Abstract
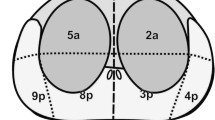
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is considered to be one of the dominant modalities used in prostate cancer (PCa) detection and the assessment of lesion aggressiveness, especially for peripheral zone (PZ) PCa. Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD), which is capable of automatically extracting and evaluating image features, can integrate multiple parameters and improve the detection of PCa. In this study, 13 quantitative image features were extracted from DWI by CAD, and diagnostic efficacy was analyzed in both the PZ and transition zone (TZ). The results demonstrated that there was a significant difference (P<0.05) between PCa and non-PCa for nine of the 13 features in the PZ and five of the 13 features in the TZ. Besides, the prediction outcome of CAD had a strong correlation with the DWI scores that were graded by experienced radiologists according to the Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System Version 2 (PI-RADS v2).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boonsirikamchai, P., Choi, S., Frank, S.J., Ma, J., Elsayes, K.M., Kaur, H., and Choi, H. (2013). MR imaging of prostate cancer in radiation oncology: what radiologists need to know. Radiographics: a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc 33, 741–761.
Chenevert, T.L., Galbán, C.J., Ivancevic, M.K., Rohrer, S.E., Londy, F.J., Kwee, T.C., Meyer, C.R., Johnson, T.D., Rehemtulla, A., and Ross, B.D. (2011). Diffusion coefficient measurement using a temperature-controlled fluid for quality control in multicenter studies. J Magn Reson Imaging 34, 983–987.
Hambrock, T., Vos, P.C., Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.A., Barentsz, J.O., and Huisman, H.J. (2013). Prostate cancer: computer-aided diagnosis with multiparametric 3-T MR imaging—effect on observer performance. Radiology 266, 521–530.
Haralick, R.M., Shanmugam, K., and Dinstein, I.H. (1973). Textural features for image classification. Systems, Man and Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions on SMC-3, 610–621.
Hoeks, C.M.A., Hambrock, T., Yakar, D., Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.A., Feuth, T., Witjes, J.A., Fütterer, J.J., and Barentsz, J.O. (2013). Transition zone prostate cancer: detection and localization with 3-T multiparametric MR imaging. Radiology 266, 207–217.
Kierans, A.S., Taneja, S.S., and Rosenkrantz, A.B. (2015). implementation of multi-parametric prostate MRI in clinical practice. Curr Urol Rep 16, 56.
Kitajima, K., Kaji, Y., Fukabori, Y., Yoshida, K., Suganuma, N., and Sugimura, K. (2010). Prostate cancer detection with 3 T MRI: Comparison of diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in combination with T2-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 31, 625–631.
Kundra, V., Silverman, P.M., Matin, S.F., and Choi, H. (2007). Imaging in oncology from the University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center: diagnosis, staging, and surveillance of prostate cancer. Am J Roentgenol 189, 830−844.
Langer, D.L., van der Kwast, T.H., Evans, A.J., Sun, L., Yaffe, M.J., Trachtenberg, J., and Haider, M.A. (2008). Intermixed normal tissue within prostate cancer: effect on MR imaging measurements of apparent diffusion coefficient and T2—sparse versus dense cancers. Radiology 249, 900–908.
Langer, D.L., van der Kwast, T.H., Evans, A.J., Trachtenberg, J., Wilson, B.C., and Haider, M.A. (2009). Prostate cancer detection with multiparametric MRI: Logistic regression analysis of quantitative T2, diffusion- weighted imaging, and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 30, 327–334.
Lin, C.C., Wang, C.N., Ou, Y.K., and Fu, J. (2014). Combined image enhancement, feature extraction, and classification protocol to improve detection and diagnosis of rotator-cuff tears on MR imaging. MRMS 13, 155–166.
Muller, B.G., Shih, J.H., Sankineni, S., Marko, J., Rais-Bahrami, S., George, A.K., de la Rosette, J.J.M.C.H., Merino, M.J., Wood, B.J., Pinto, P., Choyke, P.L., and Turkbey, B. (2015). Prostate cancer: interobserver agreement and accuracy with the revised prostate imaging reporting and data system at multiparametric MR imaging. Radiology 277, 741–750.
Niaf, E., Rouvière, O., Mège-Lechevallier, F., Bratan, F., and Lartizien, C. (2012). Computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer in the peripheral zone using multiparametric MRI. Phys Med Biol 57, 3833–3851.
Oto, A., Kayhan, A., Jiang, Y., Tretiakova, M., Yang, C., Antic, T., Dahi, F., Shalhav, A.L., Karczmar, G., and Stadler, W.M. (2010). Prostate cancer: differentiation of central gland cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia by using diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 257, 715–723.
Peng, Y., Jiang, Y., Yang, C., Brown, J.B., Antic, T., Sethi, I., Schmid-Tannwald, C., Giger, M.L., Eggener, S.E., and Oto, A. (2013). Quantitative analysis of multiparametric prostate MR images: differentiation between prostate cancer and normal tissue and correlation with gleason score—A computer-aided diagnosis development study. Radiology 267, 787–796.
Puech, P., Betrouni, N., Makni, N., Dewalle, A.S., Villers, A., and Lemaitre, L. (2009). Computer-assisted diagnosis of prostate cancer using DCEMRI data: design, implementation and preliminary results. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 4, 1–10.
Schimmöller, L., Quentin, M., Arsov, C., Lanzman, R.S., Hiester, A., Rabenalt, R., Antoch, G., Albers, P., and Blondin, D. (2013). Inter- reader agreement of the ESUR score for prostate MRI using in-bore MRI-guided biopsies as the reference standard. Eur Radiol 23, 3185–3190.
Sung, Y.S., Kwon, H.J., Park, B.W., Cho, G., Lee, C.K., Cho, K.S., and Kim, J.K. (2011). Prostate cancer detection on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: computer-aided diagnosis versus single perfusion parameter maps. Am J Roentgenology 197, 1122–1129.
Tanimoto, A., Nakashima, J., Kohno, H., Shinmoto, H., and Kuribayashi, S. (2007). Prostate cancer screening: The clinical value of diffusion- weighted imaging and dynamic MR imaging in combination with T2-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 25, 146–152.
Vargas, H.A., Akin, O., Franiel, T., Mazaheri, Y., Zheng, J., Moskowitz, C., Udo, K., Eastham, J., and Hricak, H. (2011). Diffusion-weighted endorectal MR imaging at 3 T for prostate cancer: tumor detection and assessment of aggressiveness. Radiology 259, 775–784.
Viswanath, S., Bloch, B.N., Chappelow, J., Patel, P., Rofsky, N., Lenkinski, R., Genega, E., and Madabhushi, A. (2011). Enhanced Multi-Protocol Analysis via Intelligent Supervised Embedding (EMPrAvISE): Detecting Prostate Cancer on Multi-Parametric MRI. Proceedings of SPIE—the International Society for Optical Engineering7963, 79630U.
Vos, P.C., Hambrock, T., Hulsbergen - van de Kaa, C.A., Fütterer, J.J., Barentsz, J.O., and Huisman, H.J. (2008). Computerized analysis of prostate lesions in the peripheral zone using dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Med Phys 35, 888–899.
Weinreb, J.C., Barentsz, J.O., Choyke, P.L., Cornud, F., Haider, M.A., Macura, K.J., Margolis, D., Schnall, M.D., Shtern, F., Tempany, C.M., Thoeny, H.C., and Verma, S. (2016). PI-RADS Prostate Imaging - Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. European urology69, 16–40.
Westphalen, A.C., and Rosenkrantz, A.B. (2014). Prostate imaging reporting and data system (PI-RADS): reflections on early experience with a standardized interpretation scheme for multiparametric prostate MRI. Am J Roentgenology 202, 121–123.
Zhao, K., Wang, C.Y., Hu, J., Yang, X.D., Wang, H., Li, F.Y., Zhang, X.D., Zhang, J., and Wang, X.Y. (2015). Prostate cancer identification: quantitative analysis of T2-weighted MR images based on a back propagation artificial neural network model. Sci China Life Sci 58, 666–673.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, G., Wang, C., Zhang, X. et al. Quantitative analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: differentiation between prostate cancer and normal tissue based on a computer-aided diagnosis system. Sci. China Life Sci. 60, 37–43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0389-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0389-9