Abstract
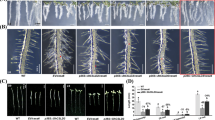
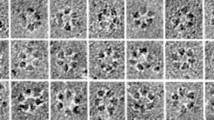
Cotton fiber is a highly elongated and thickened single cell that produces large quantities of cellulose, which is synthesized and assembled into cell wall microfibrils by the cellulose synthase complex (CSC). In this study, we report that in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) fibers harvested during secondary cell wall (SCW) synthesis, GhCesA 4, 7, and 8 assembled into heteromers in a previously uncharacterized 36-mer-like cellulose synthase supercomplex (CSS). This super CSC was observed in samples prepared using cotton fiber cells harvested during the SCW synthesis period but not from cotton stem tissue or any samples obtained from Arabidopsis. Knock-out of any of GhCesA 4, 7, and 8 resulted in the disappearance of the CSS and the production of fiber cells with no SCW thickening. Cotton fiber CSS showed significantly higher enzyme activity than samples prepared from knock-out cotton lines. We found that the microfibrils from the SCW of wild-type cotton fibers may contain 72 glucan chains in a bundle, unlike other plant materials studied. GhCesA4, 7, and 8 restored both the dwarf and reduced vascular bundle phenotypes of their orthologous Arabidopsis mutants, potentially by reforming the CSC hexamers. Genetic complementation was not observed when non-orthologous CesA genes were used, indicating that each of the three subunits is indispensable for CSC formation and for full cellulose synthase function. Characterization of cotton CSS will increase our understanding of the regulation of SCW biosynthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Als-Nielsen, J., and McMorrow, D. (2011). Kinematical scattering I: noncrystalline materials. In: Elements of Modern X-ray Physics. 2nd ed. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons. 113–146.
Atanassov, Pittman, J.K., and Turner, S.R. (2009). Elucidating the mechanisms of assembly and subunit interaction of the cellulose synthase complex of Arabidopsis secondary cell walls. J Biol Chem 284, 3833–3841.
Brown, C., Leijon, F., and Bulone, V. (2012). Radiometric and spectrophotometric in vitro assays of glycosyltransferases involved in plant cell wall carbohydrate biosynthesis. Nat Protoc 7, 1634–1650.
Brown, D.M., Zeef, L.A.H., Ellis, J., Goodacre, R., and Turner, S.R. (2005). Identification of novel genes in Arabidopsis involved in secondary cell wall formation using expression profiling and reverse genetics. Plant Cell 17, 2281–2295.
Bu, L., Himmel, M.E., and Crowley, M.F. (2015). The molecular origins of twist in cellulose I-beta. Carbohydr Polyms 125, 146–152.
Chu, B., and Hsiao, B.S. (2001). Small-angle X-ray scattering of polymers. Chem Rev 101, 1727–1762.
Cosgrove, D.J. (2005). Growth of the plant cell wall. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6, 850–861.
Cosgrove, D.J. (2014). Re-constructing our models of cellulose and primary cell wall assembly. Curr Opin Plant Biol 22, 122–131.
Cosgrove, D.J. (2018). Primary walls in second place. Nat Plants 4, 748–749.
Delmer, D.P. (1999). Cellulose biosynthesis: exciting times for a difficult field of study. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50, 245–276.
Ding, S.Y., and Himmel, M.E. (2006). The maize primary cell wall microfibril: a new model derived from direct visualization. J Agric Food Chem 54, 597–606.
Ding, S.Y., Zhao, S., and Zeng, Y. (2014). Size, shape, and arrangement of native cellulose fibrils in maize cell walls. Cellulose 21, 863–871.
Endler, A., and Persson, S. (2011). Cellulose synthases and synthesis in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 4, 199–211.
Erb, K.H., Kastner, T., Plutzar, C., Bais, A.L.S., Carvalhais, N., Fetzel, T., Gingrich, S., Haberl, H., Lauk, C., Niedertscheider, M., et al. (2018). Unexpectedly large impact of forest management and grazing on global vegetation biomass. Nature 553, 73–76.
Fernandes, A.N., Thomas, L.H., Altaner, C.M., Callow, P., Forsyth, V.T., Apperley, D.C., Kennedy, C.J., and Jarvis, M.C. (2011). Nanostructure of cellulose microfibrils in spruce wood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, E1195–E1203.
Gardiner, J.C., Taylor, N.G., and Turner, S.R. (2003). Control of cellulose synthase complex localization in developing xylem. Plant Cell 15, 1740–1748.
Giddings, T.H. Jr., Brower, D.L., and Staehelin, L.A. (1980). Visualization of particle complexes in the plasma membrane of Micrasterias denticulata associated with the formation of cellulose fibrils in primary and secondary cell walls. J Cell Biol 84, 327–339.
Gonneau, M., Desprez, T., Guillot, A., Vernhettes, S., and Höfte, H. (2014). Catalytic subunit stoichiometry within the cellulose synthase complex. Plant Physiol 166, 1709–1712.
Haigler, C.H., Singh, B., Wang, G., and Zhang, D. (2009). Genomics of cotton fiber secondary wall deposition and cellulose biogenesis. In: Paterson, A.H., eds. Genetics and Genomics of Cotton. Plant Genetics and Genomics: Crops and Models, vol 3. New York: Springer. 385–417.
Herth, W. (1983). Arrays of plasma-membrane “rosettes” involved in cellulose microfibril formation of Spirogyra. Planta 159, 347–356.
Hill, J.L. Jr., Hammudi, M.B., and Tien, M. (2014). The Arabidopsis cellulose synthase complex: a proposed hexamer of CESA trimers in an equimolar stoichiometry. Plant Cell 26, 4834–4842.
Hou, X., Fu, A., Garcia, V.J., Buchanan, B.B., and Luan, S. (2015). PSB27: a thylakoid protein enabling Arabidopsis to adapt to changing light intensity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 1613–1618.
Huang, G., Wu, Z., Percy, R.G., Bai, M., Li, Y., Frelichowski, J.E., Hu, J., Wang, K., Yu, J.Z., and Zhu, Y. (2020). Genome sequence of Gossypium herbaceum and genome updates of Gossypium arboreum and Gossypium hirsutum provide insights into cotton A-genome evolution. Nat Genet 52, 516–524.
Huang, G., Huang, J.Q., Chen, X.Y., and Zhu, Y.X. (2021a). Recent advances and future perspectives in cotton research. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 437–462.
Huang, J., Chen, F., Wu, S., Li, J., and Xu, W. (2016). Cotton GhMYB7 is predominantly expressed in developing fibers and regulates secondary cell wall biosynthesis in transgenic Arabidopsis. Sci China Life Sci 59, 194–205.
Huang, J., Chen, F., Guo, Y., Gan, X., Yang, M., Zeng, W., Persson, S., Li, J., and Xu, W. (2021b). GhMYB7 promotes secondary wall cellulose deposition in cotton fibres by regulating GhCesA gene expression through three distinct cis-elements. New Phytol 232, 1718–1737.
Kumar, M., Campbell, L., and Turner, S. (2016). Secondary cell walls: biosynthesis and manipulation. J Exp Bot 67, 515–531.
Kumar, M., Mishra, L., Carr, P., Pilling, M., Gardner, P., Mansfield, S.D., and Turner, S. (2018). Exploiting cellulose synthase (CESA) class specificity to probe cellulose microfibril biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 177, 151–167.
Kurek, I., Kawagoe, Y., Jacob-Wilk, D., Doblin, M., and Delmer, D. (2002). Dimerization of cotton fiber cellulose synthase catalytic subunits occurs via oxidation of the zinc-binding domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 11109–11114.
Lampugnani, E.R., Flores-Sandoval, E., Tan, Q.W., Mutwil, M., Bowman, J.L., and Persson, S. (2019). Cellulose synthesis—central components and their evolutionary relationships. Trends Plant Sci 24, 402–412.
Li, F., Fan, G., Lu, C., Xiao, G., Zou, C., Kohel, R.J., Ma, Z., Shang, H., Ma, X., Wu, J., et al. (2015). Genome sequence of cultivated Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum TM-1) provides insights into genome evolution. Nat Biotechnol 33, 524–530.
Li, T., Chen, C., Brozena, A.H., Zhu, J.Y., Xu, L., Driemeier, C., Dai, J., Rojas, O.J., Isogai, A., Wågberg, L., et al. (2021). Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 590, 47–56.
Little, A., Schwerdt, J.G., Shirley, N.J., Khor, S.F., Neumann, K., O’Donovan, L.A., Lahnstein, J., Collins, H.M., Henderson, M., Fincher, G.B., et al. (2018). Revised phylogeny of the Cellulose synthase gene superfamily: insights into cell wall evolution. Plant Physiol 177, 1124–1141.
Liu, J., Zhang, X., Dou, L., Li, W., Zhou, X., Liu, Y., Pei, X., Ren, Z., Zhang, W., Li, H., et al. (2020). Patterns of presence-absence variants in Upland cotton. Sci China Life Sci 63, 1600–1603.
Lundquist, P.K., Mantegazza, O., Stefanski, A., Stühler, K., and Weber, A. P.M. (2017). Surveying the oligomeric state of Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts. Mol Plant 10, 197–211.
Maes, J., Castro, N., De Nolf, K., Walravens, W., Abécassis, B., and Hens, Z. (2018). Size and concentration determination of colloidal nanocrystals by small-angle X-ray scattering. Chem Mater 30, 3952–3962.
Martínez-Sanz, M., Pettolino, F., Flanagan, B., Gidley, M.J., and Gilbert, E. P. (2017). Structure of cellulose microfibrils in mature cotton fibres. Carbohydr Polyms 175, 450–463.
Meents, M.J., Watanabe, Y., and Samuels, A.L. (2018). The cell biology of secondary cell wall biosynthesis. Ann Bot 121, 1107–1125.
Morgan, J.L.W., Strumillo, J., and Zimmer, J. (2013). Crystallographic snapshot of cellulose synthesis and membrane translocation. Nature 493, 181–186.
Mueller, S.C., and Brown, R.M. Jr. (1980). Evidence for an intramembrane component associated with a cellulose microfibril-synthesizing complex in higher plants. J Cell Biol 84, 315–326.
Mutwil, M., Debolt, S., and Persson, S. (2008). Cellulose synthesis: a complex complex. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11, 252–257.
Neutelings, G. (2011). Lignin variability in plant cell walls: contribution of new models. Plant Sci 181, 379–386.
Newman, R.H., Hill, S.J., and Harris, P.J. (2013). Wide-angle X-ray scattering and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance data combined to test models for cellulose microfibrils in mung bean cell walls. Plant Physiol 163, 1558–1567.
Nixon, B.T., Mansouri, K., Singh, A., Du, J., Davis, J.K., Lee, J.G., Slabaugh, E., Vandavasi, V.G., O’Neill, H., Roberts, E.M., et al. (2016). Comparative structural and computational analysis supports eighteen cellulose synthases in the plant cellulose synthesis complex. Sci Rep 6, 28696.
Okuda, K., Li, L., Kudlicka, K., Kuga, S., and Brown Jr, R.M. (1993). [beta]-glucan synthesis in the cotton fiber (I. Identification of [beta]-1,4- and [beta]-1,3-glucans synthesized in vitro). Plant Physiol 101, 1131–1142.
Olek, A.T., Rayon, C., Makowski, L., Kim, H.R., Ciesielski, P., Badger, J., Paul, L.N., Ghosh, S., Kihara, D., Crowley, M., et al. (2014). The structure of the catalytic domain of a plant cellulose synthase and its assembly into dimers. Plant Cell 26, 2996–3009.
Omadjela, O., Narahari, A., Strumillo, J., Melida, H., Mazur, O., Bulone, V., and Zimmer, J. (2013). BcsA and BcsB form the catalytically active core of bacterial cellulose synthase sufficient for in vitro cellulose synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 17856–17861.
Paredez, A.R., Somerville, C.R., and Ehrhardt, D.W. (2006). Visualization of cellulose synthase demonstrates functional association with microtubules. Science 312, 1491–1495.
Pear, J.R., Kawagoe, Y., Schreckengost, W.E., Delmer, D.P., and Stalker, D. M. (1996). Higher plants contain homologs of the bacterial celA genes encoding the catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 12637–12642.
Pettolino, F.A., Walsh, C., Fincher, G.B., and Bacic, A. (2012). Determining the polysaccharide composition of plant cell walls. Nat Protoc 7, 1590–1607.
Polko, J.K., and Kieber, J.J. (2019). The regulation of cellulose biosynthesis in plants. Plant Cell 31, 282–296.
Purushotham, P., Cho, S.H., Díaz-Moreno, S.M., Kumar, M., Nixon, B.T., Bulone, V., and Zimmer, J. (2016). A single heterologously expressed plant cellulose synthase isoform is sufficient for cellulose microfibril formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 11360–11365.
Purushotham, P., Ho, R., and Zimmer, J. (2020). Architecture of a catalytically active homotrimeric plant cellulose synthase complex. Science 369, 1089–1094.
Qiao, Z., Lampugnani, E.R., Yan, X.F., Khan, G.A., Saw, W.G., Hannah, P., Qian, F., Calabria, J., Miao, Y., Grüber, G., et al. (2021). Structure of Arabidopsis CESA3 catalytic domain with its substrate UDP-glucose provides insight into the mechanism of cellulose synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2024015118.
Qin, Y.M., and Zhu, Y.X. (2011). How cotton fibers elongate: a tale of linear cell-growth mode. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 106–111.
Ramírez-Rodríguez, E.A., and McFarlane, H.E. (2021). Insights from the structure of a plant cellulose synthase trimer. Trends Plant Sci 26, 4–7.
Ran, F.A., Hsu, P.D., Wright, J., Agarwala, V., Scott, D.A., and Zhang, F. (2013). Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Protoc 8, 2281–2308.
Scheible, W.R., Eshed, R., Richmond, T., Delmer, D., and Somerville, C. (2001). Modifications of cellulose synthase confer resistance to isoxaben and thiazolidinone herbicides in Arabidopsis Ixr1 mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 10079–10084.
Somerville, C. (2006). Cellulose synthesis in higher plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22, 53–78.
Sticklen, M.B. (2008). Plant genetic engineering for biofuel production: towards affordable cellulosic ethanol. Nat Rev Genet 9, 433–443.
Stork, J., Harris, D., Griffiths, J., Williams, B., Beisson, F., Li-Beisson, Y., Mendu, V., Haughn, G., and Debolt, S. (2010). CELLULOSE SYNTHASE9 serves a nonredundant role in secondary cell wall synthesis in arabidopsis epidermal testa cells. Plant Physiol 153, 580–589.
Stroud, D.A., Surgenor, E.E., Formosa, L.E., Reljic, B., Frazier, A.E., Dibley, M.G., Osellame, L.D., Stait, T., Beilharz, T.H., Thorburn, D.R., et al. (2016). Accessory subunits are integral for assembly and function of human mitochondrial complex I. Nature 538, 123–126.
Tanaka, K., Murata, K., Yamazaki, M., Onosato, K., Miyao, A., and Hirochika, H. (2003). Three distinct rice cellulose synthase catalytic subunit genes required for cellulose synthesis in the secondary wall. Plant Physiol 133, 73–83.
Taylor, N.G. (2008). Cellulose biosynthesis and deposition in higher plants. New Phytol 178, 239–252.
Taylor, N.G., Scheible, W.R., Cutler, S., Somerville, C.R., and Turner, S.R. (1999). The irregular xylem3 locus of Arabidopsis encodes a cellulose synthase required for secondary cell wall synthesis. Plant Cell 11, 769–779.
Thomas, L.H., Forsyth, V.T., Sturcová, A., Kennedy, C.J., May, R.P., Altaner, C.M., Apperley, D.C., Wess, T.J., and Jarvis, M.C. (2013). Structure of cellulose microfibrils in primary cell walls from collenchyma. Plant Physiol 161, 465–476.
Turner, S.R., and Somerville, C.R. (1997). Collapsed xylem phenotype of Arabidopsis identifies mutants deficient in cellulose deposition in the secondary cell wall. Plant Cell 9, 689–701.
Wang, K., Wang, D., Zheng, X., Qin, A., Zhou, J., Guo, B., Chen, Y., Wen, X., Ye, W., Zhou, Y., et al. (2019a). Multi-strategic RNA-seq analysis reveals a high-resolution transcriptional landscape in cotton. Nat Commun 10, 4714.
Wang, J., Elliott, J.E., and Williamson, R.E. (2008). Features of the primary wall CESA complex in wild type and cellulose-deficient mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 59, 2627–2637.
Wang, L., Cheng, H., Xiong, F., Ma, S., Zheng, L., Song, Y., Deng, K., Wu, H., Li, F., and Yang, Z. (2020). Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis of BR-defective mutant reveals a key role of GhSK13 in regulating cotton fiber development. Sci China Life Sci 63, 1905–1917.
Wang, M., Tu, L., Yuan, D., Zhu, D., Shen, C., Li, J., Liu, F., Pei, L., Wang, P., Zhao, G., et al. (2019b). Reference genome sequences of two cultivated allotetraploid cottons, Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. Nat Genet 51, 224–229.
Wang, P., Zhang, J., Sun, L., Ma, Y., Xu, J., Liang, S., Deng, J., Tan, J., Zhang, Q., Tu, L., et al. (2018). High efficient multisites genome editing in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) using CRISPR/Cas9 system. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 137–150.
Wang, T., and Hong, M. (2016). Solid-state NMR investigations of cellulose structure and interactions with matrix polysaccharides in plant primary cell walls. J Exp Bot 67, 503–514.
Watanabe, Y., Meents, M.J., McDonnell, L.M., Barkwill, S., Sampathkumar, A., Cartwright, H.N., Demura, T., Ehrhardt, D.W., Samuels, A.L., and Mansfield, S.D. (2015). Visualization of cellulose synthases in Arabidopsis secondary cell walls. Science 350, 198–203.
Weber, K., and Osborn, M. (1969). The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem 244, 4406–4412.
Wen, X., Huang, G., Li, C., and Zhu, Y. (2021). A Malvaceae-specific miRNA targeting the newly duplicated GaZIP1L to regulate Zn2+ ion transporter capacity in cotton ovules. Sci China Life Sci 64, 339–351.
Wittig, I., Braun, H.P., and Schägger, H. (2006). Blue native PAGE. Nat Protoc 1, 418–428.
Xu, W., Cheng, H., Zhu, S., Cheng, J., Ji, H., Zhang, B., Cao, S., Wang, C., Tong, G., Zhen, C., et al. (2021). Functional understanding of secondary cell wall cellulose synthases in Populus trichocarpa via the Cas9/gRNA-induced gene knockouts. New Phytol 231, 1478–1495.
Yager, K.G., Zhang, Y., Lu, F., and Gang, O. (2013). Periodic lattices of arbitrary nano-objects: modeling and applications for self-assembled systems. J Appl Crystlogr 47, 118–129.
Yang, Z., Qanmber, G., Wang, Z., Yang, Z., and Li, F. (2020). Gossypium genomics: trends, scope, and utilization for cotton improvement. Trends Plant Sci 25, 488–500.
Zhang, B., Deng, L., Qian, Q., Xiong, G., Zeng, D., Li, R., Guo, L., Li, J., and Zhou, Y. (2009). A missense mutation in the transmembrane domain of CESA4 affects protein abundance in the plasma membrane and results in abnormal cell wall biosynthesis in rice. Plant Mol Biol 71, 509–524.
Zhang, B., Gao, Y., Zhang, L., and Zhou, Y. (2021a). The plant cell wall: Biosynthesis, construction, and functions. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 251–272.
Zhang, L., Pu, H., Duan, Z., Li, Y., Liu, B., Zhang, Q., Li, W., Rochaix, J. D., Liu, L., and Peng, L. (2018). Nucleus-encoded protein BFA1 promotes efficient assembly of the chloroplast ATP synthase coupling factor 1. Plant Cell 30, 1770–1788.
Zhang, T., Hu, Y., Jiang, W., Fang, L., Guan, X., Chen, J., Zhang, J., Saski, C.A., Scheffler, B.E., Stelly, D.M., et al. (2015). Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotechnol 33, 531–537.
Zhang, T., Zheng, Y., and Cosgrove, D.J. (2016a). Spatial organization of cellulose microfibrils and matrix polysaccharides in primary plant cell walls as imaged by multichannel atomic force microscopy. Plant J 85, 179–192.
Zhang, X., Man, Y., Zhuang, X., Shen, J., Zhang, Y., Cui, Y., Yu, M., Xing, J., Wang, G., Lian, N., et al. (2021b). Plant multiscale networks: charting plant connectivity by multi-level analysis and imaging techniques. Sci China Life Sci 64, 1392–1422.
Zhang, X., Xue, Y., Guan, Z., Zhou, C., Nie, Y., Men, S., Wang, Q., Shen, C., Zhang, D., Jin, S., et al. (2021c). Structural insights into homotrimeric assembly of cellulose synthase CesA7 from Gossypium hirsutum. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 1579–1587.
Zhang, Y., Nikolovski, N., Sorieul, M., Vellosillo, T., McFarlane, H.E., Dupree, R., Kesten, C., Schneider, R., Driemeier, C., Lathe, R., et al. (2016b). Golgi-localized STELLO proteins regulate the assembly and trafficking of cellulose synthase complexes in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 7, 11656.
Zhang, Y., Jiao, Y., Jiao, H., Zhao, H., and Zhu, Y.X. (2017). Two-step functional innovation of the stem-cell factors WUS/WOX5 during plant evolution. Mol Biol Evol 34, 640–653.
Zhong, R., Cui, D., and Ye, Z.H. (2019). Secondary cell wall biosynthesis. New Phytol 221, 1703–1723.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31690090, 31690091, 31830057, 32070207) and the Foundation of Hubei Hongshan Laboratory (2021hszd014). We thank Shitang Huang for helping with the radiolabeling assay, Wenxuan Zou for assistance in the ultra-thin section, and Cao Li for GC-MS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, X., Zhai, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Molecular studies of cellulose synthase supercomplex from cotton fiber reveal its unique biochemical properties. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 1776–1793 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2083-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2083-9