Abstract
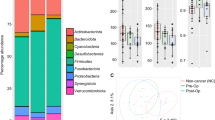
An intricate relationship exists and interactions occur between gut microbiota and colorectal cancer (CRC). Radical surgery combined with adjuvant chemotherapy (AC) serves as the mainstream therapeutic scheme for most CRC patients. The current research was conducted to assess the effect of surgery or chemotherapy on gut microbiota. Forty-three CRC patients who received radical surgery and AC were enrolled. Fecal samples were collected preoperatively, postoperatively, and after the first to fifth cycles of postoperative chemotherapy. The microbial community of each sample was analyzed using high throughput 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Compared with preoperative samples, fecal samples collected postoperatively exhibited a significant decrease of obligate anaerobes, tumor-related bacteria, and butyric acid-producing bacteria. However, a significant increase of some conditional pathogens was observed. In addition, the AC regimen (CapeOx) was found to alter intestinal microbiota dramatically. In particular, several changes were observed after chemotherapy including an increase of pathogenic bacteria, the “rebound effect” of chemotherapy-adapted bacteria, the shift of lactate-utilizing microbiota from Veillonella to Butyricimonas and Butyricicoccus, as well as the decrease of probiotics. Both radical surgery and CapeOx chemotherapy exert a non-negligible effect on the gut microbiota of CRC patients. Microbiota-based intervention may be beneficial for patients during postoperative clinical management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
André, T., Boni, C., Mounedji-Boudiaf, L., Navarro, M., Tabernero, J., Hickish, T., Topham, C., Zaninelli, M., Clingan, P., Bridgewater, J., et al. (2004). Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350, 2343–2351.
Bloom, S.M., Bijanki, V.N., Nava, G.M., Sun, L., Malvin, N.P., Donermeyer, D.L., Dunne Jr., W.M., Allen, P.M., and Stappenbeck, T. S. (2011). Commensal Bacteroides species induce colitis in hostgenotype-specific fashion in a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Host Microbe 9, 390–403.
Borchers, A.T., Selmi, C., Meyers, F.J., Keen, C.L., and Gershwin, M.E. (2009). Probiotics and immunity. J Gastroenterol 44, 26–46.
Bruneau, A., Baylatry, M.T., Joly, A.C., and Sokol, H. (2018). Le microbiote intestinal: quels impacts sur la carcinogenèse et le traitement du cancer colorectal? Bull Cancer 105, 70–80.
Bullman, S., Pedamallu, C.S., Sicinska, E., Clancy, T.E., Zhang, X., Cai, D., Neuberg, D., Huang, K., Guevara, F., Nelson, T., et al. (2017). Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic response in colorectal cancer. Science 358, 1443–1448.
Cersosimo, R.J. (2013). Management of advanced colorectal cancer, Part 1. Am J Health-Syst Pharmacy 70, 395–406.
Chen, J., Wright, K., Davis, J.M., Jeraldo, P., Marietta, E.V., Murray, J., Nelson, H., Matteson, E.L., and Taneja, V. (2016). An expansion of rare lineage intestinal microbes characterizes rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med 8, 43.
Cole, J.R., Wang, Q., Cardenas, E., Fish, J., Chai, B., Farris, R.J., Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S., McGarrell, D.M., Marsh, T., Garrity, G.M., et al. (2009). The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37, D141–D145.
Cui, C., Shen, C.J., Jia, G., and Wang, K.N. (2013). Effect of dietary Bacillus subtilis on proportion of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes in swine intestine and lipid metabolism. Genet Mol Res 12, 1766–1776.
Cunningham, D., Morgan, R.J., Mills, P.R., Nelson, L.M., Toner, P.G., Soukop, M., McArdle, C.S., and Russell, R.I. (1985). Functional and structural changes of the human proximal small intestine after cytotoxic therapy. J Clin Pathol 38, 265–270.
Danno, K., Hata, T., Tamai, K., Fujie, Y., Ide, Y., Kim, H.M., Ohnishi, T., Morita, S., Yoshioka, S., Kudo, T., et al. (2017). Interim analysis of a phase II trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (XELOX) as adjuvant therapy in Japanese patients with operated stage III colon cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80, 777–785.
DeSantis, T.Z., Hugenholtz, P., Larsen, N., Rojas, M., Brodie, E.L., Keller, K., Huber, T., Dalevi, D., Hu, P., and Andersen, G.L. (2006). Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72, 5069–5072.
Drzewiecka, D., and Lewandowska, G. (2016). Vaccines in prophylaxis of urinary tract infections caused by the bacteria from the genus Proteus. Postepy Hig Med Dosw 70, 1032–1043.
Edgar, R.C. (2013). UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10, 996–998.
Erlanger, D., Assous, M.V., Wiener-Well, Y., Yinnon, A.M., and Ben-Chetrit, E. (2017) Clinical manifestations, risk factors and prognosis of patients with Morganella morganii sepsis. J Microbiol Immunol Infection.
Fan, W., Qi, Y., Wang, R., Xu, C., Zhao, N., and Xu, F.J. (2018). Calcium carbonate-methylene blue nanohybrids for photodynamic therapy and ultrasound imaging. Sci China Life Sci 61, 483–491.
Fish, J.A., Chai, B., Wang, Q., Sun, Y., Brown, C.T., Tiedje, J.M., and Cole, J.R. (2013). FunGene: the functional gene pipeline and repository. Front Microbiol 4, 291.
Flórez, A.B., Sierra, M., Ruas-Madiedo, P., and Mayo, B. (2016). Susceptibility of lactic acid bacteria, bifidobacteria and other bacteria of intestinal origin to chemotherapeutic agents. Int J Antimicrob Agents 48, 547–550.
Gao, R., Zhu, C., Li, H., Yin, M., Pan, C., Huang, L., Kong, C., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Qu, S., et al. (2018). Dysbiosis signatures of gut microbiota along the sequence from healthy, young patients to those with overweight and obesity. Obesity 26, 351–361.
Gröbner, S., Fritz, E., Schoch, F., Schaller, M., Berger, A.C., Bitzer, M., and Autenrieth, I.B. (2010). Lysozyme activates Enterococcus faecium to induce necrotic cell death in macrophages. Cell Mol Life Sci 67, 3331–3344.
Grothey, A., and Venook, A.P. (2018). Optimizing adjuvant therapy for localized colon cancer and treatment selection in advanced colorectal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 16, 611–615.
Hill, D.A., Hoffmann, C., Abt, M.C., Du, Y., Kobuley, D., Kirn, T.J., Bushman, F.D., and Artis, D. (2010). Metagenomic analyses reveal antibiotic-induced temporal and spatial changes in intestinal microbiota with associated alterations in immune cell homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol 3, 148–158.
Hooper, L.V., and Gordon, J.I. (2001). Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 292, 1115–1118.
Huttenhower, C., Knight, R., Brown, C.T., Caporaso, J.G., Clemente, J.C., Gevers, D., Franzosa, E.A., Kelley, S.T., Knights, D., Ley, R.E., et al. (2014). Advancing the microbiome research community. Cell 159, 227–230.
Kamboj, K., Vasquez, A., and Balada-Llasat, J.M. (2015). Identification and significance of Weissella species infections. Front Microbiol 6, 670–672.
Kõljalg, U., Nilsson, R.H., Abarenkov, K., Tedersoo, L., Taylor, A.F.S., Bahram, M., Bates, S.T., Bruns, T.D., Bengtsson-Palme, J., Callaghan, T.M., et al. (2013). Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Mol Ecol 22, 5271–5277.
Kwong, T.N.Y., Wang, X., Nakatsu, G., Chow, T.C., Tipoe, T., Dai, R.Z.W., Tsoi, K.K.K., Wong, M.C.S., Tse, G., Chan, M.T.V., et al. (2018). Association between bacteremia from specific microbes and subsequent diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 155, 383–390.e8.
Lassen, K., Soop, M., Nygren, J., Cox, P.B.W., Hendry, P.O., Spies, C., von Meyenfeldt, M.F., Fearon, K.C.H., Revhaug, A., Norderval, S., et al. (2009). Consensus review of optimal perioperative care in colorectal surgery. Arch Surg 144, 961–969.
Le, B., and Yang, S.H. (2018). Efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum in prevention of inflammatory bowel disease. Toxicol Rep 5, 314–317.
Li, M., Wu, Y., Hu, Y., Zhao, L., and Zhang, C. (2018). Initial gut microbiota structure affects sensitivity to DSS-induced colitis in a mouse model. Sci China Life Sci 61, 762–769.
Liu, Z., Qin, H., Yang, Z., Xia, Y., Liu, W., Yang, J., Jiang, Y., Zhang, H., Yang, Z., Wang, Y., et al. (2011). Randomised clinical trial: the effects of perioperative probiotic treatment on barrier function and postoperative infectious complications in colorectal cancer surgery - a double-blind study. Alimentary Pharmacol Therapeutics 33, 50–63.
Lupp, C., Robertson, M.L., Wickham, M.E., Sekirov, I., Champion, O.L., Gaynor, E.C., and Finlay, B.B. (2007). Host-mediated inflammation disrupts the intestinal microbiota and promotes the overgrowth of Enterobacteriaceae. Cell Host Microbe 2, 204.
Marquet, P., Duncan, S.H., Chassard, C., Bernalier-Donadille, A., and Flint, H.J. (2010). Lactate has the potential to promote hydrogen sulphide formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol Lett 299, 128–134.
Miquel, S., Leclerc, M., Martin, R., Chain, F., Lenoir, M., Raguideau, S., Hudault, S., Bridonneau, C., Northen, T., Bowen, B., et al. (2015). Identification of Metabolic Signatures Linked to Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. mBio 6.
Montassier, E., Batard, E., Massart, S., Gastinne, T., Carton, T., Caillon, J., Le Fresne, S., Caroff, N., Hardouin, J.B., Moreau, P., et al. (2014). 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing reveals shift in patient faecal microbiota during high-dose chemotherapy as conditioning regimen for bone marrow transplantation. Microb Ecol 67, 690–699.
Montassier, E., Gastinne, T., Vangay, P., Al-Ghalith, G.A., Bruley des Varannes, S., Massart, S., Moreau, P., Potel, G., de La Cochetière, M.F., Batard, E., et al. (2015). Chemotherapy-driven dysbiosis in the intestinal microbiome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 42, 515–528.
Nagasaka, T., Mishima, H., Sawaki, A., Shimokawa, M., Inukai, M., Shinozaki, K., Tanioka, H., Nasu, J., Nishina, T., Hazama, S., et al. (2016). Protocol of a randomised phase III clinical trial of sequential capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil plus bevacizumab (Cape/5-FU-Bmab) to capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin plus bevacizumab (CapeOX/mFOLFOX6-Bmab) versus combination CapeOX/ mFOLFOX6-Bmab in advanced colorectal cancer: the C-cubed (C3) study. BMJ Open 6, e011454.
Neish, A.S. (2009). Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology 136, 65–80.
Nyhlén, A., Ljungberg, B., Nilsson-Ehle, I., and Nord, C.E. (2002). Impact of combinations of antineoplastic drugs on intestinal microflora in 9 patients with leukaemia. Scand J Infect Dis 34, 17–21.
Ohigashi, S., Sudo, K., Kobayashi, D., Takahashi, T., Nomoto, K., and Onodera, H. (2013). Significant changes in the intestinal environment after surgery in patients with colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 17, 1657–1664.
Ottosson, F., Brunkwall, L., Ericson, U., Nilsson, P.M., Almgren, P., Fernandez, C., Melander, O., and Orho-Melander, M. (2018). Connection between BMI-related plasma metabolite profile and gut microbiota. J Clini Endocrinol Metab 103, 1491–1501.
Ponziani, F.R., Bhoori, S., Castelli, C., Putignani, L., Rivoltini, L., Del Chierico, F., Sanguinetti, M., Morelli, D., Paroni Sterbini, F., Petito, V., et al. (2019). Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 69, 107–120.
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., Peplies, J., and Glöckner, F.O. (2013). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41, D590–D596.
Schwiertz, A., Taras, D., Schäfer, K., Beijer, S., Bos, N.A., Donus, C., and Hardt, P.D. (2010). Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity 18, 190–195.
Seo, B., Yoo, J.E., Lee, Y.M., and Ko, G.P. (2016). Sellimonas intestinalis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int J Systatic Evolary Microbiol 52, 951–956.
Shen, S., Lim, G., You, Z., Ding, W., Huang, P., Ran, C., Doheny, J., Caravan, P., Tate, S., Hu, K., et al. (2017). Gut microbiota is critical for the induction of chemotherapy-induced pain. Nat Neurosci 20, 1213–1216.
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Fedewa, S.A., Ahnen, D.J., Meester, R.G.S., Barzi, A., and Jemal, A. (2017a). Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67, 177–193.
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., and Jemal, A. (2017b). Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67, 7–30.
Strati, F., Cavalieri, D., Albanese, D., De Felice, C., Donati, C., Hayek, J., Jousson, O., Leoncini, S., Renzi, D., Calabrò, A., et al. (2017). New evidences on the altered gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders. Microbiome 5, 24.
Stringer, A.M., Gibson, R.J., Logan, R.M., Bowen, J.M., Yeoh, A.S.J., Hamilton, J., and Keefe, D.M.K. (2009). Gastrointestinal microflora and mucins may play a critical role in the development of 5- fluorouracil-induced gastrointestinal mucositis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 234, 430–441.
Stringer, A.M., Gibson, R.J., Logan, R.M., Bowen, J.M., Yeoh, A.S., and Keefe, D.M. (2008). Faecal microflora and beta-glucuronidase expression are altered in an irinotecan-induced diarrhea model in rats. Cancer Biol Ther 7, 1919–1925.
Sugawara, G., Nagino, M., Nishio, H., Ebata, T., Takagi, K., Asahara, T., Nomoto, K., and Nimura, Y. (2006). Perioperative synbiotic treatment to prevent postoperative infectious complications in biliary cancer surgery. Ann Surgery 244, 706–714.
Thorkildsen, L.T., Nwosu, F.C., Avershina, E., Ricanek, P., Perminow, G., Brackmann, S., Vatn, M.H., and Rudi, K. (2013). Dominant fecal microbiota in newly diagnosed untreated inflammatory bowel disease patients. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2013(170), 1–13.
Touchefeu, Y., Montassier, E., Nieman, K., Gastinne, T., Potel, G., Bruley des Varannes, S., Le Vacon, F., and de La Cochetière, M.F. (2014). Systematic review: the role of the gut microbiota in chemotherapy- or radiation-induced gastrointestinal mucositis—current evidence and potential clinical applications. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 22.
Turnbaugh, P.J., Ley, R.E., Mahowald, M.A., Magrini, V., Mardis, E.R., and Gordon, J.I. (2006). An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444, 1027–1031.
van Vliet, M.J., Tissing, W.J.E., Dun, C.A.J., Meessen, N.E.L., Kamps, W. A., de Bont, E.S.J.M., and Harmsen, H.J.M. (2009). Chemotherapy treatment in pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia receiving antimicrobial prophylaxis leads to a relative increase of colonization with potentially pathogenic bacteria in the gut. Clin Infect Dis 49, 262–270.
Vanlancker, E., Vanhoecke, B., Stringer, A., and Van de Wiele, T. (2017). 5- Fluorouracil and irinotecan (SN-38) have limited impact on colon microbial functionality and composition in vitro. Peer J 5, e4017.
Veiga, P., Pons, N., Agrawal, A., Oozeer, R., Guyonnet, D., Brazeilles, R., Faurie, J.M., van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T., Houghton, L.A., Whorwell, P. J., et al. (2014). Changes of the human gut microbiome induced by a fermented milk product. Sci Rep 4, 6328.
Wang, H., Bastian, S.E.P., and Howarth, G.S. (2013). Newly developed synbiotics and the chemotherapy-damaged gut. J Evid Based Compl Altern Med 18, 198–208.
Wang, X., Allen, T.D., May, R.J., Lightfoot, S., Houchen, C.W., and Huycke, M.M. (2008). Enterococcus faecalis induces aneuploidy and tetraploidy in colonic epithelial cells through a bystander effect. Cancer Res 68, 9909–9917.
Woerther, P.L., Antoun, S., Chachaty, E., and Merad, M. (2017). Eggerthella lenta bacteremia in solid tumor cancer patients: Pathogen or witness of frailty? Anaerobe 47, 70–72.
Workneh, M., Wang, F., Romagnoli, M., Simner, P.J., and Carroll, K. (2016). Bypass graft infection and bacteremia caused by Anaerostipes caccae: First report of human infection caused by a recently described gut anaerobe. Anaerobe 42, 98–100.
Yang, J., Liu, K., Qu, J., and Wang, X. (2013). The changes induced by cyclophosphamide in intestinal barrier and microflora in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 714, 120–124.
Yang, Y., Wang, X., Huycke, T., Moore, D.R., Lightfoot, S.A., and Huycke, M.M. (2013). Colon macrophages polarized by commensal bacteria cause colitis and cancer through the bystander effect. Transl Oncol 6, 596–IN8.
Zhang, Y., Kong, W., and Jiang, J. (2017). Prevention and treatment of cancer targeting chronic inflammation: research progress, potential agents, clinical studies and mechanisms. Sci China Life Sci 60, 601–616.
Yu, T.C., Guo, F., Yu, Y., Sun, T., Ma, D., Han, J., Qian, Y., Kryczek, I., Sun, D., Nagarsheth, N., et al. (2017). Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by modulating autophagy. Cell 170, 548–563.e16.
Zhang, Q., Wu, Y., Wang, J., Wu, G., Long, W., Xue, Z., Wang, L., Zhang, X., Pang, X., Zhao, Y., et al. (2016). Accelerated dysbiosis of gut microbiota during aggravation of DSS-induced colitis by a butyrate-producing bacterium. Sci Rep 6, 27572.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81230057, 81372615, 81472262 and 81200264), the Emerging Cutting-Edge Technology Joint Research Projects of Shanghai (SHDC12012106) and Tongji University Subject Pilot Program (162385), Lijieshou Intestinal Barrier Foundation (LJS-201701), Specialized Research Fund for the Combine Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in General Hospital of Shanghai (ZHYY-ZXYJHZX-1-201704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, C., Gao, R., Yan, X. et al. Alterations in intestinal microbiota of colorectal cancer patients receiving radical surgery combined with adjuvant CapeOx therapy. Sci. China Life Sci. 62, 1178–1193 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9456-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9456-x