2014. Geochemistry of continental subductionzone fluids. Earth Planet Space, 66: 93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, H., Zhang, L. & Guo, X. Water and partial melting of Earth’s mantle. Sci. China Earth Sci. 59, 720–730 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-015-5254-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-015-5254-8